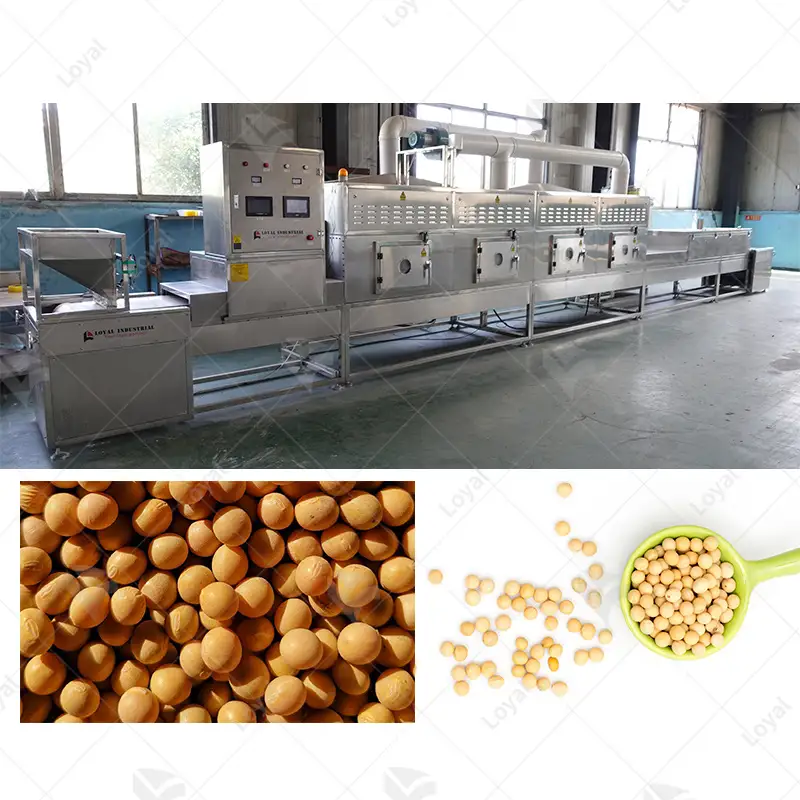
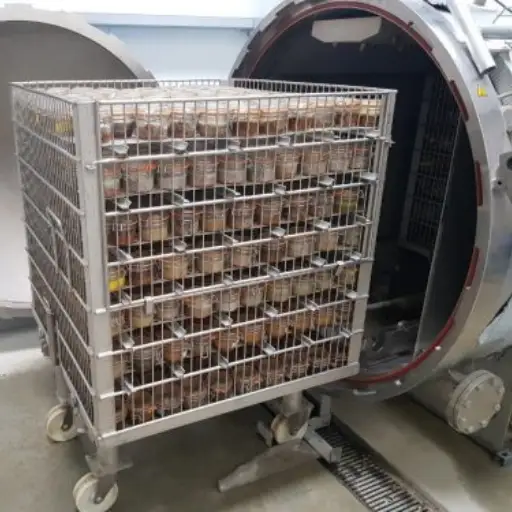
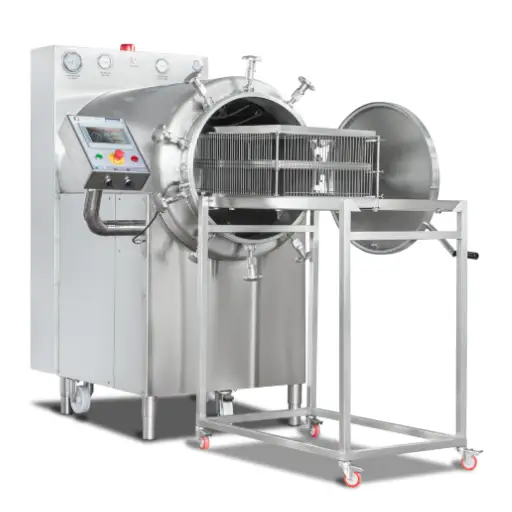
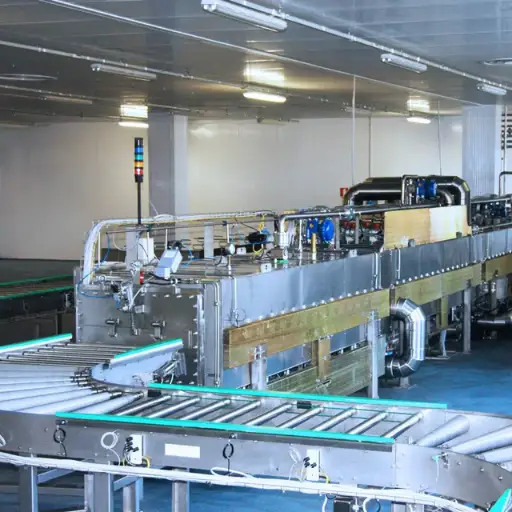
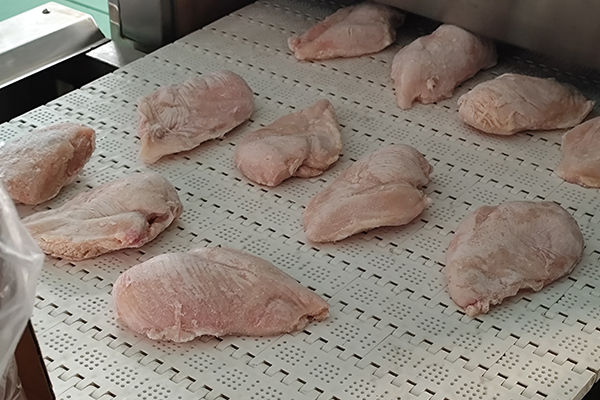
Microwave Thawing Machine is a vital invention in food technology that accelerates defrosting while preserving the original state of consumables. The microwave thawing machine uniformly propagates inside the frozen items by using microwave energy, thus defrosting them quickly and evenly. Unlike conventional methods that require long durations, hence leading to partial cooking or uneven defrosting, this method perfectly regulates temperature so as not to spoil texture or flavor. This technology particularly benefits large-scale food production facilities and catering services, where efficiency and consistency are paramount. This article will cover the principles behind microwave thawing, its superiority to other traditional techniques, and its practical applications, which position it as a valuable asset for the food industry.
What Is a Microwave Thawing Machine?
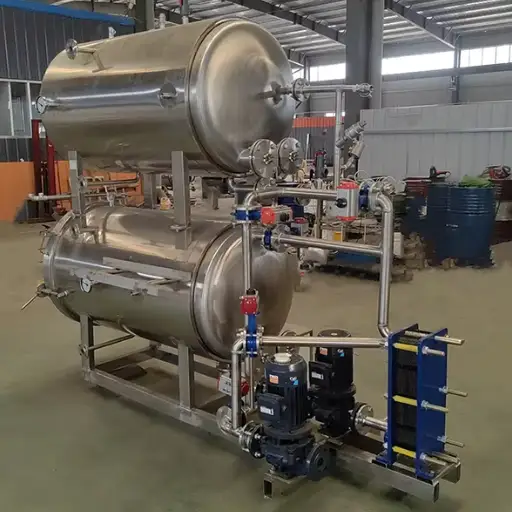
A Microwave Thawing Machine is a highly-developed equipment that has been invented to defrost frozen foods effectively and evenly using microwaves. In manner of operation, this machine works by releasing microwave energy, which can pass through frozen substances, causing water molecules present in food to oscillate, thus giving out heat. The outcome is very fast, and even thawing is done without semi-cooking or non-uniform temperature distribution. The machine was designed such that it could carefully control the process of thawing to retain the texture and flavor of food after being defrosted. This technology is more advantageous when time and consistency are essential, like catering services and large-scale food production centers.
What Is a Microwave Thawing Machine?
Microwave thawing machines serve by emitting electromagnetic waves with frequencies usually within 915 MHz or 2450 MHz range. These microwaves enter into frozen foodstuffs, causing water molecules in them to shake, hence producing heat via dielectric heating. Thus, through this method, the temperature of food gets instantly increased from the freezing point, for it turns into the soft state without localized cooking. Temperature indicators and feedback systems that are used during real-time monitoring have control over how fast FWVUs can be defrosted, thereby ensuring even heat delivery.
Main Technical Specifications:
- Frequency: Typically 915 MHz or 2450 MHz
- Power Output: Ranges from 5 kW to 100 kW depending on the scale and requirements of the application
- Uniformity Coefficient: Generally greater than 0.7 to ensure even heating
- Temperature Accuracy: ±1°C for precise control
- Defrosting Time: Significantly reduced compared to conventional methods, generally within minutes
These parameters have been diligently selected based on extensive research findings as well as empirical data meant to guarantee high efficiency and consistent thawing processes performed rapidly by microwave ovens used in industrial setups.
What Are the Basic Elements of a Thawing Machine?
Several crucial components make up a microwave thawing machine to ensure efficient and even thawing frozen foods. They involve:
- Microwave Generator: This main part produces electromagnetic waves at specific frequencies (usually 915 MHz or 2450 MHz). Industrial application requirements determine power output of this generator ranging from 5 kW to 100 kW.
- Waveguide System: This system guides the generated microwaves from a source toward foodstuffs, thus preventing energy waste and achieving uniform distribution for consistent heating.
- Thawing Chamber: This is where the frozen food goes. Its objective is to provide an equal dispersion of microwave radiation, often using reflective materials to improve the distribution of microwaves.
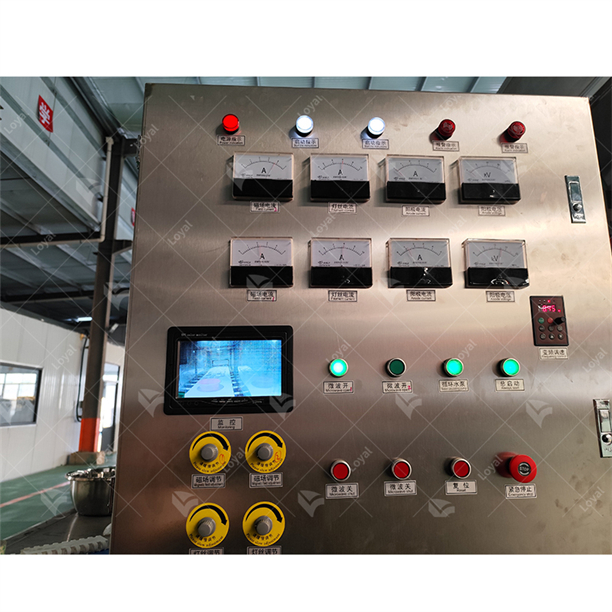
- Control System: Sensors and feedbacks are vital elements in this control system which monitor temperature changes in real-time. With ±1°C precision, such control system keeps the temperature accurate and maintains a balance between defrosting rate and power output.
- Cooling System: Essential for maintaining the electronic components’ optimal operating temperatures, preventing overheating, and ensuring machine longevity.
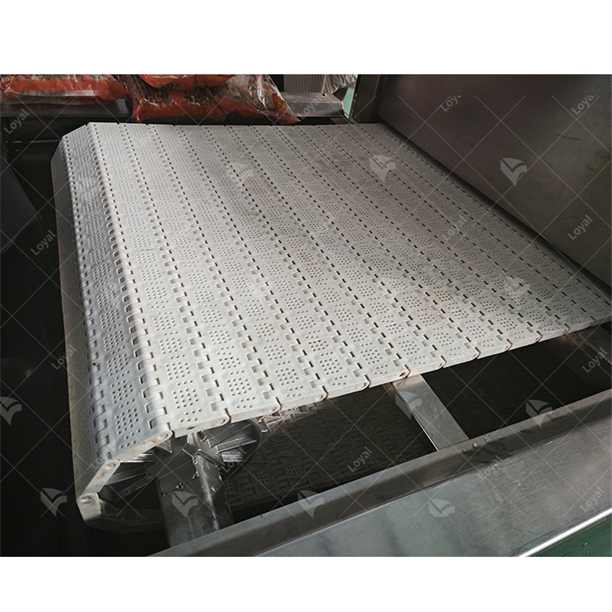
- Conveyor Belts or Rotating Tables are parts of machines used to move food products inside microwave fields so that they can be uniformly exposed to radiation.
All these were designed very carefully based on empirical studies, which ensured their efficiency and effectiveness in terms of overall reliability and performance concerning microwave thawing applications within an industrial context.
What is the purpose of using a microwave defrosting machine in the food industry?
Microwave defrosting devices used in the food industry have various advantages that make them more desirable than orthodox thawing methods. These machines take a significantly shorter amount of time to thaw, processing frozen foods within minutes as opposed to hours, which is crucial for keeping up with high volume production environments. Swift thawing ensures that there are no opportunities for microbial growth hence maintaining its health and safety.
Micro wave thawing on technical terms, has accurate heating because of well-set control systems. The temperature accuracy is maintained at ±1°C by real-time sensing units and feedbacks that adjust power outputs continuously. This eliminates possibility of either partial thaw or overheating which would compromise the quality of the product.
Moreover, microwave machines are energy efficient. Power output may range from 5 kW to 100 kW, but these appliances lose a minimal quantity of energy while delivering it directly into the food substance. Wave guide system and defrosting chamber are designed to maximize energy transfer efficiency and provide even distribution over microwaves thus making this strategy economical.
Finally, with an integrated cooling system, optimal temperatures for electronic components are maintained at all times thereby enhancing longevity through preventing overheating. This helps in ensuring uniform exposure of all parts of a meal product to microwaves inside a defrosting chamber through use conveyor belts or tables rotating within it.
To summarize, precise control systems and energy efficient design parameters coupled with large scale requirements allow microwave thawing machines to offer technologically advanced industrial solutions for unfreezing frozen products in conformity to other industries’ demands.
What Are the Benefits of Using a Microwave Thawing Machine?
Thawing machine has numerous advantages that lead to its use in the microwave. Rapid and uniform thawing is essential for maintaining food safety and quality. The microwave significantly reduces the defrosting time when compared to conventional methods, increasing efficiency in production. The precise control systems ensure that the product reaches the desired temperature uniformly, minimizing the risk of bacterial growth that can occur with uneven or prolonged thawing—Additionally, energy-efficient machines aid in reducing utility bills and lowering environmental impacts as a whole. Through consistent performance, advanced sensors and feedback mechanisms have been integrated into them; these are complemented by waveguides and rotating tables among other features which are included in their design hence ensuring even exposure of all parts of the product to microwaves.This holistic approach helps in enhancing operational efficiency coupled with supporting durability and reliability of machinery on production line.
Efficiency in Thawing Frozen Meat
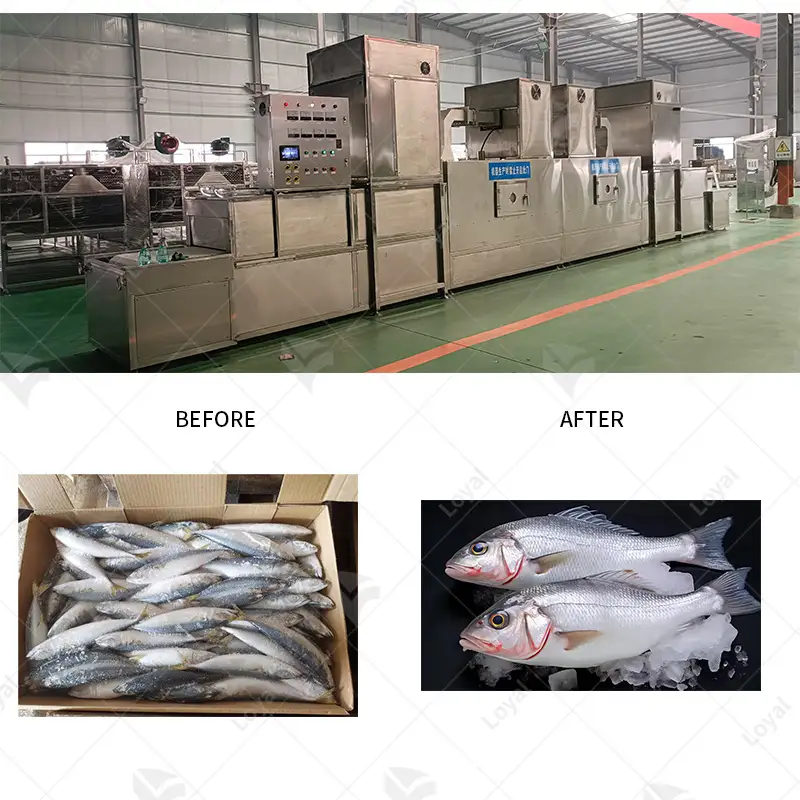
Fast and uniform penetration of food by microwaves makes them best suited for effectively thawing frozen meat. Microwave machines work by vibrating water molecules in the meat using electromagnetic waves, making it thaw fast and evenly throughout. This reduces microbial contamination risks and keeps the quality of the meat at its optimum. Unlike traditional methods that can be time-consuming and take several hours to complete, microwave defrosting is far faster and takes just a couple of minutes in most cases. Furthermore, such machines are highly equipped with advanced control systems that help avoid cold spots even as they enhance precise temperature control hence no partially frozen parts of the product. This increases production efficiency and also improves food safety within an industrial set up.
Energy Savings with Microwave Defrosting
Microwave defrosting is known for being more energy efficient than other methods, leading to cost savings and environmental benefits. For instance, microwave defrosting utilizes electromagnetic waves to speed up the thawing process, meaning that very little electrical energy will be required, unlike traditional techniques. Since these cycles usually take only a few minutes while working, they will involve fewer resources, subsequently reducing electricity consumption.
One of these saving measures may be expressed through specific power consumption per unit during microwave defrosting, which ranges from 0.65 to 1.2 kWh/kg. What makes this relevant is that when considering large quantities of meat like this when employing conventional techniques based on air or water immersion alone could lead to losses surpassing four times greater than those realized with modern methodologies. Additionally, new models come with adjustable wattage options together with smart controls, allowing them to optimize power supply depending on necessary conditions associated with any particular load during thawing operations, thus further enhancing their efficiency.
Studies carried out by experts who compare energy usage patterns of traditional thawing and microwave defrosting have determined that incorporating such advanced features can reduce overall energy consumption by up to 70%. Furthermore, the short time needed for defrosting also means lower amounts of total power used, hence making this process even more ecologically acceptable. The utilization of improved insulation, together with optimized waveguide designs during construction, leads to highly efficient machines that have better performance and consume less energy.
Improved Safety and Hygiene
Microwave defrosting ensures energy efficiency and improves many aspects of safety regarding hygiene in food handling. Other methods of defrosting like water immersion or thawing at room temperature often result into long periods when food remains at temperatures suitable for the growth of bacteria. On the other hand, microwave defrosting reduces how long food remains at a “danger zone” (40°F to 140°F, according to the FDA) where disease-causing strains of bacteria thrive. The speedy heating by microwaves equally makes it easy for food to move through these crucial temperatures, hence reducing the chances of getting sick from eating.
Technical parameters related to safety and hygiene include uniform heating patterns that prevent certain parts from being exposed to extended non-frozen states in microwaves. Advanced microwave defrosting units have sensors and control systems that monitor and regulate power levels as well as the length of time needed for each defrosting cycle. These attributes guarantee that foods are even when they thaw, thus minimizing cold spots, which can provide a conducive environment for bacterial multiplication.
Moreover, many contemporary microwave defrosters have been made with ease of cleaning in mind. For instance, materials used in their construction like stainless steel with antimicrobial properties boost general cleanliness through prevention against bacterial attachment and growth. Detachable components and smooth surfaces enhance regular cleaning schedules ensuring adequate sanitization on top of compliance with standards about safe handling.
In conclusion, advanced control systems, uniform heating characteristics, and hygienic design elements combine to make microwave defrosting a superior choice when it comes to improving safety regarding hygiene around food, according to top sources on this matter. Not only do these improvements guarantee adherence to regulations that protect against food contamination, but they also help safeguard consumer welfare by mitigating risks associated with inadequately done thawings.
How Does Microwave Thawing Compare to Other Thawing Methods?
Microwave thawing is often compared with traditional methods such as refrigeration, cold water thawing, and room temperature thawing. Unlike refrigeration, which takes a longer time (from several hours to days) to safely defrost food, microwaving cuts down defrosting time significantly to some few minutes. While faster than refrigeration, cold water thawing has to be done manually by changing the water regularly so that it remains cold which can be very laborious. However, room temperature thawing is less recommended due to the likelihood of foodborne pathogens growing due to long periods of keeping the food within danger zone (40°F – 140°F). Microwave defrosting addresses these issues very well with advanced sensor and control systems providing swift even defrosting in order that the food does not stay at unacceptable temperatures for long time. A key benefit, therefore, is microwave defrosting a more efficient, safe, and reliable way of preparing frozen food urgently.
Microwave Vs. Water Thaw
Several technical parameters differentiate microwave thaw from water thaw. Firstly, electromagnetic waves are used during microwave frying in order to excite water molecules inside foods, thus generating heat for fast cooking them, while in the case of water preparation, the conductive heating process by the surface layer is slower and inefficient.
One advantage of microwave thawing is its speed; authoritative sources state that microwaving can reduce defrost times to only minutes, while depending on the size and thickness of products, it may take about an hour or more when using running tap water. Additionally, microwave defrost has better control features like sensors with power setting adjustments so that perfect levels are adjusted automatically for uniform heating.
There is a safety concern regarding bacterial multiplication rate demands for minimal duration of stay within the danger zone (40°F —140°F). This happens especially if it is not possible to closely monitor and sustain water temperature below 70°F when doing water-based unfreezing. Similarly, some ways of defrosting always require a constant supply of running water to keep it cold, but this may cause water wastage and demand continuous checks.
Lastly, because there is little water loss in microwave thawing, food quality is best preserved compared to water thawing, avoiding texture and flavor degradations. During the process of defrosting, these systems are responsible for controlling the food’s cellular integrity thus ensuring that its texture does not change.
In conclusion, however, both methods are appropriate for freezing food. Microwave thawing is best considered given its quick processing times, enhanced safety controls, and preservation of quality, while the former indicates that it remains an advanced way forward in relation to speedy, safe preparation of frozen foods.
Benefits of Using Microwave Technology in Thawing
Microwave defrosting exploits diverse technological advancements for efficient and safe food preparation. One of the main advantages is its speed. Unlike the traditional method, modern microwaves that have inverter technology achieve consistent power delivery, leading to significantly reduced thawing time. For example, most foods can be defrosted within ten minutes, compared to other customary methods that may take hours. Moreover, integrated sensors on these gadgets can accurately measure humidity levels and temperature while making necessary adjustments to settings, thereby maintaining favorable conditions for defrosting.
From a safety perspective, microwaves ensure that food remains out of the bacterial danger zone (40°F – 140°F). More sophisticated models possess electrical safeguards capable of monitoring food internal temperatures in order to minimize uneven defrosting responsible for fostering the growth of bacteria. This will help ensure that the freezing process does not result into unsafe temperatures for the food.
Moreover, microwave-thawed foods retain their quality better through controlled defrosting cycles which minimize moisture losses. Inverter technology-based appliances avoid energy fluctuations via high-and-low cycles shown by technical parameters that can damage cells.Consequently, taste and texture are preserved giving rise to more delicious finished products.
In conclusion, microwave thawing offers unparalleled efficiency, advanced safety features, and better preservation of food quality, making it far superior to traditional methods.
Common Problems Encountered with Microwave Thawing and Their Solutions
A common problem here is uneven thawing where some portions of the food may start cooking while others remain frozen at point zero degrees centigrade or below this level. To solve this issue therefore it is crucial not only to employ a microwave’s auto-defrost feature but also rotate or turn over perishables frequently during this processing period respectively such as beef fillets or turkey breasts.Moreover one should take note of possible water loss occasioned by dryness which might lead to parched meat.Considering, therefore, the use of a microwave-safe cover or wrapping it with moist paper towel can help maintain moisture. Furthermore, the wrong choice of containers, for instance, leads to food poisoning due to the leaching of dangerous chemicals. Consequently, one should only go for those containers that are specifically made of high-temperature resistant material in order to avoid degradation.By following these guidelines, one can ensure a safer and more effective microwave thawing experience.
What Types of Microwave Thawing Machines Are Available?
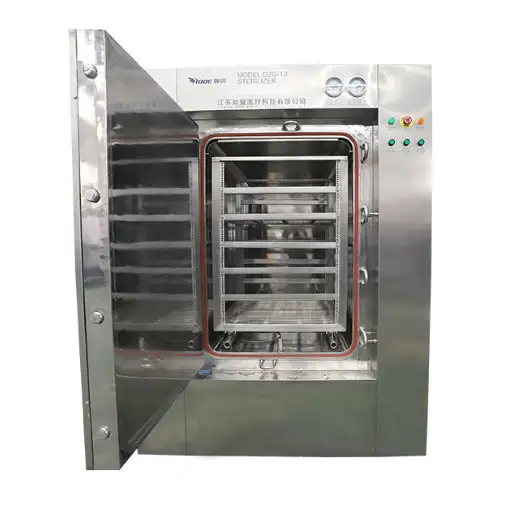
Different types of microwave thawing machines are available to suit different needs and sizes of operations. Consumer grade microwaves are the most commonly used in households with kids, and they have simple defrost settings that can be used for small amounts of food. These products also often come with a defrosting option that uses sensors which uses sensors to ascertain the time and power needed for best results.
Commercial microwave thawing machines are made for restaurants and food service firms since they handle large amounts of foods constantly. They use inverter technology and programmatic cycles that ensure even melting when dealing with food in bulk therefore reducing the overall preparation time considerably.
Industrial microwave thawing systems are typically employed in large-scale food processing. The systems, using continuous belt or batch designs, maximize throughout but maintain high-quality food. This yields industrial defrosters with integrated monitoring functions, including exact temperature control, thereby delivering mass melt functionality like no other.
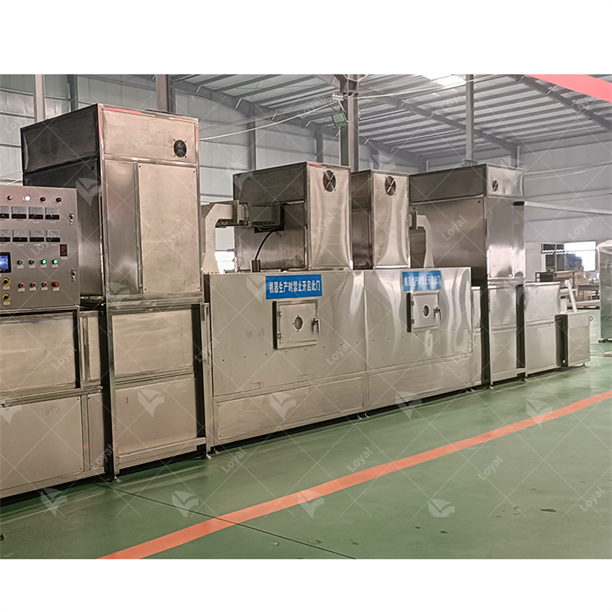
Overview Of Tunnel Type Microwave Thawing Machines
Tunnel type microwave thawing machines are aimed at industrial food processing applications where products need to be unfrozen continuously in great quantities. Such designs are usually incorporated into conveying equipment where microwaves get emitted inside a tunnel. Thus, this design ensures even distribution while making sure that the energy is applied uniformly for quick defrosting processes across all regions – both coming together, if you will, through the rapid freezing stage before entering the corresponding go or stay state depending on whether the freshly grown cell was frozen. What has been done here again? Modern tunnel type machinery has advanced controlling units for regulating temperature as well as power levels required during precise melting without compromising on quality or health safety aspects such as those concerning meat spoilage due its bacterias growth because no one wants their chicken sold out already cooked dinner packaged uncooked tomorrow It cannot manage various kinds like fish apples pear etc so it limits usage within limited scope of these types products; hence not suitable as alternative choice towards any kind situations related to thawing processes taking place within large scale production facilities.
Comparing Tunnel Microwave Thawing to Batch Process Machines
Tunnel microwave thawing machine and batch process machines each have their own unique advantages that make them suitable for different purposes. This is so because tunnel microwave thawing, unlike batch systems, can handle huge quantities of foodstuffs without any stoppage. It is perfect for high-capacity operations which require a steady supply of materials, thereby ensuring little or no downtime and maximum output. In addition, the continuous belt in these tunnels ensures that there is consistent exposure to microwave energy, hence resulting in even defrosting times over a certain area. On the other hand, batch processing may be used flexibly as well as controlled meaning it lets operators process specific amounts of food at one time only whereas this might be useful when dealing with less amount or frequent exchanges between the many products being offered on daily basis by most convenience stores located near our homes today; also known as “small shops” where we usually just pick up whatever we want without worrying about whether they will run out before closing down next morning either Side Note: What kind types products? Like Noodles chicken meat etc … The second option is generally more accurate due its sensitive nature thus requiring delicate handling techniques especially treating fragile items such as those made from egg whites… both brand new are equipped latest safety features available market nowadays I’d stick my old ones rather than purchasing something which might not last long enough because there still lots other things needing bought too such clothes shoes toiletries etc. Consequently, while both incorporate advanced temperature control and monitoring technologies for ensuring overall product quality and security reasons, decision-making should depend upon precise requirements existing within processing establishments themselves.
Attributes to Consider in Thawing Gear
You must take into account several essential characteristics when choosing defrosting equipment for efficient performance. Firstly, it is vital that the equipment should be efficient and fast besides having a high thaw rate to reduce processing time and increase productivity. Secondly, homogeneity of thawing matters as temperature variations could expose food safety and quality to risk. These are some machines with advanced microwave distribution systems or precise airflow control for consistent results. Besides, cleanliness and maintenance requirements also play a part; the best appliances would employ accessible components made of hygienic materials that meet sanitation’s strictest demands. Moreover, different food sensitivities require different thaw parameters such as temperature and time. Lastly, looking at energy consumption and cost-effectiveness ensures the suitability of the devices not only for operational requirements but also sustainability in terms of finance.
How to Maximize Efficiency with Tempering and Defrosting Systems
A combination of advanced technologies and best practices is required for efficient operations in tempering and defrosting systems. Firstly, calibration and maintaining equipment regularly will be obligatory to ensure its optimal performance. In this regard, all checks and servicing are necessary to avoid any operational inefficiencies. Secondly, they should install programmable logic controllers (PLCs) and automated systems that permit temperature and power level adjustments as well as time in order to cope with the requirements of individual food products. Thirdly, it is useful to separate batches depending on the size or type of product for thawing with a view to increasing uniformity as well as quickening up the process, which will result in the reduction of total process time. Moreover, using real-time monitoring in addition to data analytics can help track performance metrics and identify areas requiring improvement. Lastly, incorporating energy-saving technologies and practices enables minimizing costs while preserving high throughput levels coupled with proper quality controls. These strategies will enable operating facilities achieve better efficiency, productivity and cost-effectiveness when dealing with tempering or defrosting.
Optimizing the Thawing Process for Frozen Meat
This paper highlights several essential strategies that are geared towards optimizing the thawing process for frozen meat. Firstly, employing water-based thawing systems such as air-assisted water system or water immersion leads to faster and more even thaw when compared to air-based techniques alone. Advanced immersion system circulates temperature-controlled water around meat leading to regular heat transfer rates that are rapid enough.Secondly,bacterial growth risk is reduced by reducing thawing time through continuous flow thawing where meat moves through controlled temperature zones.Thirdly,this technology can hasten the thaw at microwave assisted while still ensuring quality of meat has not been tampered with hence reducing drain loss.This technology uses microwave energy selectively thus ensuring even external and internal heating during thawing.Additionally,pulsed electric fields (PEF), have been shown to enhance the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) have a better quality and texture.It is, therefore, evident that incorporating these modern techniques and approaches will enhance frozen meat thawing with consideration of quality, safety and efficiency aspects.
Balancing Microwave Tempering for Different Food Products
An approach that acknowledges each product’s unique characteristics must be used when balancing microwave tempering for different food products. Firstly, it is necessary to consider the specific heat transfer properties as well as moisture content while setting microwave power and duration of heating. For instance high fat meats may need lower microwave power settings in order to avoid spotty heating or frying of fats. Secondly, temperature at which the product starts should be closely observed; different set up can be required if the product starts from deep-freeze compared to slightly thawed ones. A controlled temperature gradient can help ensure uniform tempering. Thirdly, geometric shape as well as size of the food product plays a major role; products that vary in thickness may require rotation or flipping during tempering process so as to achieve even heat distribution.Additionally,infrared thermography used in continuous monitoring provides real time feedback on temperature profile enabling adjustments along with the process.Implementing such specific detailed alterations enables efficient balance across diverse foods for microwaves hence improving general quality together with safety purposes.
What Are the Maintenance and Safety Considerations for Microwave Thawing Equipment?
To ensure prolonged life and safety, proper maintenance and safety considerations for microwave thawing equipment are essential. Key among them is routine cleaning of the equipment to remove food residues and prevent microbial contamination. This will involve cleaning the inner surfaces by wiping them and following the manufacturer’s guidelines as far as such removable parts as are concerned. Regularly check microwave components, like magnetron, waveguide and others, for any signs of tear or malfunction affecting performance. This keeps the equipment within its specified limits; correct alignment of power settings minimizes chances of overheating or uneven heating. Furthermore, keeping clear records on usage and maintenance helps in monitoring its state over time. There are important protocols like regular calibration as well as use of personal protective devices that should be observed alongside operational instructions during operation so that these risks can be mitigated accordingly. Thus, all these measures help maintain efficient, safe, reliable performance of microwave thawing equipment.
Regular Maintenance Needs for Microwave Thawing Systems
Regular maintenance needs for microwave thawing systems are essential for both their best possible performance and safety considerations in operations. First thing which should be done regularly is cleaning the system. In particular, this entails removing food particles from it plus sanitizing its inner or outer surfaces with chemicals that kill germs like bacteria causing diseases such as cholera or typhoid fever according to several guidelines provided by industry leaders.
One way to preserve these systems is through periodic inspections. For instance monthly inspections should include checking key components such as magnetrons, waveguides ignition transformers cooling fans among others involved in the process of defrosting meals at high temperature due these procedures malfunctions may show up incomplete cooking.
It is also necessary to control technical parameters periodically because they often change with time or operation conditions. For example, one can always evaluate how stable a certain frequency that microwave operates at (approximately 2.45 GHz) is to ensure that it consistently thaws well. Power output stability should also be measured (usually ranging from 1000 to 3000 watts, depending on the type) so that the desired thawing temperature and time are not affected.
Finally, safety first. This is done by verifying that radiation does not leak out through door seals, as can be determined using a microwave leakage detector. Furthermore, equipment should be regularly calibrated, and detailed logs of all maintenance activities should be kept, as this helps in identifying any repeated faults and planning preventive actions accordingly. Therefore, such practices increase the life expectancy and improve the performance of defrosting systems.
Safety Best Practices for Operating a Microwave Defrosting Machine
When using a microwave defrosting machine, it is important to adhere to certain safety regulations so as to protect both the user and the appliance itself from damage. First of all one must always follow manufacturer’s instructions clearly stipulated in their operational manuals which give safety tips and guidelines for operating these appliances to avoid accidents or injuries. Proper earthing ensures there are no potential electric shocks especially because some high-power devices produce up to 3000 W which may cause accidents thus machines should have electrical grounding.
Secondly there are regular checks carried out on safety measures that must never be neglected. It means examining electrical parts such as magnetron transformers, among others, for signs of wear or faultiness is vital before they can get damaged completely. In addition this implies checking if doors are properly sealed preventing dangerous emission of radiations that might even lead to cancer; such activity may require use of an instrument called microwave leakage detector ensuring FDA confirmed levels do not exceed 5mW/cm2
Thirdly, the temperature and frequency parameters need to be checked carefully. This machine’s typical operating frequency is around 2.45 GHz, and stability within this range should be maintained for efficient thawing. Calibrated measuring tools are used to ascertain that these are maintained within their defined operational limits.
Finally, it is crucial to wear gloves that can withstand heat to guard against accidental burns from hot surfaces or food containers. Issues such as what to do during emergencies, like isolation of the device from the power supply, and first aid measures against microwave radiation exposure should be made explicit.
In conclusion, operators of microwave defrosting machines can avoid hazards related with such machines by following these safety best practices.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What is an Industrial Microwave Thawing Machine?
A: An Industrial Microwave Thawing Machine is a specialized microwave oven designed for fast and efficient defrosting of frozen products like meat, seafood, and other frozen food items. It uses microwave energy to rapidly defrost and temper the products, making it ideal for the food processing industry.
Q: How does an industrial microwave defrosting system work?
A: Industrial microwave defrosting systems use microwave energy to penetrate frozen food and heat it from the inside out. This allows for an even and rapid thawing process, reducing the time required compared to traditional thawing methods.
Q: What are the benefits of using industrial microwave thawing machines over traditional methods?
A: Using industrial microwave thawing machines offers several benefits, including faster defrosting times, improved quality of the meat, reduced drip loss, and minimal bacterial growth. This makes it a more efficient and hygienic method for defrosting and tempering of food.
Q: Can industrial microwave thawing machines be used for all types of frozen food?
A: Yes, industrial microwave thawing machines can be used for a wide variety of frozen food products, including meat, seafood, vegetables, and ready-to-eat meals. They offer versatility in defrosting different types of frozen products efficiently.
Q: What is the difference between a microwave tempering system and a microwave dryer machine?
A: A microwave tempering system is used to thaw or temper frozen food items to a state where they can be further processed, while a microwave dryer machine is used to remove moisture from products. Both use microwave energy but serve different purposes in the food processing industry.
Q: How does the quality of the meat benefit from microwave thawing systems?
A: The quality of the meat benefits from microwave thawing systems as they provide rapid thawing without cooking the surface of the meat. This helps in retaining the meat’s texture, flavor, and nutritional value, ensuring high-quality meat defrosting.
Q: Are there specific maintenance requirements for an industrial microwave oven used for defrosting?
A: Yes, maintaining an industrial microwave oven used for defrosting involves regular cleaning of the microwave cavity, checking for any signs of wear or damage, and ensuring that all components are functioning correctly. Regular maintenance helps in ensuring efficient operation and longevity of the equipment.
Q: How do industrial microwave thawing machines contribute to the overall productivity in the food processing industry?
A: Industrial microwave thawing machines contribute to the overall productivity in the food processing industry by reducing the time required for the defrosting process, leading to faster production cycles. This efficiency allows for higher throughput and better utilization of resources.