In the endlessly changing world of food preservation, machines for sterilizing food have become lifelines for preserving the freshness and safety of packaged foods. This guide is inclusive in presenting readers with a complete understanding of how these devices operate, their benefits, and practical tips. If you are a home cook wanting to extend the shelf life of your meals or someone who owns a small business that wants to boost its food safety standards, then this guide will offer you guidance on fundamental principles and practices of sterilization.
What is Food Sterilization, and Why is it Important?

Image source: https://www.wnapt.com/
Food sterilization is designed to kill or reduce harmful microorganisms in food products, such as bacteria, viruses, and fungi, thus increasing their safety and extending their shelf life. This typically involves food exposure to high temperatures or chemical agents that could be used to kill pathogens. The importance of food sterilization arises from its ability to prevent foodborne illnesses, retain nutrients, and augment the general quality of packed foods. Properly sterilizing foods ensures that consumers get safe and high-quality products while at the same time reducing waste, hence improving inventory management by businesses that produce them themselves.
The Role of Sterilization in Food Safety
In food safety, sterilization is essential as it effectively reduces the risks associated with foodborne illnesses. It ensures that the harmful organisms are killed or inactivated, which is crucial in protecting public health. Properly sterilized foods remain of high quality for a long time and thus can be consumed safely by people. In addition, methods such as heat treatment and irradiation lengthen the period during which products can stay on shelves and retain essential nutrients, thereby contributing to a balanced diet. Ultimately, strict adherence to sterilization standards helps food producers meet safety regulations, ensuring consumer confidence and satisfaction.
How Sterilization Helps Preserve Food
Sterilization is crucial in food preservation as it effectively inhibits spoilage microorganism growth so that the latter stays safe for consumption over extended periods. According to FSIS (Food Safety and Inspection Service), heat sterilization techniques destroy pathogens and enzymes, leading to food spoilage; thus, these methods maintain the quality of products and extend their shelf lives. Furthermore, a publication in the International Journal of Food Microbiology indicates that sterilization procedures, including high-pressure processing and aseptic packaging, drastically decrease microbial load while leaving nutritional value intact. In conclusion, these processes assist in waste minimization and ensure consumers obtain safe nutritious articles.
Difference Between Sterilization and Pasteurization
Food security relies on sterilization and pasteurization but differ in means and results. Sterilization is a process that kills all microbial life, including all spores, through high temperatures or chemical agents, thereby increasing the shelf life of consumables. This technique is often used in canned foods and other shelf-stable goods. Pasteurization, on the other hand, uses lower temperatures for a shorter duration to kill or inactivate harmful bacteria without damaging food’s nutritional quality or taste. It is commonly practiced in dairy and juice processing industries, where it does not render them completely sterile but reduces the amount of microorganisms to safe levels. Understanding these differences enables food makers to choose what method would be more suitable for maintaining the safety and the quality of their products.
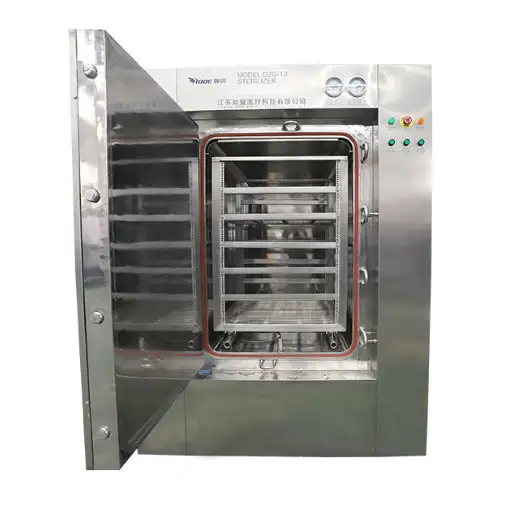
Types of Food Sterilization Machines and Equipment

Different machines and equipment can realize food sterilization, each made for specific processing requirements. Some common types include:
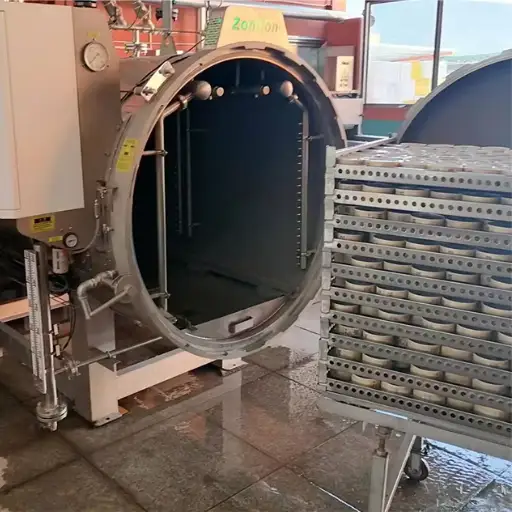
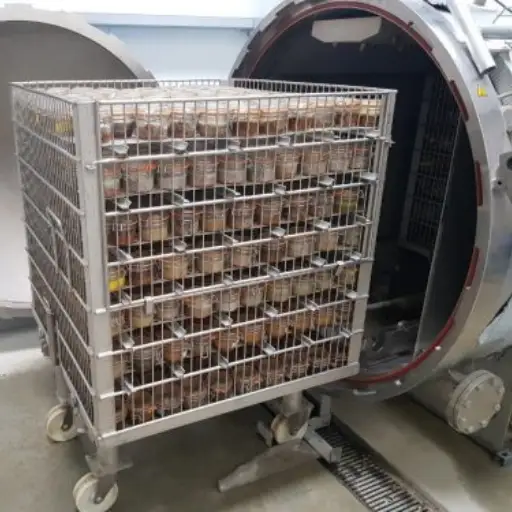
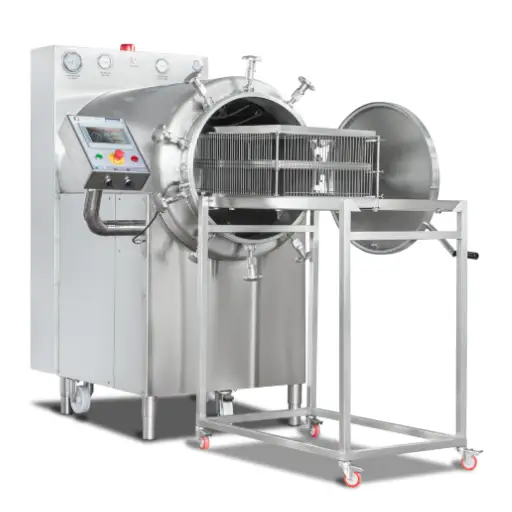
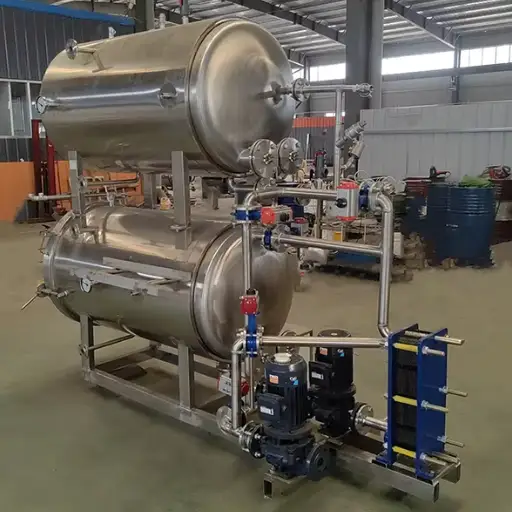
- Autoclaves: These steam pressure cookers are widely used for canning and aseptic processes. They kill off any form of life while ensuring quality food storage.
- Heat exchangers: They are found in pasteurizing sections where they quickly heat liquids so that pathogens are destroyed without impacting the taste and nutrition of the product.
- Retorts: These are particular types of pressure cookers specifically designed for retort pouches. They provide high-temperature conditions with increased pressures necessary to keep canned foods from going bad.
- Ultraviolet (UV) light systems: Non-thermal techniques using ultraviolet lights on surfaces of water and food products help disinfect them in an environmentally friendly way, eliminating risks associated with chemical use.
- High-pressure processing (HPP) machines: This advanced technology eradicates pathogens in fresh produce while retaining its sensory attributes, making HPP increasingly popular among processors.
The right choice of sterilizing equipment allows manufacturers to enrich their merchandise with safety features, increase its durability, and preserve product excellence.
Overview of Sterilizers Used in the Food Industry
The food industry depends on sterilizers to ensure that products are safe to consume and stay in good condition. Different forms of sterilizers include:
- Batch Sterilizers: These systems process products in designated batches, allowing for uniform treatment. They are often used for products that require specific temperature and time parameters.
- Continuous Sterilizers: Unlike batch systems, continuous sterilizers operate flow-through, ideal for high-volume production. They maintain consistent sterilization conditions and are commonly used in juice and liquid food processing.
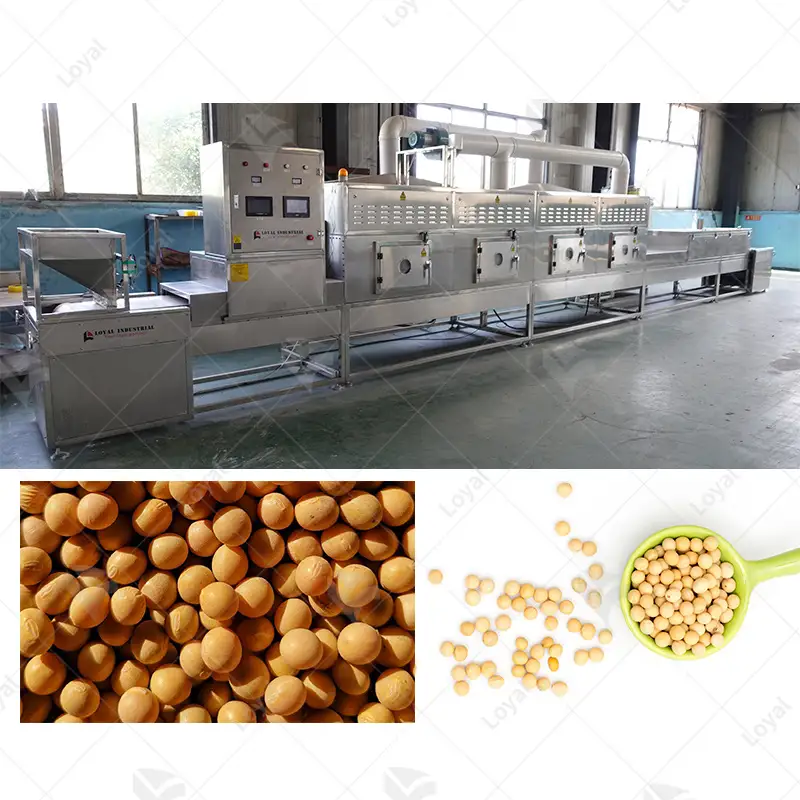
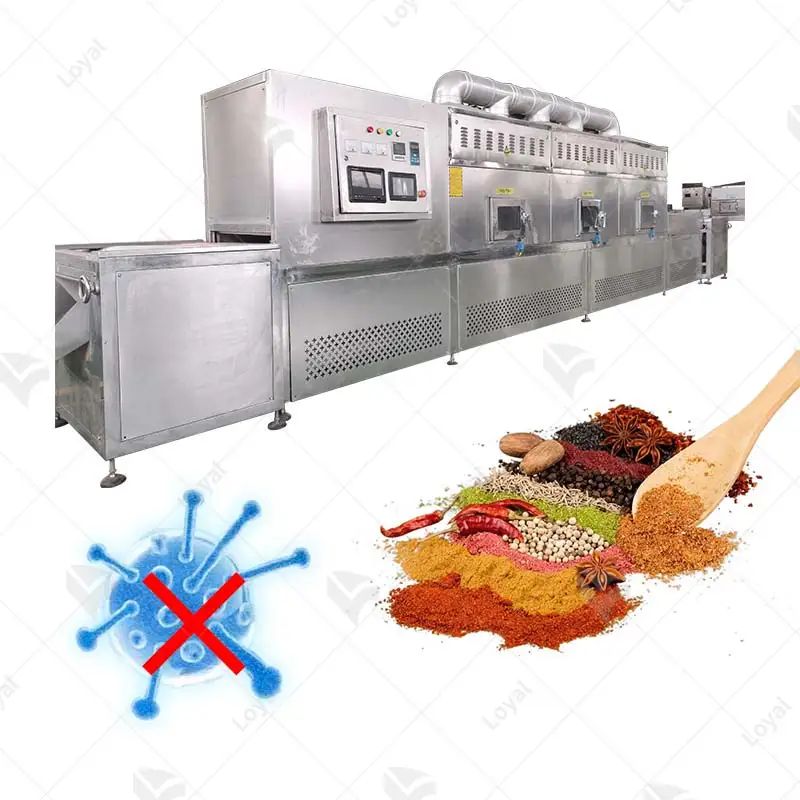
- Microwave Sterilizers: Microwave sterilizers use microwave technology to heat food items to destroy various microbes rapidly. They have grown increasingly popular over the years due to their speedy operation and energy-efficient nature.
Food producers can leverage these tools by understanding what each can do and where it is applied to improve food safety and quality assurance.
How Autoclaves Work in Food Processing
Autoclaves provide effective steam-pressure-based sterilization during food processing. At this stage, food materials are first loaded into the autoclave chamber before its subsequent sealing. Once the chamber is closed, steam is introduced, raising the temperature and pressure inside the chamber. It effectively kills all microorganisms, including bacteria, viruses, and spores, thereby rendering the food fit for human consumption.
It depends on several factors, such as the nature of the packaging material and its contents, that dictate the duration and temperature settings of an autoclave cycle. Usually, temperatures no less than 121°C (250°F) must be maintained for not less than 15 minutes to ensure complete sterility. After completion of the forced death process, the pressure is reduced steadily until it can be removed safely from inside without any harm being done to them or exposed to harm by getting burnt with hot water vapor or steam produced within autoclaved reactors. Autoclaving also preserves nutritional value as well as taste, making it a preferred choice in the food industry considering both product safety issues and processed product sensory attributes.
Understanding Microwave Sterilization Techniques
Microwave sterilization is an innovative technique that employs electromagnetic waves to quickly and effectively heat food products. Microwaves shake water molecules in the food so fast, producing steam that kills microorganisms. The cooking of various foods using this method usually goes on at temperatures between 60°C and 140°C (140°F and 284°F). One of the main advantages of microwave sterilization is that it retains nutrients while preserving the taste and texture of food. Additionally, this technique can be incorporated into continuous processing systems, thus leading to improved efficiency and throughput for food producers. Being energy-efficient, microwave sterilization remains one of the most prospective trends in the industry to comply with up-to-date food safety and quality requirements.
Innovations in Thermal Processing Equipment
Recent improvements in thermal processing equipment have focused on increasing efficiency, safety, and sustainability in food manufacturing. First, implementation of the IoT systems can allow monitoring of live events and data analysis during heating processes, enabling operators to ensure good conditions and hence improve operational output. Second, advancements in energy recovery systems are being implemented to minimize energy consumption during operations. This also comes with reduced operating costs at large-scale levels and a decreased carbon footprint throughout the entire life cycle of the food production process. Finally, automated systems, together with robotics development, enhance thermal processing accuracy and consistency, thereby leading to better product quality and reducing human error. All these innovations aim to satisfy emerging needs within a sector, such as the demand for safe foods with high levels of productivity without compromising their standard outputs.
How to Choose the Right Food Sterilization Machine

There is a whole range of factors to consider when selecting an appropriate food sterilization machine; this means an individual must make the right decision. You should assess your production line’s specific requirements first and foremost, including which type of foodstuff is being processed and the length of time for which it can be stored. Determine its performance and throughput capacity in a manner that will suit your operational needs. The technology used, i.e., microwave or thermal method, must also be considered since they have a bearing on nutrient preservation and taste quality. Another consideration is energy efficiency in reducing costs and allowing equipment integration into existing processes without affecting productivity. Lastly, look at support and maintenance services from the manufacturer because this determines how long it will last with high performance.
Factors to Consider When Selecting Sterilization Equipment
When choosing sterilization equipment, the following are essential factors to consider:
- Tech Type: Find out if the system uses steam, gas, or microwave technologies, then decide which one is best for the given products. Each has unique strengths when it comes to effectiveness and maintaining edibility.
- Regulatory Compliance: Make sure that any machine you buy complies with industry guidelines, such as FDA or USDA regulations for safe food.
- Automation Capabilities: Find appliances with improved automation options. These options make appliances more hassle-free during operation while enhancing accuracy, lowering manual requirements, and increasing overall efficiency.
- Maintenance and Support: Look at how good the company’s customer service reputation is before deciding what brand/model you prefer. This can minimize downtime if machines have excellent customer care programs plus easy-access maintenance alternatives.
- Size and Footprint: Check out the physical dimensions of machines so that they fit within site space yet still allow room expansion sometime in the future.
- Cost of Ownership: Beyond the initial price tag, take into account total ownership costs such as electricity bills, servicing/maintenance charges, plus the likelihood of being idle intermittently
Overall, these factors combined will guide you to choose an efficient and dependable sterilizer customized for your facility’s specific needs.
Comparing Different Sterilization Techniques
When assessing sterilization methods, it is essential to consider their different procedures and uses.
- Steam Sterilization: This process uses highly pressurized steam to kill microorganisms. It has been praised for its efficiency and ability to sterilize a wide variety of materials. Steam sterilization is commonly applied in hospitals and food processing places, as it can be used on heat-and-moisture-stable items.
- Chemical Sterilization: It involves the use of chemical agents like ethylene oxide (EtO) or hydrogen peroxide. It finds use in equipment or materials sensitive to heat and cannot tolerate high temperatures. Yet, some chemicals may be toxic and require careful handling and ventilation.
- Radiation Sterilization: Radiation sterilizations employ gamma rays or electron beams that pass through packaging and materials to kill any pathogens present. This method is extensively used to ensure safety when single-use medical supplies need to be sterilized together with food products that require a long shelf life.
Each approach has advantages and disadvantages; therefore, the selection depends on factors such as the sterilized objects, regulatory compliance requirements, and operational efficiency, among others. Balancing these parameters will help guide the choice of the most appropriate option for specific needs.
Cost and Efficiency of Various Sterilizers
When evaluating the cost and efficiency of sterilization methods, it’s crucial to consider both the initial investment and ongoing operational expenses
- Steam Sterilization: This technique generally has lower operating costs due to its reliance on easily available water and electricity. The initial cost of equipment can vary but is usually offset by efficiency during routine sterilization processes. Studies indicate that steam sterilizers usually run at a cycle price between $0.15 and $0.20, making them economically viable in numerous healthcare settings.
- Chemical Sterilization: These can be expensive, especially regarding quantities needed or particular agents employed, e.g., ethylene oxide prices can fluctuate widely per volume required, while machinery might not be so costly. The cost per cycle may range from $0.50 to $2.00 under the influence of compliance and safety measures which may be required when using chemicals.
- Radiation Sterilization: Although radiation sterilization equipment may require high initial investments, sometimes amounting to several hundred thousand dollars, its efficiency can justify it. The cost per cycle tends to be lower in terms of production scale, especially for single-use items. Generally, depending on the materials and volume being treated, operational costs could span from as low as $0.10 per unit to around $0.50.
Ultimately, not only cost but also efficiency are important when selecting the sterilization method based on specific environmental and operational factors like regulation adherence or the nature of the items being sterilized.
Steps for Properly Using a Food Sterilization Machine

- Preparation: Ensure all food items are clean, free from residues, and appropriately packed in containers designed for sterilization.
- Load the Machine: Carefully arrange the containers in the sterilization machine, ensuring they are not overcrowded to allow for proper steam or chemical circulation.
- Select Sterilization Settings: Based on the food type and sterilization method, choose the appropriate temperature, pressure, and cycle time. For specific guidelines, refer to the machine’s manual.
- Start the Process: Start the sterilization cycle by activating the machine and monitoring the settings to ensure they remain stable.
- Cooling Down: After finishing a cycle of running it through a cooling phase, it would be necessary to prevent accidents that may occur before opening.
- Check the Seal: Verify that effective seals have been maintained on each container while inspecting them against signs of spoilage or leaks
- Store Properly: To avoid contamination after steaming, store these sterilized edibles away from moisture in a hygienic place that meets health standards
Preparation and Setup of Sterilization Machines
To efficiently prepare and set up sterilizers, ensure they are clean and work well. The first step is following manufacturer instructions for initial setup, including checking all connections and settings. Before placing any foodstuff in them, check out their condition for possible damages, if any, then fit to be used for this purpose. Containers should be arranged loosely inside these machines, thus allowing free movement of chemicals or steam. Depending on whether you are using equipment like autoclave bags, baby bottle microwave sterilizers, or others, there will always be different parameters that can be set, such as duration taken for heating at specific temperatures, among other factors which vary depending upon what kind of item has been put inside one given box but needs immediate attention if ever anything breaks down during usage it could become hazardous hence must maintain regular services to guarantee its reliability over time without endangering anyone’s life whatsoever.
Understanding Sterilization Temperatures and Times
Temperature and time control are necessary for successful sterilization that destroys dangerous microorganisms. Usually, steam processes have sterilization temperatures of between 121oC and 134oC (250oF to 273oF) with a minimum duration of at least fifteen minutes at 121°C, depending on the load size and type of material. It takes approximately one or two hours for dry heat sterilization at temperatures ranging from 160 –1800 C (320 -3560 F). Some food items may require specific adjustments based on their moisture content and packaging. Monitoring devices and indicators confirm that the required temperatures and exposure times were achieved, hence the effectiveness of the sterilization process.
Monitoring the Sterilization Process
During monitoring of the sterilization process, it is essential to ensure that the desired temperature and exposure time have been attained. This can be done using calibrated thermometers for temperature readings, pressure gauges to monitor pressure levels inside a chamber, and timers for recording time in different cycles. Biological indicators such as spore tests can also show whether a sterilizer is effective because it responds to conditions there. Regular calibration practice should exist for all monitoring equipment. The records maintained in every sterilizing run would be helpful when demonstrating efficiency changes over a period and adherence to safety requirements. This aspect further improves quality assurance compliance through regular audits of the sterility process.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting Tips for Sterilization Machines

Common problems affecting sterilization efficiency include inconsistent temperature readings and uncalibrated or poorly calibrated equipment. Therefore, ensure that monitoring instruments are regularly checked and calibrated following the manufacturer’s instructions. Another problem is inadequate cycle time which may require adjustments depending on the load size and material type. Sterilization failure calls for investigation into possible moisture contamination or incorrect loading, as overcrowding prevents proper steam penetration. Keeping detailed operational performance records can also help identify trends and provide opportunities for troubleshooting.
Dealing with Ineffective Sterilization
This poses a considerable risk, allowing pathogens to survive and contaminate sterile items. Dealing with this challenge successfully involves carrying out several steps based on insights from industry experts:
- Establish the Root Cause: Possible contributing causes could include wrong settings (temperature or time), incorrect device loading, or faulty equipment. Thoroughly inspect the sterilizer to ascertain any possible malfunctioning components.
- Revisit Sterilization Protocols: All staff should be adequately trained to operate sterilization systems and adhere to set protocols. Regular training and reminders on what works best will reduce the chances of human errors.
- Use Biological Indicators: To ensure that sterilization has been achieved, biological indicators should be used in some instances, such as spore testing, which needs to be performed every cycle. These indicators provide feedback on the sterilizer’s performance consistently.
- Regular Maintenance: Plan a weekly schedule for maintenance checks to keep your sterilizers functioning optimally. This includes calibrating thermometers and pressure gauges and cleaning the sterilizing chamber.
- Document and Monitor: Maintain detailed records for each sterilization cycle, noting any failures or deviations from normal parameters. Such data highlights inefficiencies by revealing patterns that might otherwise go unnoticed.
Thus, proactive measures like these will help healthcare facilities maintain effective patient safety techniques through successful practices for disinfection process issues.
Maintaining Sterilization Equipment
To effectively maintain sterilization equipment, creating and following a comprehensive maintenance schedule that includes regular inspections and servicing is essential. By the latest industry standards, the following vital practices are suggested:
- Regular Calibration: Ensure that all temperature and pressure monitoring devices are calibrated per their manufacturer’s specifications to ensure the sterilization process runs within prescribed parameters.
- Routine Cleaning: Clean the sterilizer’s interior and exterior regularly to prevent dust or contaminants from accumulating. Use suitable cleaning solutions compatible with the equipment to avoid damaging it.
- Component Checks: Check for wear and tear on vital components like seals, gaskets, valves, etc. Replace any parts showing signs of degradation to maintain optimal performance.
- Frequency of Maintenance: Schedule maintenance checks at least semi-annually or as recommended by the manufacturer of this equipment to identify possible threats before they affect sterilization efficacy.
- Documentation of Maintenance Activities: Keep detailed records of all maintenance activities, such as dates, findings, and corrective actions taken. This record is useful for compliance purposes and for tracking trends over time.
By implementing these maintenance strategies, sterilizing apparatuses can be prolonged in life while maintaining their efficiency; this ensures consistent results, which improve patient safety.
Troubleshooting Common Machine Errors
Challenges may be problematic in cases where errors are encountered while working with sterilization equipment.
- Error Code: E01 – Temperature Inconsistency
- Cause: This can happen due to defective temperature sensors or inaccurate calibration.
- Solution: Start by calibrating the temperature sensors as per manufacturer guidelines. After that, check for any loose connections, if not replaced the sensors.
- Error Code: E02 – Pressure Drop
- Cause: A decline in pressure could indicate an issue with a system leak or faulty pressure gauge.
- Solution: Visually inspect hoses and connections for leaks or damage. If no problem is found, consider replacing the pressure gauge or visiting a technician.
- Error Code: E03 – Cycle Failure
- Cause: Several causes might lead to this situation, such as wrong loading or equipment breakdown.
- Solution: Ensure that the sterilizer is loaded appropriately according to manufacturer specifications and look for any obstruction. If the cycle still fails, run a diagnostic test or refer to the troubleshooting section for more information on how to solve this problem.
By promptly addressing these typical error situations, producers ensure effective sterilization processes that conform to safety norms. Also, it’s recommended to regularly update knowledge about machine troubleshooting since both technology and guidelines change over time.
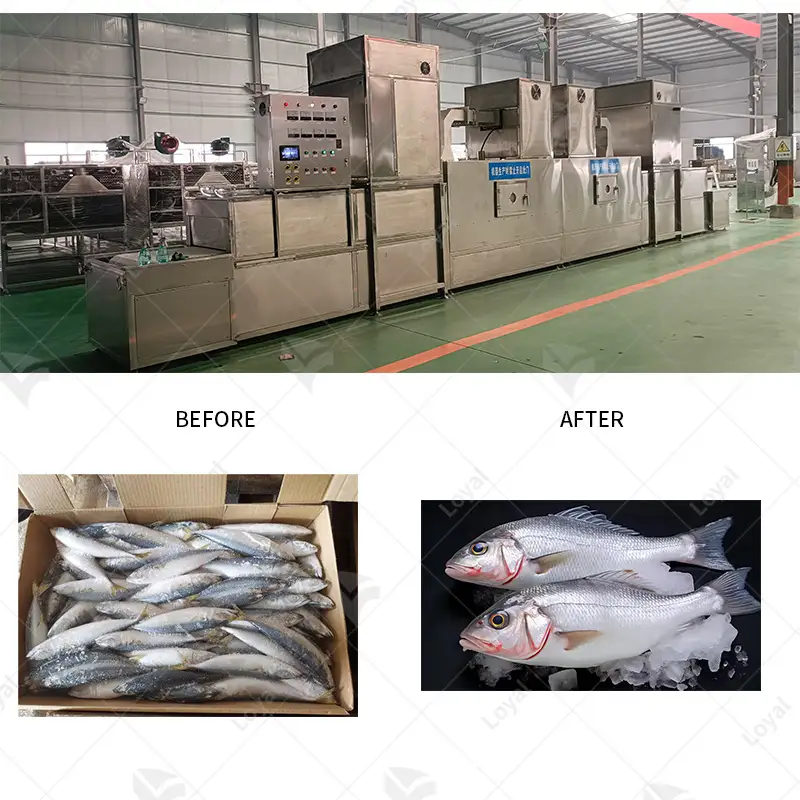
Impact of Sterilization on Food Quality and Shelf Life

The extension of foodstuff life is done by the process of sterilization, it gets rid of harmful microorganisms that causes spoilage. Food is heated to a level where all pathogens are killed, making consumption safe. Although sterilization helps decrease spoilage and increase shelf life, it may also influence certain sensory aspects of foods, such as taste, texture, and nutrition. For example, at higher temperatures, some vitamins may degrade while others may have their texture softened or consistency changed. Therefore, proper balance in the sterilization process is essential to achieve excellent food safety and quality. Another source states that ‘through careful attention to sterilization techniques, desired attributes of food products can be preserved while maximizing their shelf-life.
Preserving Nutritional Value During Sterilization
To maintain nutrients during sterilization, appropriate methods and temperature regimes must be chosen to minimize loss. This can be achieved through lower temperature treatments for shorter periods, ensuring the preservation of heat-sensitive vitamins like vitamin C and B complex. Additionally, hot water baths or steam sterilizations may take less time than traditional techniques, making more nutrient content remain intact. This is facilitated by vacuum packing before subjecting them to any form of sterilization, reducing oxygen entry and maintaining sensitive compounds’ integrity. Eventually, nutritional value can be preserved if the right environment for sterility is put in place; for example, how long should you cook something at what temperature, and under what conditions should one store particular goods inside sealed containers?
Effects on Shelf Life and Food Safety
Sterilization has several essential and multiple effects on food safety and shelf life. Good sterilization techniques can go a long way in reducing spoilage microorganisms and pathogen populations by making the food last longer than without sterilization. According to leading sources of food safety information, adequate sterilization prevents foodborne diseases by effectively eliminating harmful bacteria. For example, pressure cooking or retort sterilization methods have been shown to achieve higher safety standards, allowing products to remain safe for consumption over extended periods. In addition, these methods enhance food safety and extend its shelf-life, thus making them so important for both buyers and sellers alike. Generally speaking, proper interplay between good sterilization practices and appropriate food safety measures is crucial for maintaining the required standards in public health and food preservation.
Long-term Storage of Sterilized Food Products
Long-term storage of these items ensures their continued safety and quality after sterilization. According to the most recent advice from top websites specializing in advising on how people can safely store foods at home, keeping them in cool, dark, dry places is imperative. This helps against thermal degradation, enhancing the nutritional integrity of the item consumed. Again, maintaining temperatures consistently below 75°F (24°C) avoids fluctuations that could affect the integrity of the packaging seal. Equally important is thoroughly examining preserved items periodically for possible signs of spoilage or tampering with the package design. Finally, observing the recommended shelf-life guidelines for different kinds of preserved foods will guarantee their wholesomeness even after they are in the ready-to-eat stage after being processed all along this time period.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What is a food sterilization machine, and how does it help preserve packaged food?
A: A food sterilization machine is a device used to eliminate viable microorganisms in food, ensuring safety and extending shelf life. It helps preserve packaged food using heat or other sterilization methods to prevent spoilage and contamination.
Q: Why is sterilization necessary for canned food?
A: Sterilization is crucial for canned food as it ensures the elimination of harmful microorganisms, which can cause spoilage and foodborne illnesses. Proper sterilization prevents the growth of bacteria, yeast, and molds, extending canned food’s shelf life.
Q: How does a food sterilizer work in the packaged food sterilization process?
A: A food sterilizer applies heat, steam, or other methods to sterilize packaged food. This process kills or inactivates microorganisms, ensuring the food remains safe for consumption and has an extended shelf life.
Q: What is the typical sterilization time required for different types of packaged food?
A: The sterilization time varies depending on the type of food, packaging material, and sterilization method used. Generally, it can range from a few minutes to over an hour. Detailed guidelines are provided, along with the food sterilization equipment, to ensure effective sterilization.
Q: Can I get wholesale food sterilization equipment from a Chinese wholesaler?
A: You can get wholesale food sterilization equipment from various Chinese wholesalers. Websites like alibaba.com offer various food sterilization machines and solutions from verified suppliers.
Q: What types of food can be sterilized using a food sterilization machine?
A: A food sterilization machine can sterilize fruits and vegetables, meats, dairy products, and various types of packaged and canned food. It is versatile and compatible with different food types to ensure safety and preservation.
Q: What is in-container sterilization, and how is it used in food packaging?
A: In-container sterilization involves placing the packaged food in a sterilization chamber subjected to high temperatures or other methods. This process ensures that both the food and the container are sterilized, thereby maintaining the food’s sterility until it is opened for consumption.
Q: What is batch sterilization in the context of food preservation?
A: Batch sterilization refers to sterilizing a large quantity or batch of food products simultaneously using a sterilization autoclave or similar equipment. This method efficiently processes large volumes of food and ensures consistent sterilization across all items in the batch.
Q: How can I select the right food sterilization machine for my needs?
A: To select the suitable food sterilization machine, consider the type of food you need to sterilize, the volume of food to be processed, and the specific sterilization requirements. Checking reviews, consulting with suppliers, and exploring options on platforms like Alibaba.com can help you make an informed decision.
Q: What is the current trend in the food sterilization equipment market?
A: The food sterilization equipment market is growing due to the increasing demand for safe, long-lasting food products. Innovations in sterilization technology and the availability of advanced equipment from Chinese wholesalers are driving this trend. Businesses and consumers increasingly adopt these solutions to ensure food safety and preservation.