Sterilization is essential in many industries, such as health and food production, as it helps free products from dangerous microorganisms. Various traditional sterilization techniques like heat treatment, chemical disinfectants, and irradiation have been used extensively to ensure this. Nevertheless, microwave sterilization technology is emerging as a viable option due to recent technological milestones. This article discusses the process involved in microwave sterilization and compares its pros and cons and effects on conventional sterilizing processes. Understanding how these methods work and their efficiencies will give readers insights into which is preferable for specific applications and industries.
How Does Microwave Sterilization Technology Work?

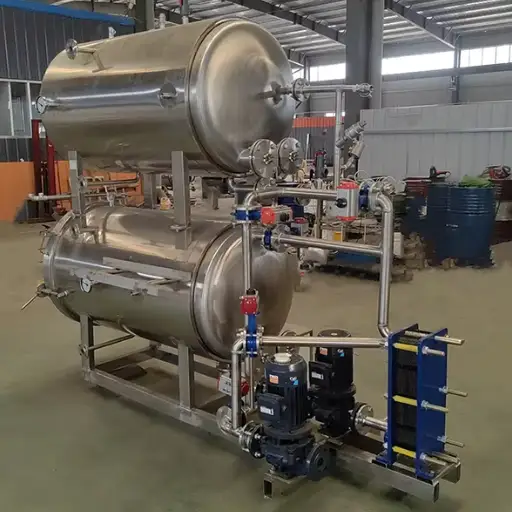
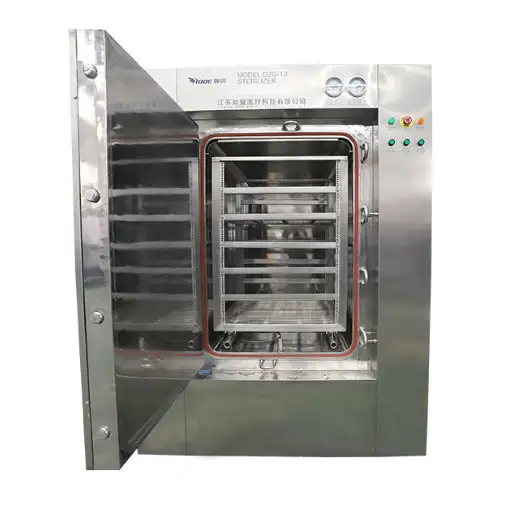
Image source: https://www.bxdrymachine.com/
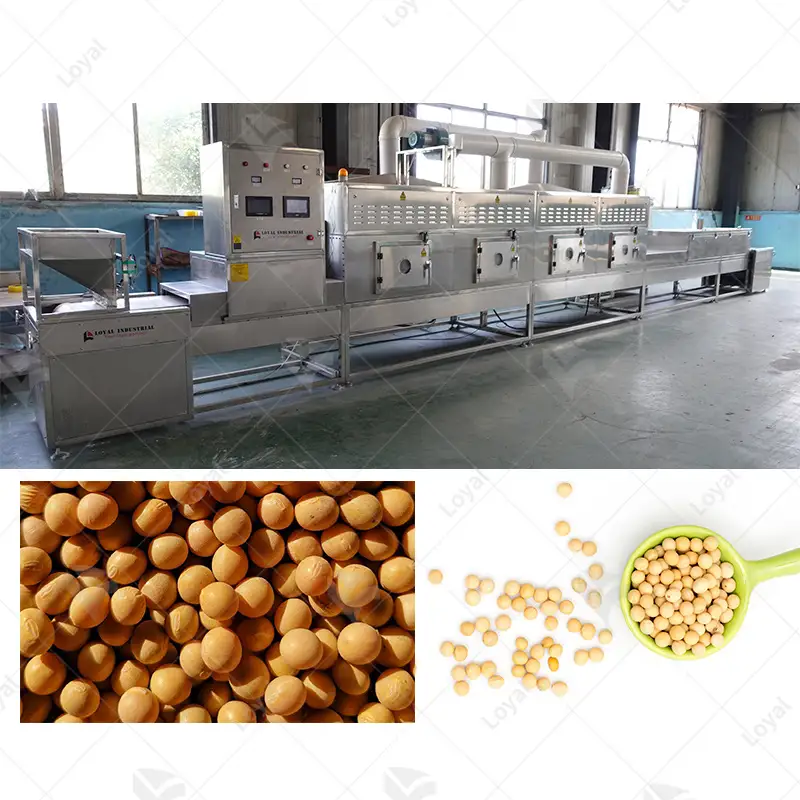
Microwave sterilization technology uses the power of microwaves to create heat in the product needing sterilization. In this technique, a product is put into a microwave chamber and exposed to microwaves. The microwaves penetrate the product, giving its water molecules an oscillating motion and thereby causing frictional heating. This internal heating occurs fast and evenly, hence killing all microorganisms present. Unlike other methods, microwave sterilization does not depend on outer forms of heat; thus, even a core reaches the desired temperature for sterilizing it.
Understanding the Microwave Sterilization Process
The procedure of microwave sterilization commences with the placement of the sterilizing product in a specialized microwave chamber. Turning it on causes water molecules inside the item to vibrate, thereby being heated. This is because as these molecules vibrate, they produce heat, increasing temperature evenly throughout the item. Such prompt and even warming guarantees the swift death of microbes, leaving no chance for pathogens to survive within the product. Microwave sterilization also takes less time than traditional methods; hence, it is faster to retain food quality and nutrient content.
The Role of Microwave Energy and Water Molecules
The sterilization process requires microwave energy to interact directly with water molecules in the product. The polar nature of these molecules is why they oscillate quickly when subjected to microwave radiation. Such oscillatory movements lead to the production of frictional heat, which, in turn, raises the temperature of the product evenly. Generated internally, this heat guarantees that all areas within the product receive enough heating to eliminate bacteria. This method also ensures that microwave sterilization maintains the quality and integrity of products.
915 MHz Microwave and Its Relevance in Sterilization
The sterilization process is best served by using 915 MHz microwave frequency because of its ability to penetrate deeper into objects and due to its reduced power consumption. Compared to the more famous 2450 MHz, the 915 MHz can penetrate thick loads more effectively ensuring even heating throughout the product. This deep internal penetration is essential in sterilizing large or dense items since it is crucial to eliminating microorganisms by having equal heat distribution throughout the article. Also, this frequency operates at a level where electromagnetic energy can be efficiently converted into heat, thereby minimizing energy wastage and increasing efficiency on the whole in the process of sterilization. Consequently, all these features render 915 MHz microwave frequency a preferred choice for industrial-scale sterilization applications where consistency and reliability are required as requisites.
What Are the Applications of Microwave Sterilization in Food Science?

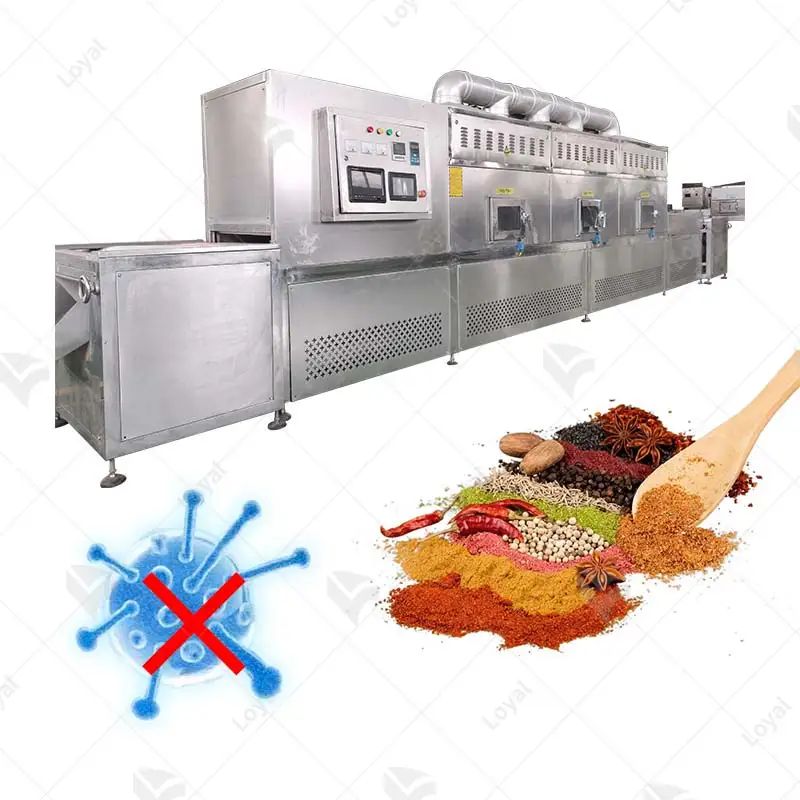
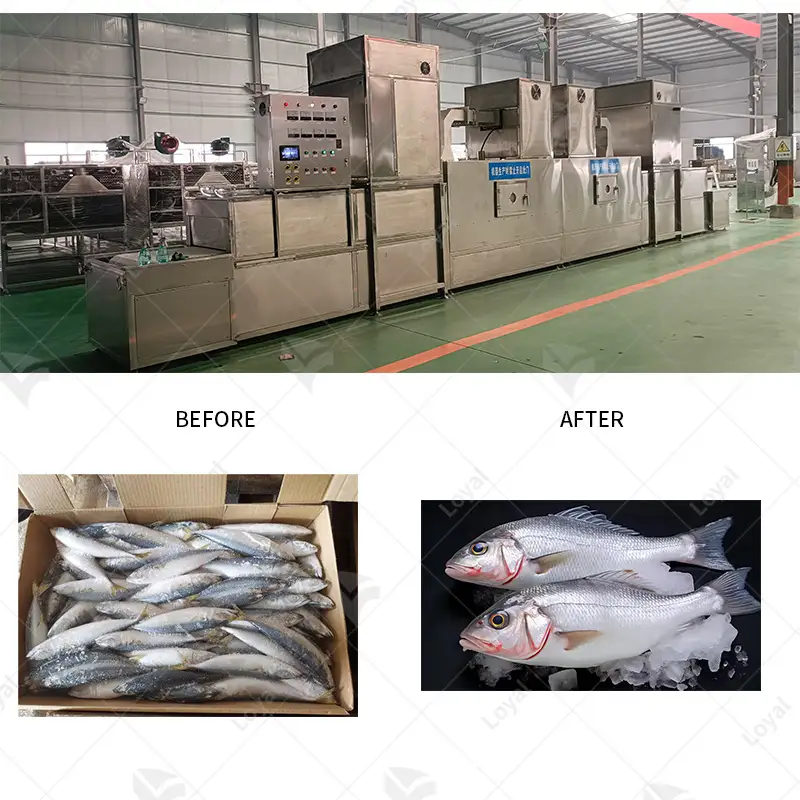
Microwave sterilization is broadly applicable in food science, where it enhances the safety and shelf life of various foods. It is especially effective for sterilizing ready-to-eat meals, where they can be preserved with their nutrition and taste without chemical preservatives. This technology is also used to process liquid foods like soups and dairy products so they are safe to consume for long periods. Furthermore, microwave sterilization aids in decontaminating packaging materials, thus preventing microbial growth during storage and transportation. Therefore, its applications in microwave sterilization play a vital role in modern food safety, quality improvement, and waste reduction efforts in general.
Microwave Heating in the Food Industry
Microwave warming in the cooking area is a life-transforming technology that ensures that various foodstuffs are quickly and uniformly heated. Microwaves cook food effectively by shaking the product’s water molecules, leading to instant heat energy transfer. The method also leads to a significant reduction in cooking time and processing time; this is advantageous in preserving nutritional content and improving productivity. Additionally, microwave heating can be applied for different purposes, such as cooking, pasteurizing, or blanching. It guarantees even distribution of heat and low energy usage and serves as a significant driver behind getting healthier fast-food types. All these advantages make it clear that microwave heating is becoming an increasingly important aspect of modern-day food industry.
Ensuring Food Quality and Safety with Microwave Sterilization
For practical exposure to microwave sterilization, understanding its basics and advantages is essential to keep food quality and safe. By using electromagnetic waves that generate heat by shaking water molecules present in food, microwave sterilization functions to deactivate pathogens and spoilage microorganisms. Speed and uniformity are essential considerations when applying microwave sterilization since they result in low temperatures and thus retain food’s nutritional value and organoleptic properties. This makes it possible to use the method to sterilize both liquid and solid foods making it a valuable tool in the food industry. To add to this point, chemical preservation is reduced through this process, making it an eco-friendly means that also cuts down on energy used in production. It also meets contemporary requirements for safe food and consumer preferences for natural products that require minimal processing or none concerning being environmentally friendly.
How Does Microwave Sterilization Compare To Conventional Methods?

Microwave sterilization is superior to conventional methods in several respects. First, it saves a lot of time because of the rapidly produced heat by electromagnetic waves, thereby increasing efficiency and sustaining food quality. On the other hand, boiling or autoclaving, which are traditional techniques, takes long hours to cook foods at high temperatures that can cause damage to them. Secondly, microwave sterilization heats more evenly, minimizing the cases of hot and cold spots common in conventional thermal processes. In addition, the low power consumption of microwave sterilization makes it a green technology, unlike other traditional methods that consume large amounts of energy. Lastly, there is less exposure to chemical additives with microwave sterilization, which aligns with trends in clean-labeling and minimally processed foods, giving it an upper hand over traditional approaches.
Comparing Thermal Processing Methods
Three methods of heat treatment that are often compared are conventional thermal processing, high-pressure processing (HPP), and microwave sterilization. Traditional thermal processing, such as autoclaving and canning, is because it has been known to be reliable. Still, nutrient loss occurs in most cases due to prolonged high-temperature exposure, leading to poor food quality. In contrast, high-pressure processing uses extreme pressure to inactivate pathogens without significantly raising the temperature, thus preserving the nutritional and sensory properties better than any other method. Still, it may be more expensive and challenging to implement.
As mentioned earlier, microwave sterilization provides a compromise between fast and homogeneous heating of food that reduces the degradation of nutrients and the time taken for processing. It also tends to be more energy-efficient following sustainable practices. Each method has unique advantages and is chosen based on specific food product requirements, cost considerations, and desired quality outcomes.
Advantages and Limitations of Using Microwave vs. Autoclave
Advantages of Microwave Sterilization
- Rapidity and Efficiency: Microwaving sterilization is much faster compared to traditional autoclaving. It heats up rapidly and evenly, so processing times are significantly reduced.
- Preserving Nutrients: Microwave sterilization technology shortens the exposure to high temperatures and helps retain food quality in terms of nutrition and sensory attributes.
- Energy Saving: Shorter processing time and direct heating by microwaves use less energy, causing less environmental harm.
- Security: Microwave sterilization requires fewer chemical preservatives than conventional methods, thus meeting consumer demand for more natural products.
Limitations of Microwave Sterilization
- Cost of Equipment: Compared to conventional autoclaves, microwave equipment could have a higher initial cost.
- Uniformity Issues: Although microwaves generally heat the product uniformly, some areas may show distortions due to the food item’s varying shapes and content.
- Scalability: However, when it comes to large-volume processing, scaling up may be a significant constraint for microwave sterilization in comparison with autoclave systems.
Advantages of Autoclave Sterilization
- Proven Dependability: For decades now, autoclaving has been known as an efficient method for obtaining sterile items that can be depended on consistently over time.
- Multifunctionality: They can handle different types and forms of materials, making them applicable not only in food but also in other sectors, such as medicine.
- Scalability: These systems are scalable enough to manage large batches effectively.
Limitations of Autoclave Sterilization
- Long processing times: Long duration at high temperatures during autoclave treatments might impair the quality characteristics (nutritional and sensory) associated with foods before packaging or storage.
- Consuming Energy: Prolonged heating uses more energy, thus leading to higher operational costs.
-
Nutrient Depletion: Exposure for extended periods often significantly reduces the nutrients contained in foods, lowering their overall quality.
Heat Distribution and Handling Cold Spots in Microwave Sterilization
The effectiveness of microwave sterilization depends mainly on achieving uniform heat distribution for complete microbial inactivation. Nevertheless, cold spots, which are areas that do not get enough heat because of differences in energy absorption, can undermine sterilization.
- Stirring Mechanisms: Rotating plates or stirring systems can increase the evenness of microwave energy movement and diminish the possibility of cold spots.
- Packaging Design: Applying specialized chirped containers or dielectric materials could improve energy penetration and distribution, leading to more uniform heating.
- Preheating and Pulsed Microwaves: Evenly distributed thermal energy can be achieved by preheating to a uniform temperature or employing pulsed microwaves to control cold spots properly.
- Combination Techniques: Concurrently combining microwave sterilization with either infrared or conventional heating methods could enhance heat homogeneity and overall sterilization process efficiency.
Furthermore, more accurate product thermal imaging monitoring based on sensor feedback ensures all parts reach the required temperatures for effective cleaning.
What is the Effect of Microwave Sterilization on Different Microorganisms?

It has been demonstrated that microwave sterilization can kill various microorganisms, such as bacteria, viruses, and fungi, by quickly increasing the temperature to lethal levels. The susceptibility of different microorganisms to microwave-induced thermal impacts varies widely, for instance spore-forming bacteria like Clostridium botulinum tend to be more resistant than non-spore-forming ones such as Escherichia coli. Moreover, rapid heating causes the denaturation of microbial proteins and nucleic acids, leading to the efficient destruction of the microbes. Uniformity in heat distribution with these techniques also ensures that even the most resistant strains are targeted, thus enhancing the overall microbial safety of the food product.
Elimination of Spores and Other Pathogens Using Microwaves
Spores and other pathogens can be effectively killed by microwave sterilization because it uses high temperatures to increase internal temperatures to fatal levels quickly. By using this method, spore-forming bacteria like Clostridium botulinum and other challenging organisms are efficiently destroyed. The cell structure is disrupted by microwave treatment, leading to the denaturation of proteins and nucleic acids that effectively kill the microbes. This process would involve preheating, pulsed microwaves, and combination methods with infrared or conventional heating that facilitate heat distribution, thereby ensuring complete sterilization. These investigations have revealed that microwave energy goes more profound than the traditional approaches, offering uniform heat and guaranteeing the elimination of all the toughest pathogens.
The Impact of Radiation and Frequency on Microorganisms
The effect of radiation and frequency on microorganisms significantly differs based on the kind of radiation and its intensity. For instance, microbial DNA can be disrupted by exposure to ultraviolet (UV) light used in sterilization through thymine dimers, thereby inhibiting replication and leading to the death of cells. Conversely, microwave heating occurs due to heat generation using dielectric heating, resulting in the thermolysis of structures found within microbial cells. On microwaves, lower frequencies imply deeper penetration but slower warming, while high frequencies portray speedy surface warming and little penetration.
According to research, combining UV with microwave or other frequencies can improve antimicrobic activity by targeting multiple parts of bacteria at a time. Combining thermal and non-thermal influences ensures the killing of numerous pathogens for public health safety and extending shelf life.
The Role of Packaging Materials in Ensuring Sterility
Packaging components are critical in maintaining the cleanliness of products, especially in the food and medical sectors. The right choice and application of packaging materials can prevent microbial infection and lengthen the life of products on shelves. Other materials like polyethylene, polypropylene, or multilayer laminates are excellent shields against bacteria, water, and air. Additionally, sterile packages do not allow penetration until one opens them; this is done through aseptic techniques during their design. Sterility is further enhanced by other methods, such as modified atmosphere packaging (MAP) and vacuum packaging that change the package’s atmosphere, thus prohibiting microbial growth. Preserving product sterility and consumer safety calls for the reliability of these packages to remain intact.
Why is Microwave Sterilization Technology Considered Revolutionary?

It is a revolutionary technology in microwave sterilization because it can quickly and uniformly destroy many different types of bacteria without compromising the quality of the product. Unlike conventional thermal methods, it uses electromagnetic waves to generate heat inside the product, enabling deeper penetration and even heating. This technology considerably cuts down the processing time while maintaining food’s nutritional and sensory qualities and increasing energy usage efficiency. Incorporating other antimicrobial treatments with microwave irradiation adds value to its use, making it an adaptable and advanced approach for safeguarding food safety and prolonging shelf-life.
A Review on the History of Sterilization Techniques in Food Processing
Food processing sterilization practices have changed rapidly for hundreds of years to keep up with increased food security and preservation demand. The first was thermal sterilization, which has been around for a long time as it involves heating foods at higher temperatures, killing the germs. Unfortunately, this method is powerful, but not without weakening taste values and nutritional contents.
On the other hand, technological advances led to alternatives, such as pasteurization, which Louis Pasteur invented in the 19th century. Pasteurization uses lower temperatures compared to traditional thermal sterilization methods, hence reducing degradation risks while effectively removing infectious microorganisms.
Emerging techniques like High-Pressure Processing (HPP) and Pulsed Electric Fields (PEF) have dramatically changed. It only breaks down microbial cell membranes without involving heat, preserving food’s original flavor and nutrients through high pressure, which is employed during HPP. However, PEF kills bacteria by interfering with cellular function using short bursts of high voltage, thus keeping food quality unchanged.
This is a highly advanced microwave sterilizing technology that we have today; it can exterminate pathogens uniformly and quickly. This approach keeps food’s properties intact while enhancing energy consumption, effectiveness, and duration of the treatment process. Hence, the historical development from basic thermodynamic processes to sophisticated microwave techniques signifies ongoing progress toward ensuring a safe, nutritious food supply within the food processing industry.
Innovations and Advancements in Microwave Sterilization Equipment
There has been considerable improvement in microwave sterilization equipment to make it more efficient, uniform, and energy-saving. In addition to this, today’s designs include advanced computational algorithms that help in optimizing the distribution of microwaves, thereby ensuring uniform sterilization for various food brands. Moreover, integration with Internet of Things (IoT) technologies offers real-time monitoring and control, which enhance precise adjustments and improve process reliability. Besides, innovation in packaging materials compatible with microwave sterilization has also played a role in protecting food quality through better thermal stability while preventing contamination. Further still, there is the use of energy-saving magnetrons or solid-state generators, which have cut operational costs yet allowed more flexible frequency control into the process. These developments prove the industry’s commitment to enhancing food safety standards without compromising nutritional and sensory characteristics.
Future Prospects and Research in Microwave-Assisted Thermal Sterilization
The future of microwave-assisted thermal sterilization (MATS) has great potential, and ongoing research concentrates on improving its effectiveness and scope. One main area of interest includes developing hybrid systems that merge microwave heating with other sterilizing methods, such as high-pressure or infrared heating, to better eliminate microorganisms while maintaining food quality. On the same note, researchers are studying how varied microwave frequencies and pulsing techniques can optimize the sterilization process for different food matrices.
Moreover, there is also an ongoing investigation into improving process modeling and simulation. Advanced computational models have been developed that can accurately predict the thermal and electromagnetic behavior of foods subjected to microwaves for sterilization, helping in better design and scaling up industrial equipment. Furthermore, artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms are increasingly being used to adjust processing parameters dynamically during microwave sterilization, thus further improving the consistency and efficiency of the entire procedure.
Nevertheless, sustainability is a vital aspect of MATS’ future. The focus is on research aimed at developing energy-efficient components and utilizing renewable energy sources to power microwaves. Finding biodegradable and recyclable packaging materials suitable for use in microwave sterilizing is very significant when it comes to reducing the environmental impact of food industry processing.
However, integrating advanced technologies alongside a strong orientation towards sustainability and efficacy will drive MATS’s evolution, making it a centerpiece of modern food safety and preservation.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What is microwave sterilization technology?
A: Microwave sterilization technology uses microwave power to generate an electric field that heats and sterilizes food products. This technology can effectively sterilize and pasteurize food by heating it to high temperatures, targeting microorganisms such as spores.
Q: How does microwave sterilization compare to conventional retort methods?
A: Compared to the conventional retort methods, microwave sterilization can significantly reduce the sterilization time and potentially improve the quality of food products by avoiding overcooking. Conventional retort methods use steam or hot water to heat food, often leading to longer processing times and potential degradation of food quality.
Q: What are the advantages of using microwave-assisted thermal sterilization?
A: Microwave-assisted thermal sterilization offers faster processing times, reduced energy consumption, and improved food safety. This sterilization method can uniformly heat food products, reducing the risk of cold spots that may harbor harmful microorganisms.
Q: Are there specific microwave frequencies used in microwave sterilization?
A: Yes, the expected microwave frequencies used in microwave sterilization are 915 MHz and 2450 MHz. These frequencies are chosen based on their effectiveness in heating food products evenly and efficiently.
Q: What food products can be treated using microwave sterilization technology?
A: Microwave sterilization technology can treat a variety of food products, including packaged foods, liquids, and semi-solids. This technology is particularly useful in the food industry for extending shelf life while maintaining food quality and safety.
Q: Can microwave sterilization be used for both solid and liquid foods?
A: Yes, microwave sterilization can effectively sterilize both solid and liquid foods. The technology can uniformly heat and sterilize food products, ensuring comprehensive microbial inactivation.
Q: What role does packaging material play in microwave sterilization?
A: Packaging material plays a crucial role in microwave sterilization. It must be microwave-compatible to ensure that it does not absorb microwave energy and allows even heating of the food products. Proper packaging also helps prevent post-sterilization contamination.
Q: How is microwave sterilization’s heating process different from conventional heat methods?
A: In microwave sterilization, the microwave process involves converting electrical energy into microwave energy to generate heat within the food product. In contrast, conventional heat transfers heat from external sources, such as steam or hot water, to the food product, which takes more time and can result in uneven heating.
Q: Is microwave sterilization effective in ensuring food safety?
A: Yes, microwave sterilization is highly effective in ensuring food safety. It can quickly achieve the necessary high temperatures to inactivate harmful microorganisms, including spores, thereby reducing the risk of foodborne illnesses.
Q: What factors influence the effectiveness of microwave sterilization?
A: The effectiveness of microwave sterilization can be influenced by several factors, including microwave power, frequency (such as 915 MHz), the nature of the food product, the packaging material, and the uniformity of the heating process. Properly calibrated microwave systems can ensure thorough and consistent sterilization.