Microwave sterilization is a fresh method of making various items safe and durable. This uses microwave power to kill bacteria and other harmful germs effectively. This article will discuss what underlies microwave sterilization, its merits over conventional techniques, and recent developments in this area. By comprehending how it works and why it is good, the reader will know how much change can be brought about by microwave sterilization in fields like the food processing industry, medical care, etcetera. Let’s unveil some aspects of this advanced type of disinfection, which may affect peoples’ wellness en masse.
What is Microwave Sterilization?

Image source: https://industrialmicrowave.com/
Microwave sterilization is a process that utilizes microwave power to create warmth in a product and thereby kill bacteria and other disease-causing organisms until it becomes safe for consumption. This works by sending waves through an object so it can vibrate its water molecules, which then produces heat energy, thus destroying all germs on it. Unlike traditional methods such as using heat from outside or chemicals, this technique saves time because it does not require any other form of energy except microwaves, making them fast enough for different uses like food processing or even medical instruments’ disinfection.
Overview of microwave sterilization technology
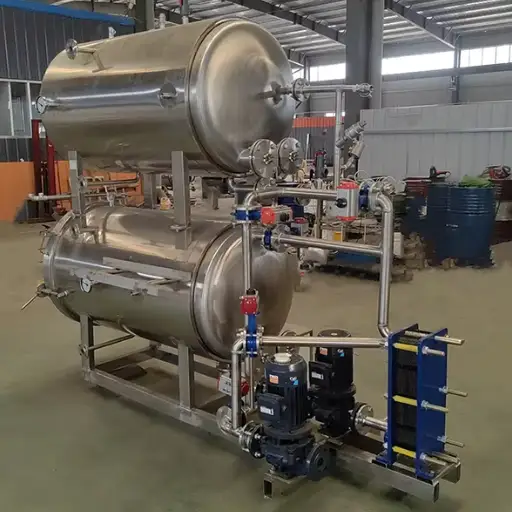
Microwave sterilization technology emits microwaves that go through a product to create internal heat and kill dangerous microbes. The rapid processing speed and energy efficiency are why this method is better than traditional sterilization methods. Some crucial advancements in this sector include the invention of accurate control systems that ensure even heating and sophisticated monitoring instruments for optimizing the real-time sterilizing process. Current microwave systems for sterilizing are designed to serve different industries with personalized solutions that can be used for large-scale industrial applications or even delicate procedures like medical device sterilities. It ensures the safety of products while keeping their qualities intact.
How does microwave energy contribute to the sterilization process?
Microwave energy helps in sterilization through dielectric heating. Polar molecules such as water oscillate rapidly when microwaves permeate products caused by their power. This generates heat through molecular friction, which raises the temperature of an object evenly. The raised heat level destroys cell structures in microorganisms, thus deactivating them or killing them altogether. This technique is faster than other methods for sterilizing because it uniformly heats quickly, often cutting down on the time needed for total sterility. Moreover, microwave power protects against thermally spoiling goods while conserving their quality and functional features.
Benefits of using microwave technology in sterilization
Sterilization through microwave technology has a lot of advantages that attract many people from various sectors. To begin with, sterilization saves time compared to other methods, thereby improving efficiency at large. Secondly, microwaves ensure that heat is distributed evenly, leading to consistent results and eliminating cold points where bacteria can survive. Thirdly, this technique is energy-saving because it consumes less power, reducing operational costs. Also, it is generally safer and friendlier to the environment since no or few dangerous chemicals are used, in addition to reduced waste production. Finally, this approach preserves quality standards and functional properties such that medical devices remain intact throughout their stages of sterilization.
How Microwave Sterilization Compares to Conventional Methods

Microwave sterilization has a lot of advantages over regular methods. Autoclaving and chemical sterilization take up much time because they are less quick than the other methods. It is energy, too, since it uses less power than dry heat when it comes to traditional techniques used for sterility purposes. This will mean higher productivity levels within the same period, reducing operational costs organizations incur. Furthermore, microwaves ensure that every part gets heated uniformly, significantly reducing complete sterility attainment time-lapse on items being processed through them. In addition to being safe for use by people who work around these machines or nearby thereof, microwave ovens do not produce harmful fumes, thus making them eco-friendly compared to harsher chemicals employed during such procedures. Some types of conventional systems can destroy the quality of goods due to longer exposure hours at high-temperature points. Still, this type can help keep them intact until required for use again without affecting their functional features. Neither should any manufacturer worry about efficiency standards being compromised with microwave sterilization over other methods if safety precautions are taken into account throughout production lines, especially for those sectors that are more concerned about efficiency improvement alongside product enhancement.
Advantages of microwave sterilization
Microwaves offer numerous benefits over traditional techniques:
- Rapidity and Efficacy: Microwave sterilization is much quicker than other methods. It saves time by shortening cycle times overall, which in turn increases throughput and productivity. Electromagnetic waves are employed to quickly generate heat inside the thing being processed, thus making it sterile within a fraction of what autoclaving or dry heating takes.
- Energy Saving: Because microwave sterilization is fast in heating, it consumes less power than any other method with similar results. This process focuses directly on the products, thereby minimizing energy dissipated into the surrounding environment. In addition to reducing consumption levels, such heating reduces operational costs associated with energy use.
- Safety and Environmental Friendliness: The technology eliminates or dramatically reduces the use of hazardous chemicals for disinfection, thereby protecting operators and users from possible harm and preventing pollution. Unlike some chemical approaches that can lead to the creation of dangerous waste materials, microwaving represents a cleaner alternative that contributes to healthier working conditions.
- Retaining Quality Of Items Treated: Microwave sterilizers ensure items maintain their quality and functionality due to shorter exposure time and efficient warming up. Prolonged exposure to high temperatures can cause damage, especially when dealing with sensitive products, but this does not happen if medical equipment or drugs are subjected to a microwave machine.
These merits, therefore, serve as motivating factors for organizations desiring improved efficiency levels within operations while at the same time cutting down expenses incurred during production stages. They also ensure safety standards are maintained along with product excellence measures met within industries.
Limitations and challenges when compared to conventional methods
While microwave sterilization has many advantages, it has its limitations and problems. For one thing, microwaves don’t penetrate very deep, so they may not heat evenly or eliminate all bacteria in more oversized or densely packed items. Secondly, the cost of buying initial equipment for microwave sterilization can be higher than with more traditional methods, which might discourage smaller operators. Also, there’s a lack of universally accepted guidelines and rules from regulatory bodies on how best to use microwaves for this purpose; therefore, many people may not know what they’re supposed to do or whether it’s safe enough to try something new like that in their place without any precautions taken beforehand either by themselves or someone else who is knowledgeable about such matters being present at all times while they are performing these tasks themselves even if those persons aren’t qualified as experts since anyone can still make mistakes when dealing with dangerous things. Moreover, various materials have different compatibility levels with microwaves, whereby some cannot withstand exposure, thus restricting the range of articles that can be disinfected using this method. These are just a few examples among others wherefore more investigations need to be carried out to perfect microwave sterilization techniques throughout different applications and also ensure their dependability plus efficiency.
What are the Applications of Microwave Sterilization?

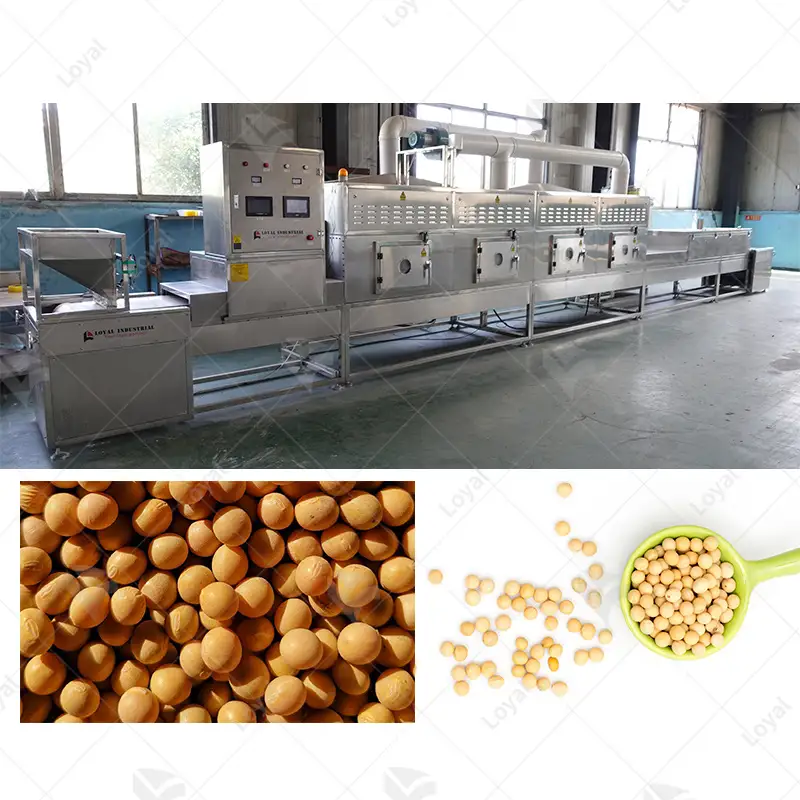
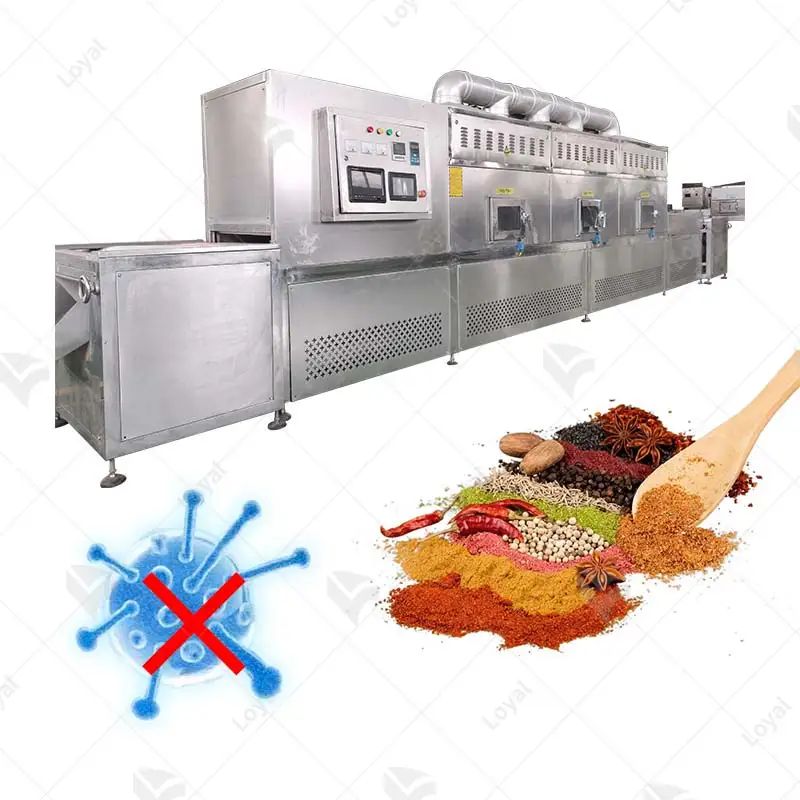
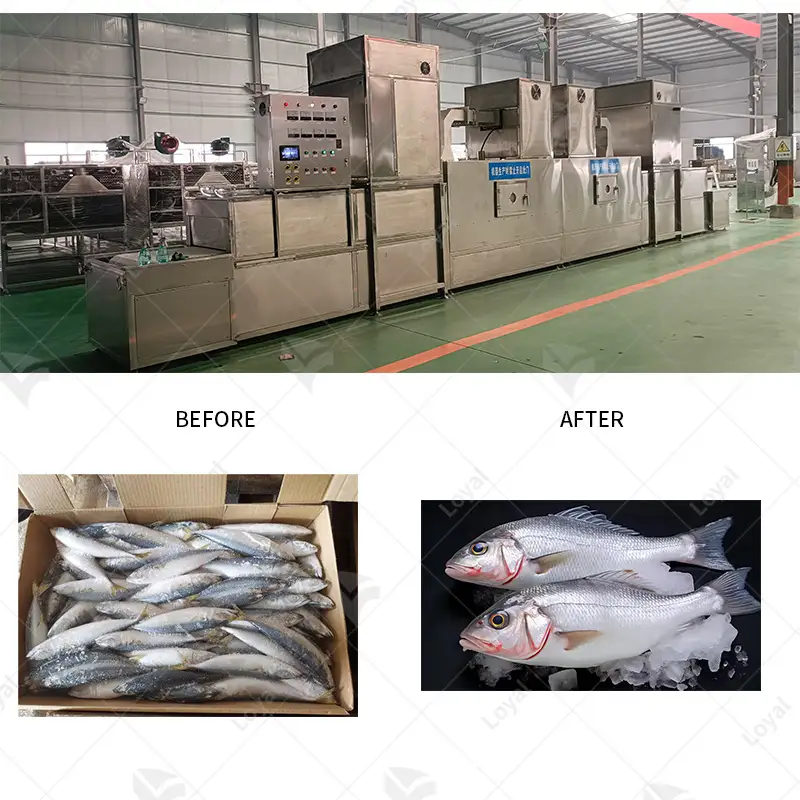
Due to its efficiency and effectiveness, microwave sterilization has many applications across industries. Regarding the food industry, this method keeps packaged goods fresh longer while maintaining nutrition safety from bacteria or other microorganisms. The pharmaceutical field employs microwave sterilization to prevent drug sterility during the production process; medical instruments should also be sterile before being used on patients – the same goes for lab equipment, too! In healthcare settings where surgeries take place every day, there need to be enough tools available. Still, they must always remain clean until needed again, which is why hospitals use microwaves for disinfecting surgical items. Furthermore, it can also be used within waste management systems where biomedical waste such as needles or laboratory waste needs proper handling before disposal to prevent contamination with diseases like HIV or hepatitis C virus (HCV). All these different uses show just how versatile and essential microwave sterilization can be in many other areas of life that are considered vital.
Use of microwave technology in the food industry
Microwave technology is critical in the food industry since it provides various functions for food safety and shelf life extension. Microwaves help with pasteurization and sterilization by targeting microorganisms, thereby ensuring minimal nutritional losses in this process. They are liked because they are quick and heat evenly, which means all items will be uniformly cleaned during sterilization, thus improving their quality.
Apart from individuals at home, microwaves have also become handy for energy saving while cooking in hotels and restaurants. Microwave-assisted thermal sterilization (MATS) has revolutionized things by combining microwave energy with traditional heating methods, resulting in products that do not need refrigeration but remain tasty and have a good texture.
Moreover, microwaving supports the creation of ready meals and packaged foods so they can be conveniently consumed without any additional preparation. This technology guarantees accuracy in preserving the desired sensory properties of food products, hence becoming invaluable for packaging them today.
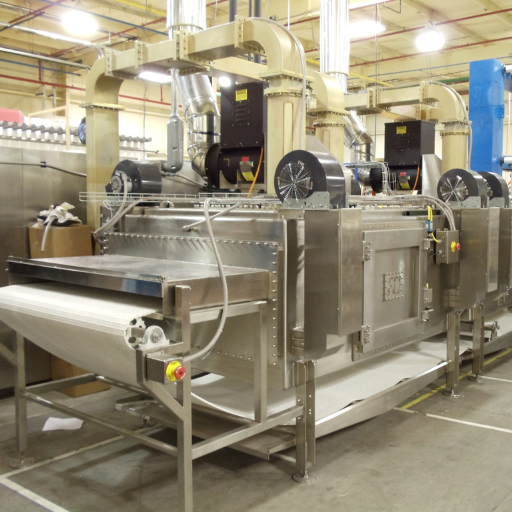
Applications in industrial microwave systems
Due to their efficiency and versatility, industrial microwave systems are widely used in many fields. In the food industry, they make fast cooking, drying, and tempering possible, reducing process time and energy consumption significantly compared to traditional methods. They are also used in the rubber and plastic industries, among others, where quick curing bonding or drying is required for uniformity and quality of the end product.
Industrial microwave technology is also used in waste treatment to decontaminate hazardous and non-hazardous materials effectively. For example, medical waste can be treated using microwaves, which reduces its volume while killing all the germs, making it safer for disposal. Additionally, chemicals can undergo processing with these machines since they provide accurate heat delivery, thus enhancing reaction efficiency during synthesis processes.
These examples show how wide-ranging industrial microwave applications can improve productivity control measures within different sectors while ensuring safety.
How microwave sterilization affects food quality
There are several ways in which food quality can be affected by microwave sterilization. First, it eliminates germs and other tiny living things effectively but without causing extreme heat damage as regular thermal methods do, thus making food safe. In this way, the product’s nutritional value is saved with sensory characteristics like taste, texture, or color. Secondly, rapidity in microwave sterilizing prevents vitamin loss that could occur during conventional processes where heating takes more extended periods since it also heats up at faster rates. All microwaves contribute to the even distribution of heat inside products being treated, thus reducing the chances of cooking one part too much while leaving another uncooked, maintaining uniformity throughout such goods.
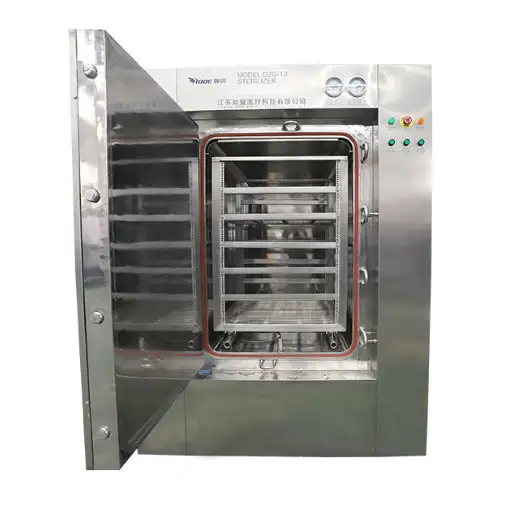
How Does a Microwave Sterilization System Work?

The sterilization system uses microwave functions by creating microwave power and directing it toward the meal. Water molecules in the foodstuff absorb such energy, leading to quick vibration and heat generation due to friction. This heat destroys pathogens and other microorganisms effectively. The process is done by keeping food in sealed containers that allow microwaves to pass through them, uniformly heating all parts of the food. To avoid spoiling, nutritional value sensors check temperature levels necessary for destroying bacteria without overdoing it while keeping nutrients intact. Controlled warming combined with supervision produces good results in sanitizing items faster and safer than any other method currently available.
The role of microwave cavities and microwave generators
Microwave sterilization systems heavily rely on microwave cavities and microwave generators. Microwave cavities function as specialized chambers that enclose and guide the produced microwave energy; their design aims to guarantee uniform distribution of microwaves across the food item through even heating. Alternatively, while microwave generators produce actual microwaves, the primary type being magnetrons, they change electrical energy into microwave energy, which is later passed into the cavity. The heat needed for sterilization comes from the interaction between food’s water molecules and those in the cavity through microwaves. This optimizes energy efficiency and ensures that all foods are equally safe when sterilized by these components.
Understanding the single-mode microwave setup
According to many, a single-mode microwave setup implies that the energy of the microwave is directed into one particular pattern or mode within a section of the cavity. This arrangement allows heating to be done in a very controlled and consistent manner since it directs energy precisely. The importance of this design lies in its capability to minimize hot spots and cold spots within food products while ensuring even temperature distribution throughout, which is necessary for effective sterilization. It provides all parts of an item to reach the required temperatures for killing germs without compromising quality because such knowledge guarantees success. In addition, compared with multi-mode systems, a single-mode setup saves power, leading to more efficient sterilization processes. Therefore, single-mode microwave setups are the best option for reliably producing safe and high-quality preserved foods.
Components of microwave sterilization equipment
Microwave sterilizing equipment includes several vital parts that work together to achieve efficient and effective sterilization. The main components are as follows:
- Microwave Generators: These are magnetrons, usually, as previously mentioned, that emit microwaves. The generators transform electrical power into microwave energy necessary for heating.
- Waveguides: These items direct the microwaves from the generator to the sterilizing cavity. They are designed to minimize energy loss while guiding properly for even heat distribution.
- Cavity (Chamber): This is where food products are placed for sterilization. It is created to enhance microwave distribution, control exposure time, and provide favorable conditions for good thermal treatment.
- Temperature Sensors: These help regulate product temperatures during the sterilization process by monitoring them closely at all times. They ensure safety and quality by ensuring every part of the item reaches the required heat level.
- Control System: This controls the entire sterilization operation, regulating power output and duration, among other important parameters. Advanced control systems can allow fine-tuning, leading to consistent results obtained through this food preservation method.
With these parts integrated, microwave sterilizing equipment can efficiently kill bacteria on foodstuffs, guaranteeing their safety and better quality standards.
What Are the Key Factors in the Microwave Sterilization Process?

Synonyms are essential in the microwave sterilization process, such as:
- Microwave Power Level: The quantity of power generated by microwaves determines the heating speed and evenness.
- Exposure Time: How long the food stays under microwaves determines how well it will be disinfected.
- Product Composition and Properties: Microwaves behave differently with food depending on their thermal properties, water content, density, etc.
- Temperature Distribution: If sterilization is to take place effectively, it is essential to have a uniform heat distribution throughout the product.
- Equipment Calibration and Maintenance: Equipment used during this process should be regularly calibrated and maintained so that outcomes can remain constant while remaining reliable at all times.
- Packaging Material: The packaging materials’ efficiency may affect microwave absorption and overall heat distribution, thus impacting process efficiency.
These factors should be monitored and controlled carefully for safe and effective microwave sterilization.
Effect of microwave power and sterilization time
Microwave power and sterilization time are critical parameters that affect how well microwaves sterilize things. Increasing microwave power leads to higher heating rates, which may reduce the time to achieve sterility. However, too much wattage causes uneven heating by creating hotspots that can spoil products.
The sterilization period should kill all germs while maintaining food safety. In other words, shortening exposure times at higher powers can work best if temperatures do not rise unevenly due to a lack of proper management; on the contrary, long exposures at low wattages might uniformly heat, but this consumes more energy and alters texture besides nutritional values.
Ultimately, one must balance saving energy during sterilizations with microwaves and eliminating pathogens from foods without compromising quality. To ensure this happens all the time, routine equipment calibration plus continuous monitoring of operational variables throughout different batches used in an establishment are needed to achieve reliable results consistently.
Impact of water molecules and cold spots in the sterilization
Water molecules are key regarding microwave sterilization since they have dielectric heating capabilities. Microwaves move through water by interacting with polar molecules, thus making them vibrate, which creates heat. This warmth is necessary for effective sterilization because it kills harmful bacteria.
One problem with microwaving things to kill germs may be that there might still be some “cold spots.” A cold spot is an area inside the food where all parts don’t get heated equally and could be left unsterilized. These appear due to uneven distribution of microwave energy and different types or densities of materials that make up the meal being treated. Such cold spots can be managed by ensuring ovens are designed with appropriate cavity shapes, continuous monitoring, and stirring devices or turntables, providing more even heating throughout.
Improving the distribution patterns of water molecules to deal with ‘cold spots’ becomes very important if we want microwaves to become a reliable method for sterilization. By understanding and controlling these aspects, safety levels will increase while at the same time enhancing overall quality standards for processed foods.
Optimization of process time and efficiency
Various crucial approaches are used to optimize the time and effectiveness of the microwave sterilization process. Firstly, it is essential to control the level of microwave power and duration of exposure to perform complete sterilization without over-processing, which may lead to degradation of food quality. Efficiency can be significantly increased by more sophisticated control systems that respond dynamically to these variables according to feedback obtained at that particular moment. Secondly, uniform heating is facilitated by designing microwave cavities, while cold spots and under-processed sections are minimized by employing rotating turntables or stirring devices during this process. Lastly, energy utilization uniformity can be enhanced during the pre-conditioning phase, where the composition and moisture content of the food product are adjusted, thus leading to better absorption. Integration and proper understanding of all these methods may result in effective microwave sterilization processes that are safe for our foods while at the same time ensuring their quality standards are met.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What is the microwave sterilization process?
A: Microwave sterilization is a technique that uses microwave heating to sterilize food products and packaging material. This method utilizes the heating process generated by microwaves at specific frequencies, such as 915 MHz, to achieve the high temperatures necessary for sterilization.
Q: How effective is microwave heating in sterilizing food products?
A: Microwave heating is highly effective in sterilizing food products because it can generate rapid and uniform heat distribution. This method can quickly reach the high temperatures required for thermal sterilization, reducing the time needed compared to conventional heat treatments.
Q: What are the advantages of using microwave-assisted thermal sterilization?
A: Microwave-assisted thermal sterilization offers several advantages, such as faster processing times, more uniform heating, and better retention of food quality compared to conventional sterilization methods. It is also more energy-efficient and can help maintain food products’ nutritional and sensory attributes.
Q: Can microwave ovens be used to sterilize food at home?
A: While household microwave ovens can heat food, they are not typically suitable for achieving the controlled conditions required for effective sterilization. Industrial microwave sterilization systems are designed to ensure precise control of temperature and microwave frequencies for proper sterilization of food products.
Q: What is the role of microwave frequencies, such as 915 MHz, in the sterilization technique?
A: Microwave frequencies, such as 915 MHz, are crucial in sterilization because they determine food products’ energy absorption and heating patterns. Different frequencies can affect the efficiency of the microwave process, influencing the distribution of heat and the overall effectiveness of the sterilization.
Q: How does the microwave heating system compare to conventional heat sterilization methods?
A: The microwave heating system offers several benefits compared to conventional heat sterilization methods. This includes faster heating times, uniform temperature distribution, and often better food quality and nutrient preservation. The continuous microwave process can also improve manufacturing efficiency and food safety.
Q: What types of food products are suitable for microwave-assisted thermal sterilization?
A: Microwave-assisted thermal sterilization suits various food products, including liquids, semi-solids, and solid foods. It is particularly effective for foods sensitive to long heating times, such as certain fruits, vegetables, and ready-to-eat meals.
Q: What is the significance of the sterilization chamber in the microwave sterilization technique?
A: The sterilization chamber is a critical component in the microwave sterilization technique as it ensures the controlled environment necessary for effective sterilization. It helps maintain the temperature and electric field required for the thermal process, ensuring consistent and reliable results.
Q: Are there any challenges associated with the microwave sterilization process?
A: Some challenges associated with the microwave sterilization process include the need for precise control of microwave heating parameters and the potential for uneven heating if not correctly managed. Additionally, integrating microwave systems into existing food processing lines and the initial equipment cost can be potential barriers.