Preserving fruits and vegetables for long-term storage can be a hard thing to do. But if you go for the old methods like sun drying or oven drying, you know that it may take time and rely on factors such as weather conditions. One better option is microwave drying, which is both practical, efficient, and modern. This guide will cover how to dry food using a microwave, its advantages, the process involved, and some recommendations on how to get the best possible outcomes. Once this article ends, you will completely comprehend how best you can preserve your fruits and vegetables using a microwave to retain their nutritional value, taste, and feel.
What is the Microwave Drying Process?

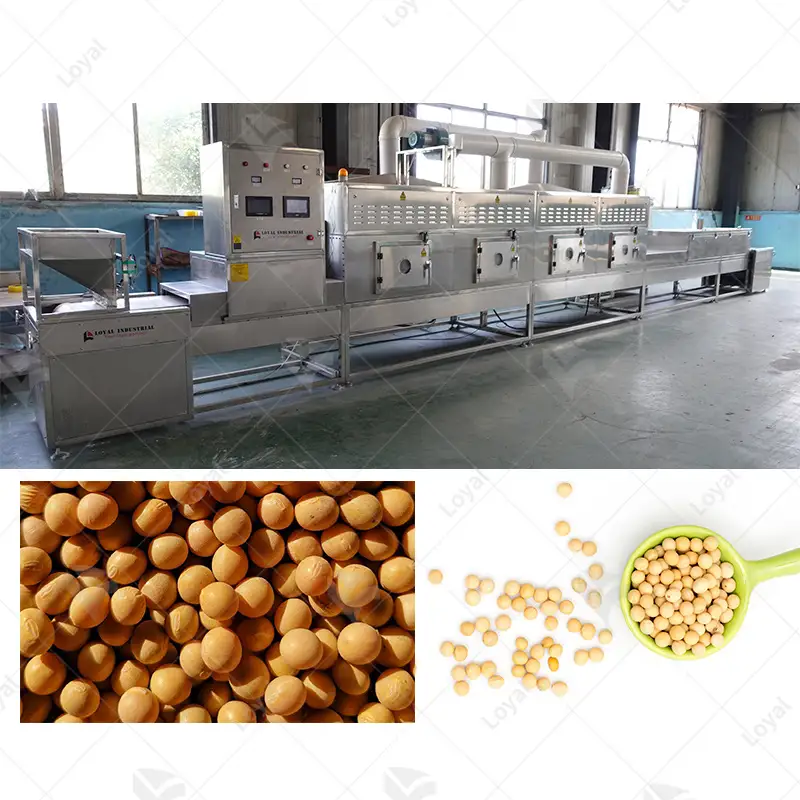
Image source: https://www.microwavedrying.net/
Microwave drying is used to dry fruits and vegetables using microwave energy effectively and rapidly. The penetration level achieved by the microwave drying technique in food is more uniform and quicker. A fraction of the duration required for using traditional systems is enough to preserve fruits and vegetables which maintain their nutritional value, flavor, and texture after drying. This involves placing the produce in a container that can be microwaved and then exposing it to some microwave rays to generate heat, which results in the vibrations of water molecules, causing them to evaporate, hence removing moisture from such produce. The method involves putting the product into a microwave-safe container and then exposing it to microwaves that cause water molecules within to vibrate, generating heat.
How does Microwave Heating Work?
When food is heated in a microwave, it is exposed to electromagnetic radiation that causes its water molecules to vibrate at a high frequency. This creates heat through molecular motion, which spreads quickly over the food, heating it uniformly and rapidly. In contrast to traditional cookeries, where heat is transferred by direct contact with external heat sources, microwaves penetrate foods for internal warming. The method not only hastens cooking and drying but also retains the nutritional value of food being reheated while maintaining the taste and feel of food.
Understanding Microwave Power in the Drying Process
Microwave power is a significant factor in the drying process of fruits and vegetables. During the drying process, power levels will affect how quickly microwaves heat up food, leading to efficiency and quality problems. Higher power levels for microwaves lead to faster drying times, which helps preserve nutrients and taste. Nevertheless, heavy power can cause overheating and nonuniform drying, which could destroy the texture and nutritional elements. Conversely, lower power settings may take time but are more even and controlled when drying. Therefore, when it comes to effective drying of produce, one should consider appropriate microwave power levels because this is an essential step in selecting optimal results.
Advantages of Using Microwave for Fruit and Vegetable Drying
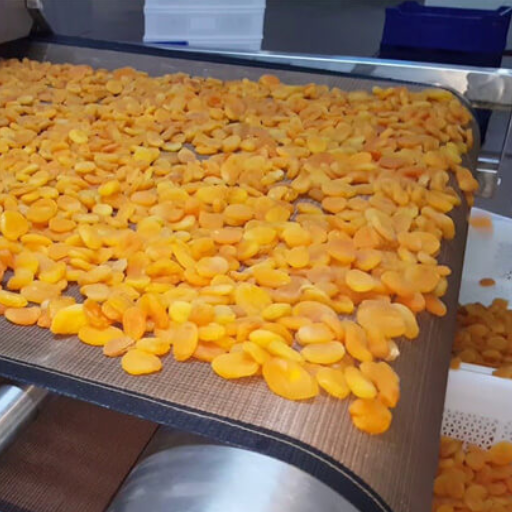
Microwave drying is much better than traditional drying methods in some ways. To begin with, the speed of microwave drying is much faster; hence, it dramatically reduces processing time and generally improves efficiency. However, the fruits and vegetables’ original nutrients, flavors, and colors are preserved by this intense dryness that helps keep their quality. Besides, controlled drying prevents microbial contamination, thus increasing its shelf-life as a dried food. Microwave drying is also energy efficient because it often uses less energy than conventional drying techniques. In addition to reducing operating expenses, this lowers power consumption, fostering environmental preservation.
What are the Different Drying Methods for Fruits and Vegetables?

Several techniques can be used for drying fruits and vegetables, each with its own merits and demerits.
- Sun Drying: This is a traditional way of preserving food by putting it under direct sun. It is cost-effective but weather-dependent and slow, which may cause microbial destruction.
- Air Drying: It’s like sun drying, only in a cool place with good air circulation. This method offers better protection from harmful UV rays while requiring favorable climatic conditions and substantial time investment.
- Oven Drying: Another way involves placing produce inside an oven at low temperatures. This method has more uniformity than others, like sun or air drying. However, it uses more energy and sometimes may even cook instead of drying the produce.
- Dehydrator Drying: In this process, warm air is moved around the produce through an electrical dehydrator. The technique is efficient, allows accurate monitoring of drying conditions, and produces high-quality dried products, though initial costs are required.
-
Microwave Drying: This type forces the water to evaporate faster by applying microwave energy to it. It is swift, saving power while maintaining nutrients and colors. However, it has to be overseen so that overheating or nonuniform drying does not occur.
The Role of Air Drying versus Vacuum Drying
Air and vacuum drying play different roles in dehydrating fruits and vegetables, with their strengths and weaknesses.
For example, air drying removes moisture from food by exposing it to air in a shaded area with good airflow. Air drying is cheap and easy to carry out, as it requires few pieces of equipment. However, it is time-consuming and influenced by weather patterns. Moreover, due to the long duration of drying, microbial contamination can easily occur, thus affecting nutritional value.
Another method known as vacuum drying expels air from the drying chamber. This leads water to an evaporation point with lower temperatures than before because of a decrease in boiling point. As a result, this technique allows for faster healing time while maintaining more nutrients and better color quality than other methods. Vacuum dehydration is recommended for heat-lowel production since it prevents thermal degradation. Nonetheless, despite its effectiveness, vacuum drying requires specialized equipment, making it expensive compared to air drying.
In conclusion, even though it is cheap and simple to undertake, air dying lacks quality with regard to preservation measures for food’s nutritional composition, unlike vacuum dying, which gives high-quality finished products regarding nutritional content retention.
Exploring Hybrid Drying Techniques
Hybrid drying techniques combine the advantages of traditional and modern drying methods to optimize efficiency, quality, and nutrient retention in dehydrating fruits and vegetables. These methods often integrate processes like air drying, vacuum drying, microwave drying, and freeze drying to maximize their combined powers.
Microwave-Vacuum Drying: This method exploits microwaves for heating purposes while employing vacuums to lower water’s boiling point, thus speeding up the process of evaporation without necessarily having to subject products to high-temperature conditions. This ensures that moisture is removed uniformly, resulting in more effective preservation of nutrients and color than conventional ones.
Solar-Assisted Drying: Solar-assisted drying combines solar energy with traditional or forced-air drying, using heat from the sun to minimize energy consumption. This approach is more advantageous, especially in areas with abundant solar radiation, because it offers an environment-friendly solution that helps save on costs while maintaining product quality.
Freeze-Vacuum Drying: The freeze-vacuum technique combines freeze-drying and vacuum-drying, fusing freezing that occurs under low temperatures to prevent nutrient loss with quick water removal by means of a vacuum condition. It is a suitable hybrid method for delicate products requiring minimal heat degradation and maximum nutrient preservation.
By employing these hybrid techniques, manufacturers can achieve greater efficiency in the process of dehydration, appeal better in terms of nutrition retention, and produce high-quality dried fruits and vegetables that cater to the increased demand for healthy dried foods with good taste standards from health-conscious consumers.
Benefits of Microwave-Vacuum Drying
Microwave vacuum drying has several benefits that make it a better method of drying fruits and vegetables. To begin with, it helps cut the time spent on drying compared to traditional methods by heating the water molecules of the produce using microwaves in the presence of a vacuum to quicken moisture elimination. Moreover, this approach saves more nutrients and coloring, which implies that vitamins, minerals, and pigments are maintained, hence getting an attractive product both for its sight and healthy eating. Finally, lower temperature exposure reduces the risks of thermal degradation, enhancing the tastes and textures of dried products. Lastly, microwave-vacuum drying is an energy-saving process whereby less power is used to dry compared to other methods, lowering operational costs and saving the environment.
How to Ensure High Quality of Dried Products?

Several factors should be considered for their excellent quality in producing dehydrated products. The first important thing is to ensure that fresh and high-quality raw materials have been chosen, as the initial quality directly affects the final product. To preserve its nutritional value, color, and texture, optimum drying parameters must be utilized, including temperature, time, and vacuum pressure. By monitoring these conditions continuously during the drying process, uniformity is ensured, as well as avoidance of over/underdrying. Furthermore, proper storage methods will help protect dried products from moisture re-absorption or microbial contamination by using airtight containers and low-humidity environments.
Impact of Drying Kinetics on Product Quality
The quality of dried products is influenced to a great extent by drying kinetics. A fast moisture removal rate can decide the texture, color, and nutrient content. High drying rates are often helpful in maintaining the integrity of structure and appearance by reducing shrinkage or color change. However, rapid drying can prompt ‘case hardening’ where the outer layer dries out rapidly and becomes stiff, trapping moisture inside that could encourage microbial growth. Ideal kinetics for drying encompass a trade-off between preservation of nutritional qualities in which faster processing leads to nutrient destruction due to longer exposure time to heat. Thus, understanding and managing these processes is vital for ensuring good quality products.
Influence of Drying Time and Microwave Energy on Quality
The quality of dried products can depend on how they are dried, which is influenced by drying time and the application of microwave energy. Using microwave energy to shorten drying periods has improved color preservation, texture retention, and nutrient stability. This method also helps maintain or improve quality by shortening drying times due to its even heating; thus, it reduces the duration of this process. However, when the time for drying is elongated, nutrients are destroyed by heat. In contrast, others, such as pigments affecting color and making texture less desirable, may be altered unfavorably because of prolonged exposure. Additionally, with traditional methods of drying one challenge encountered is case hardening which can be prevented through use of microwave energy that enhances moisture evaporation uniformly to address this problem. Healthy growing food has always been a priority for many people all over the world because they want their children not just to eat well but also to live healthier lives than themselves. The two factors must therefore be optimized towards an equilibrium between efficiency and product quality. Outlining the significance of optimizing both drying period and microwave power level used on efficient and effective processing. Drying periods should be minimized so as not only raise overall efficiency but also ensure that enough moisture content is depleted from foods. In conclusion, therefore, balancing process efficiency with the final product’s quality involves proper optimization of drying time and microwave power levels used.
Comparing Microwave Drying to Conventional Drying
Differences between microwave drying and conventional drying methods affect the quality of the final product. In general, this type of drying is known for its quickness because it heats up from within to eliminate moisture, hence decreasing the time of exposure to heat, which is good for maintaining color, texture, and nutrient value that are otherwise destroyed by a lot of heating. This is advantageous when handling components that lose color, texture, or other nutrients through excessive heating, such as pigments and proteins.
On the flip side, traditional drying operates through heat transfer from outside, which means it may take longer to dry things and uneven water dispersion in them. Long-term thermal exposure causes irreversible effects such as case hardening and nutrient degradation.
Additionally, research has revealed that microwave drying can reduce energy consumption since it takes less time and energy overall to obtain the required dryness level compared to conventional drying methods. However, some industries may consider the cost of setting up microwave drying systems to be a disadvantage. The two types of drying each have their pros and cons. Still, microwave drying seems to be better able to produce high-quality dehydrated products more consistently and efficiently than any other method.
What are the Effects of Microwave Drying on Nutritional and Sensory Properties?

Dried products’ nutritional and sensory properties are significantly affected by microwave drying. In terms of nutrition, this technique is essential in retaining vitamins sensitive to heat and antioxidants as it reduces the time they are exposed to high temperatures. Nutrient retention like this helps maintain the health benefits associated with food. Microwave drying also positively influences sensory attributes such as color, texture, and flavor. This fast-drying method helps preserve natural pigments, leading to brighter colors.
Moreover, this makes the texture more desirable due to fast drying, which minimizes the possibility of case hardening or textural degradation. Lastly, good flavors are often maintained since not much time has been used for drying, and this implies lesser losses of volatile compounds, which contribute to the taste and aroma of any product. Thus, microwave drying offers a promising method to maintain nutritional integrity and sensory quality in dried foods.
Microwave Drying and Retention of Nutrients
It has been demonstrated that microwave drying effectively maintains vital nutrients in dried foods. Heat-sensitive vitamins, antioxidants, and phytochemicals, which traditional drying techniques would have otherwise destroyed, can be preserved using this method. This process takes a very short time to dry, thus reducing the degradation of these nutrients and ensuring that the dried products remain nutritionally rich. Furthermore, it minimizes the loss of water-soluble vitamins during long drying periods, like Vitamin C and B-complex vitamins, which are often destroyed in lengthy drying processes. In essence, microwaves serve as the most excellent way of enhancing shelf life and retaining the nutritional value of foodstuffs.
Analyzing the Sensory Qualities of Microwave Dried Products
The sensory characteristics of dried products can be improved by microwave drying in several essential ways. This method retains bright colors as it hastens the drying process, which minimizes pigment degradation. Furthermore, case hardening is prevented through rapid drying, which maintains a better texture and, hence, a more consistent and desirable result. Besides that, flavor retention is much better because the quick drying reduces the loss of volatile compounds responsible for their taste and aroma. In sum, microwave drying is helpful to maintain and improve the sensory qualities of dried foods so that they remain nutritious and pleasurable to eat.
How to Optimize the Microwave Drying Process?

In order to make the microwave drying process ideal, it is essential to control relevant parameters, including power level, drying time, and food initial moisture content. For instance, the energy level in the microwave oven could be regulated so that water is evaporated while not overheating. What’s more, cutting food into equal portions aids in drying out, reducing under-drying or over-drying. In addition, pre-treatments such as blanching may be helpful for better conservation of nutrients and colors during drying. Thus, through tight monitoring and minor adjustments to his process, a dry method can be introduced in practice to balance the steps of quality and efficiency perfectly.
Strategies to Reduce Drying Time
A more intense microwave power setting can be one efficient measure to reduce drying time. The moisture removal rates in the product increase because of a step up in power level, leading to a shorter drying duration. An alternative option is the employment of a vacuum microwave dryer, which decreases the boiling point of water and enhances drying efficiency. Besides, the overall drying time can be reduced by combining intermittent microwave drying and other driers, such as hot air dryers, without compromising quality. Combining these approaches will result in an improved drying process by decreasing energy and time consumed without compromising sensory or nutritional attributes in dried foods.
Enhancing the Drying Rate with Microwave Energy
By optimizing the microwave supply process, one can significantly improve the rate of drying. The method is called pulsed microwave drying, and there are intervals in the application of microwaves. It also means moisture can evaporate effectively without overheating and damaging food quality. Finally, there is the controlled and targeted microwaving technique, where microwaves are focused and adjusted to react to real-time moisture content readings, resulting in uniform drying and increased efficiency. Lastly, it can boost the drying rate and improve energy efficiency by marrying microwave drying with other technologies, such as vacuum or freeze drying, which create optimal conditions for removing moisture. These approaches combine multiple techniques for increasing drying speed while still keeping nutritional values and sensory attributes intact in foods.
Understanding Drying Curves and Drying Efficiencies
These curves represent the drying process in graphical form by plotting moisture content against time. They always manifest several phases, consisting of the constant rate period, during which moisture is evaporated from the surface, and the falling rate period, during which internal moisture movement controls the drying rate. Understanding these curves is essential to optimizing the drying parameters.
Factors such as initial moisture content, drying temperature, air velocity, and type of drying technology can affect drying efficiency. Innovations like microwave drying have been developed to enhance efficiency through accurate control and integration with other methodologies. Optimizing these parameters would lead to uniformity and a faster rate of drying that saves energy while maintaining product quality.
Using controlled microwave energy combined with techniques like vacuum drying achieves the optimal conditions for high drying efficiencies. On the other hand, intermittent or pulse microwave drying assists in overcoming restrictions pertaining to conventional approaches to preserving nutritional profiles and sensory attributes.
Studying and enhancing these curves with advanced technological initiatives could result in significant energy utilization and time-saving advancements.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What is microwave vacuum drying, and how is it different from traditional drying methods?
A: Microwave vacuum drying is a novel drying technique that combines microwaves with a vacuum environment. Unlike traditional methods such as hot air drying and convective drying, which use high temperatures and airflow to remove moisture, microwave vacuum drying reduces the drying time and temperature, preserving the quality of dried fruits and vegetables.
Q: What are the benefits of microwave vacuum drying for fruits and vegetables?
A: The benefit of using microwave vacuum drying lies in its short drying time and lower temperatures, which help better retain the nutrients, color, and flavor of dried food. This method minimizes the degradation of heat-sensitive compounds, leading to higher-quality dried vegetables and fruits.
Q: How does the application of microwave drying compare to other drying technologies?
A: Microwave drying can be more efficient and quicker than other technologies like spray drying, fluidized bed drying, and infrared drying. The microwave energy penetrates the food material, heating it from the inside out and leading to a uniform drying process, enhancing the quality of dried fruit and vegetables.
Q: Can microwave drying be combined with other drying methods?
A: Yes, microwave drying is often combined with other methods to optimize the process. For example, vacuum-microwave and microwave freeze drying are hybrid techniques that use microwaves in the drying process, as well as different approaches to achieve better results in the dehydration of fruits and vegetables.
Q: What are the drying characteristics of microwave vacuum drying?
A: Microwave vacuum drying’s drying characteristics include rapid moisture removal, uniform heating, and shorter drying times. It allows for precise control of the drying process, which is beneficial for maintaining the quality of dried fruits and vegetables.
Q: How does microwave drying affect drying temperature compared to traditional methods?
A: Microwave drying allows for lower temperatures than traditional methods like hot air drying. This is because microwaves penetrate the food and heat it internally, reducing the temperature of microwave drying and helping maintain the food’s natural properties.
Q: What types of fruits and vegetables can be effectively dried using microwave vacuum drying?
A: Various fruits and vegetables, such as apple and pumpkin slices, can be effectively dried using microwave vacuum drying. This method can be particularly advantageous for produce sensitive to high temperatures and extended drying times, ensuring high-quality dehydrated vegetables and fruits.
Q: Why is microwave drying considered a novel drying technique?
A: Microwave drying is considered a novel technique because it significantly advances over traditional methods. The technology’s ability to reduce the drying time and temperature while maintaining the integrity and quality of the food distinguishes it from more conventional drying systems.
Q: How does microwave vacuum drying impact the quality of dried fruit?
A: Microwave vacuum drying can significantly enhance the quality of dried fruit by preserving its nutritional content, color, and flavor better than traditional drying methods. The reduced exposure to high temperatures minimizes nutrient loss and degradation, producing superior-quality dried food.
Q: How does microwave dehydration work in a microwave oven for fruits and vegetables?
A: Microwave dehydration in a microwave oven involves using microwaves to generate internal heat within the fruits and vegetables, causing the moisture to evaporate more quickly. This method can be combined with vacuum environments to create a more efficient and gentler drying process, ideal for ensuring high-quality dehydration of fruits and vegetables.