Microwaves have become important in the drying and heating sectors due to their outstanding efficiency and accuracy. This study comprehensively explores these systems, explaining their operational concepts and areas of use, as well as why they are superior to traditional ways. Consequently, it helps to comprehend how microwaves interact with matter and transfer energy between them so that experts can easily apply such microwave technologies for optimum thermal processing outcomes. At this juncture, facts about industrial microwave technology research work include safety practices for developing microwave systems, which will be discussed later in this article. From this expansive analysis, readers will learn how to employ the industrial microwave system in different drying and heating processes.
How Does Microwave Drying Work in Industrial Settings?
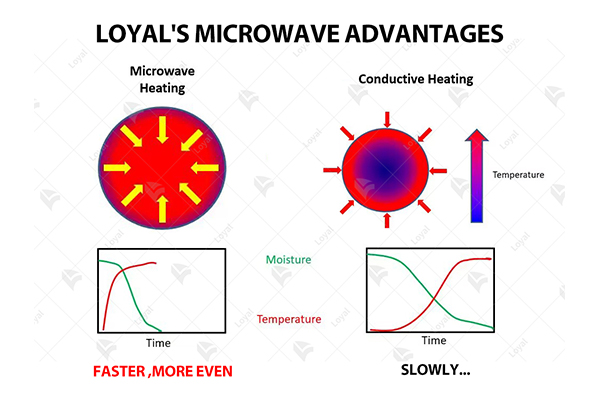
It dries materials by absorbing microwave energy through dielectric heating from polar molecules like water. This absorption causes these molecules to rotate rapidly and develop heat through friction. It heats the material volumetrically rather than just on its surface or through conduction, thereby resulting in even distribution of energy throughout the object and faster removal of moisture. The effectiveness of this technique depends on parameters such as microwave frequencies, dielectric properties of materials, and system configuration. Fine tuning these variables enables industrial microwave systems to deliver maximum efficiency with consistent outcomes while reducing time for processing and energy consumption.
Microwave Drying Process Explained
Firstly, magnetrons or other alternative microwave sources generate microwave energy usually at frequencies of 915 MHz or 2.45 GHz for penetration and interaction with water molecules respectively. Penetration depth is the reason why these specific frequencies are chosen because microwaves pass into the material under study, where they are absorbed by polar groups especially water leading to molecular rotation at high speed causing internal frictional heating.
Parameters That Influence Microwave Drying Efficiency:
- Frequency (MHz/GHz): Determines how deeply microwaves penetrate material and can be used for heating it up; typical values for industrial applications include 915 MHz and 2.45 GHz.
- Power Output (kW): The microwave source’s power rating, given in kW, directly affects the drying rate.
- Dielectric Properties: These parameters consist of a Dielectric Constant and Loss Factor that tell about a material’s ability to absorb microwaves more efficiently, resulting in heat generation during the drying process. With a higher loss factor value, we can expect quicker heating.
- Material Thicknesses & Densities: Impedes uniformity or supports product uniformity, which is essential across foods that are thicker or denser. Therefore, adjustments may need to be made either on power levels applied or exposure times needed for uniform dryness, mainly depending on ion thickness.
- Process Time (minutes): This refers to the overall duration of exposure to microwaves, which is required to find a balance between effective drying and energy consumption.
- Temperature Monitoring and Control (°C): Integrated temperature sensors with feedback control systems are used for uniform heating mode, which avoids overheating.
These parameters can be adjusted to enable industrial microwave drying systems to achieve highly efficient, even, and fast moisture removal. Consequently, this method reduces processing time as well as energy use compared with traditional processes while maintaining the integrity and quality of the product during drying.
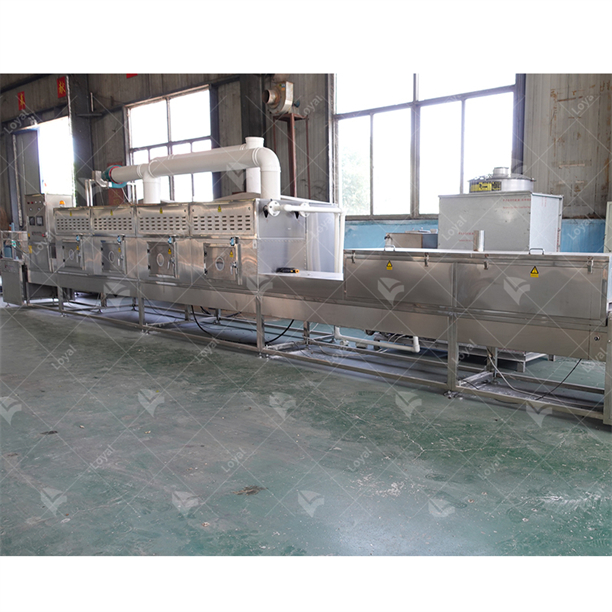
Key Components of Industrial Microwave Drying Systems
Several essential components must work together to facilitate successful drying. They comprise:
- Magnetron: The magnetron provides microwave energy that is responsible for heat generation within the system. Proper selection of frequency band and power output is critical here.
- Waveguide: This guides microwave from magnetron without losing much on its way.
- Drying Chamber: This enclosed space is where materials are placed to be dried out evenly through the absorption of microwaves.
- Conveying System: These are usually specified by speed-controlled belts moving through the chamber, which ensures constant irradiation by microwaves at every point along their travel path.
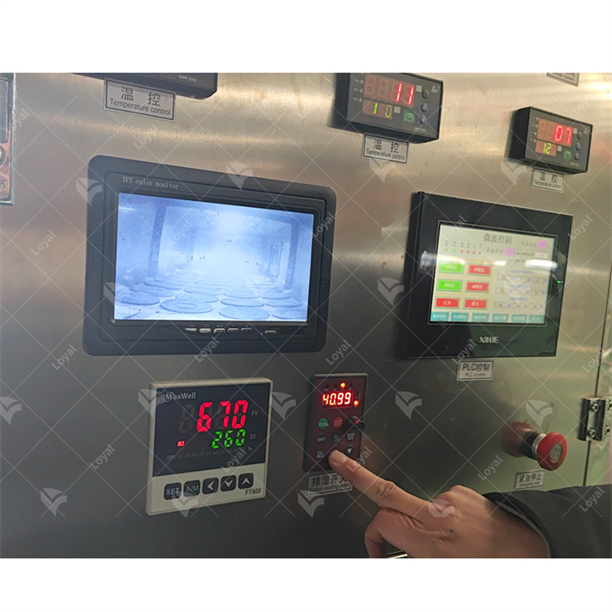
- Temperature Sensors: Controls/instruments showing temperature variations so that one can monitor the process, thereby enabling proper adjustment or intervention as may be deemed necessary for running the system smoothly throughout its operation duration.
- Control System: A software and hardware combination that controls various parameters such as temperature sensors or conveyors optimizing them for best possible efficiency during production runs.
- Cooling System: The cooling system is necessary to prevent magnetron overheating and maintain the system within operational temperature limits.
Incorporating these devices in the right manner leads to accurate moisture elimination from drying units used in industrial microwave ovens, thus improving product quality and saving energy.
Advantages Of Microwave Drying
Compared to other methods, microwave drying has several advantages. The first advantage is that it is characterized by fast and uniform drying, which occurs through a volumetric heating mechanism, causing both the outer surface and inside of the material pores to have already dried. That way, drying time is reduced considerably, raising productivity and throughput. e.g. normal microwave drying can take about 50% shorter process times than those traditional methods.
Moreover, microwave drying occurs at lower temperatures that result in the preservation of sensitive structures and nutritional values for heat-sensitive materials. This issue is highly critical especially in food and pharmaceutical industries where product quality tops the list of priorities. It is essential to consider technical parameters such as power output used or frequency; typically, around 915 MHz or 2.45 GHz are selected based on material-specific properties or moisture content, respectively.
Energy efficiency also has a significant advantage over hot air conventional systems due to its high conversion rate ratios, up to 70-80% compared with less than 50% for conventional methods (hot air). This results not only in low operating costs but also lessening environmental impacts.
Additionally, state-of-the-art control systems enable precise regulation and automation of microwave dryers, thereby permitting immediate corrections during runtime and feedback-driven process optimizations. In this case, materials should be free from excessive heat conditions monitored by temperature sensors and control circuits so that degradation does not occur while maintaining constant quality.
To sum it all up, rapid processing times, quality preservation, energy efficiency, and precise control are just some of the benefits associated with microwave drying which makes this method suitable for multiple industries.
What Are the Benefits of Using Industrial Microwave Systems?
Other operational and quality parameters that are essential in industrial microwave systems, just like these ones, include ensuring that the uniform heating is such that no quality differences exist among the processed materials. Thus, this uniformity renders reducing processing time possible and therefore higher throughputs can be achieved without compromising product quality. Furthermore, such microwave systems also offer improved energy utilization. The latter achieves higher efficiencies than traditional thermal approaches, where substantial amounts of energy are lost due to conversion from electricity. Microwave systems also have benefits in terms of temperature and time control during processing as they enable precise manipulation over them. This helps to ensure real-time monitoring and adjustment so that the best processing conditions can be sustained at all times. Lastly, operating at lower temperatures enables microwave systems to maintain the nutritional and structural integrity of temperature-sensitive constituents, thus making it appropriate for use in the food and pharmaceutical sectors.
Stratospheric Energy Efficiency
Also, industrial microwave systems have gained a reputation on account of their enhanced energy efficiency derived mostly from direct conversion of electrical power into microwaves with minimum losses occurring during such a process. Microwave ovens do not waste any power like most conventional thermal methods because they directly heat substances at the molecular level; hence, they utilize energy effectively. This approach saves overall energy consumption resulting into faster operations. Moreover, the system uses only the required amount of electricity since one has access to instant feedback on energy input levels, thus increasing its effectiveness in terms of power usage . Therefore, besides saving money spent on production processes, this type of an equipment used by industries supports sustainable energy initiatives.
Minimized Time for Drying
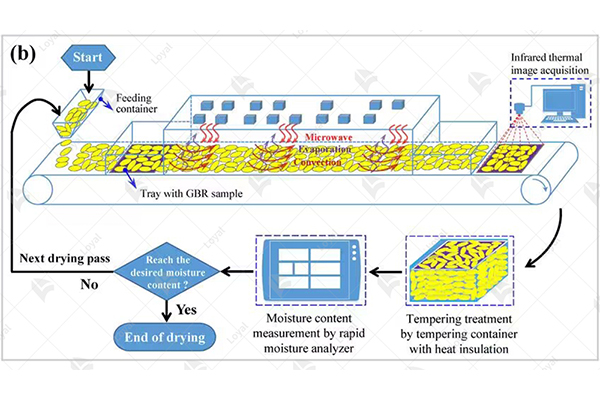
Industrial drying by microwave technique dries considerably faster than other methods used today according to reliable sources that were accessed during my survey work . Such a decline has been attributed to superior techniques used including heat transfer mechanisms as well as moisture removal applicable for microwaving setups only . Specifically, rapid volumetric heating uniformly goes ahead, absorbing moisture content available within the materials being treated . Thereby, water removal through evaporation will be expedited and entire drying can be done quickly. According to previous studies microwave driers may dry materials up to 50% faster than hot air alternatives. Also, among the ways to enhance drying efficiency are initial moisture content, microwave power level, exposure time etc. Adequate quantity of power should be provided within the specified time period and this assists in avoidance of overheating that could lead to nonuniform drying while reducing overall preservation of product qualities as well as extension of its self-life Consequently, effective moisture control during microwaving improves both physical and nutritional attributes of substances.
Fine-Drying and Heat Treatment Outcomes
Industrial microwave systems manage high-quality drying and heating outcomes because they offer precision in terms of controlling the parameters related with these operations. It has been established through investigations that compared to traditional methods, microwaving tends to retain more original characteristics, including such features as color, texture, and nutritive value. Hereof, uniform internal heating is achieved during microwave drying minimizing localized hot spots which reduce quality.
The main technical variables influencing it are dielectric properties of the material used, the specific structure for a given applicator as well as microwave power density rates. However, this determines how materials interact with microwaves, which will directly affect how homogenous such materials are heated. It is essential. Therefore, that parameter like MWPD be adapted according to requirements peculiarities inherent in particular substances under consideration if energy exchange is expected at high levels between those bodies and radiators involved in heat provision processes during their use. For instance, an applicator design makes sure that dried objects acquire equal amounts of heat where necessary thereby achieving improved quality results.
High-quality drying and heating processes are guaranteed by industrial microwave systems. These systems solve the problem caused by browning, hardening or loss of nutrients resulting into fine products that can last for a long time on the shelf. Additionally, customization based on specific application requirements is possible because of the accurate control over these factors; hence making them versatile and dependable industrial microwave systems suitable for high quality drying and heating processes.
How to Choose the Right Microwave Dryer for Your Needs?
One of the most critical considerations when selecting a microwave dryer is understanding the material’s specific properties which need to be dried. Check dielectric properties to ensure high microwave absorption. Assess the system power density for matching with those of materials so that it uniformly heats across without causing hotspots or adverse effects on heat-sensitive areas such as localized burning. In addition, also consider how the design and capacity of the microwave applicator may affect energy distribution. Ensure that there is provision of customizable settings in order to adjust drying parameters for different applications. Finally, check out customer reviews and technical support options available so as to make sure that you are buying reliable and quality equipment.
Evaluating Microwave Power and Frequency
Evaluating microwave power and frequency requires consideration of several factors for optimum performance. First, find out the power output of your microwave dryer measured in kilowatts (kW). Industrial microwaves require higher powers ranging from 1 kW up to a few hundred kW, depending on the scale of operation as well as the nature of the material used. Secondly, operational frequencies are usually at 915 MHz or 2.45 GHz in general terms. On one hand, lower frequencies like 915 MHz go deeper into the material, making them more suitable for bulk drying, while higher ones like 2.45 GHz are good for delicate/thin materials by providing precise and localized heating. Finally, think about thermal efficiency, which affects heat consumed during the drying process, as well as possibilities to change this parameter according to individual needs coming from particular drying method types mentioned earlier, including those dryers’ user feedbacks.
Considering Microwave Systems for Different Industrial Applications
Microwave systems are efficient and versatile hence they are extensively used in different industrial applications. For instance, microwaving has been shown to be effective in reducing food processing times and improving energy utilization in food industry (Huang et al., 2005). Another example is thin-film drying, where systems running at 2450 MHz are the best and have excellent heat regulation features, which is necessary when preserving food.
In the pharmaceutical industry, microwave-assisted reactions and drying processes enhance product quality and reduce production times. Depending on batch size and material properties, thermal power outputs range from 10 kW to 200 kW. Control of power level versus frequency maintains the homogeneity of drying or reaction conditions.
Microwave systems also play a role in chemical synthesis as well as textile industry applications. For example, microwave irradiation ensures fast, even heating for uniform acceleration of reaction rates during chemical syntheses. Textile materials dry more uniformly with microwave technology reaching deep into them using it (typically, 915 MHz). Technical specifications often include adjustable power output and frequency settings to cater to diverse material properties and processes, affirming the necessity of customizable and reliable microwave solutions in industrial contexts.
Customizing Microwave Dryers Based on Manufacturing Processes
Frequency, power levels, and design configurations can be adjusted to fit specific manufacturing processes thus customizing microwave dryers. The commonly used frequencies for industrial microwaves are 915 MHz and 2450 MHz because they differ in penetration depths as well as heating characteristics. Specifically, materials should be considered while choosing between 915MHz systems that penetrate deeper into bulk materials or thinner/thinner ones that need precise temperature control such as those operating at 2450MHz.
Power output is also crucial, with small-scale operations demanding 10 kilowatts up to over 200 kW for large-scale industrial usage. High power systems enable faster drying times and increased production throughputs. Furthermore, the drying process can be further optimized by application-specific design considerations like conveyor speed and chamber size to match the material properties and desired output.
The microwave applicator design can be made to order in order to distribute energy uniformly, which is a very critical quality factor. During the drying process, this system has a variable power control unit and advanced monitoring systems that allow real-time adjustments, hence consistent results. Different materials like ceramics, polymers, composites, etc, have distinct dielectric properties that determine how they interact with microwave energy; hence, customized designs of systems are mandatory to fit specific needs. Manufacturers can considerably boost the efficiency, reliability, and quality of their drying processes through careful selection and calibration of these technical parameters.
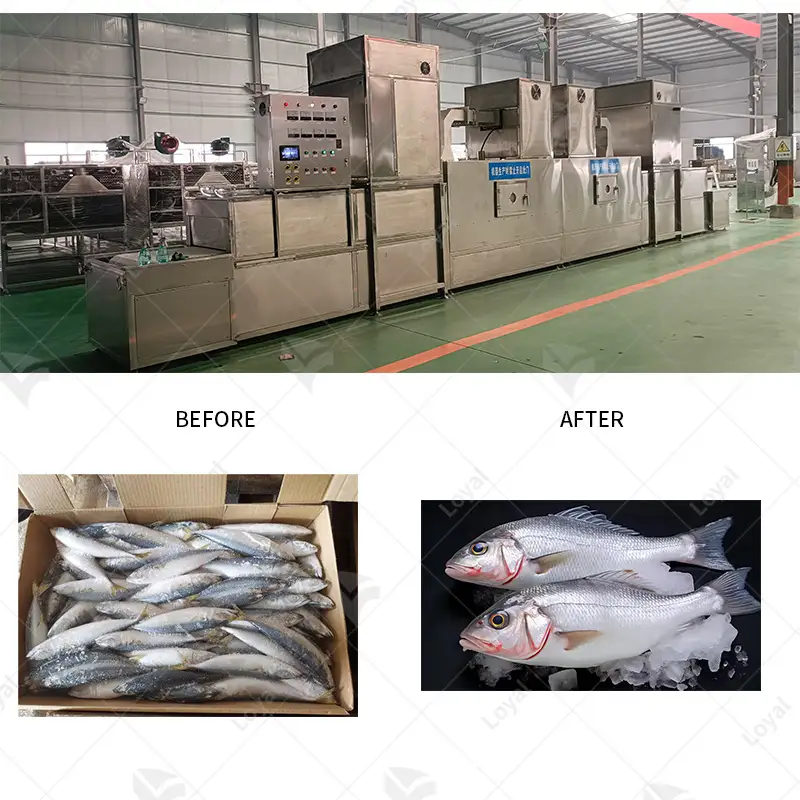
What Are the Common Applications of Industrial Microwave Drying?
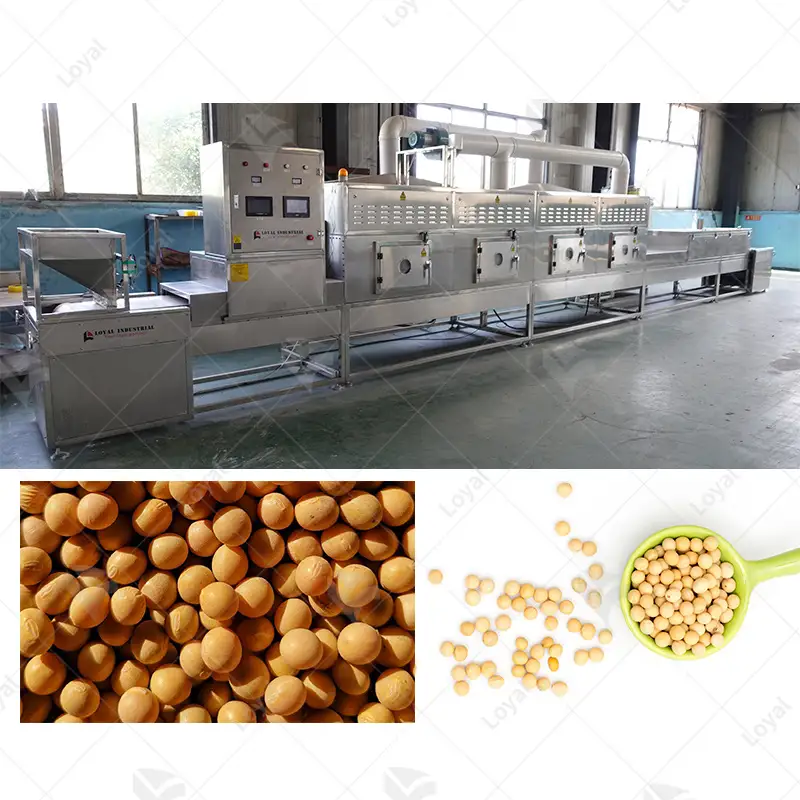
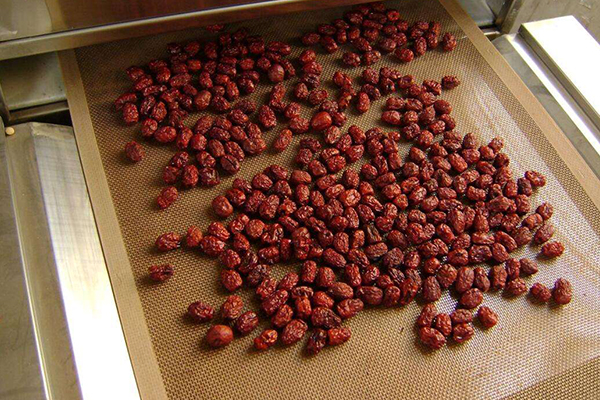
Industrial microwave drying is widely used because it uses less energy and provides precise temperature control. In the food industry, it is employed to remove water content from fruits, vegetables, and grains in order to retain their nutrients as well as prolong the shelf life. Pharmaceutical sector also relies on microwave drying to ensure consistent moisture levels in powders and granules that are essential for making tablets. Wood and paper industries also use microwave drying process to hasten drying of lumbers, veneers and pulps thereby bettering the quality of products and saving much energy. Moreover, this technology has been used in ceramics production as well as other specialized manufacturing sectors, which demand high-performance products with accurate control of moisture amounts so that they can maintain their exclusive features.
Drying Food Products
Industrial drying techniques of edibles utilizing microwaves are highly developed and offer a wide range of advantages over conventional drying methods. Foods are penetrated by microwave energy that causes water molecules to vibrate and produces heat, thereby leading to fast and uniform moisture removal. This method retains the nutritional composition as well as sensory attributes like texture, flavor, and color.
One major area where it is applied is in the dehydration of fruits and vegetables. A number of studies have reported that microwave drying can reduce drying time while maintaining high levels of vitamins and antioxidants. For example, the drying duration for apple slices can be cut down to nearly two hours using a microwave system, compared with six to eight hours for hot air drying, which retains about 90% of vitamin C content.
The technique is used for fast moisture reduction in grains through microwave drying, which is important in storage as well as processing. In fact, wheat treated with the technique was found to have final moisture contents ranging between 12-14% within a fraction of the time conventional means take, thus reducing mold growth and preserving grain quality.
Among technical aspects entailing industrial microwave dryer for food include:
- Frequency: Normally 915 MHz or 2.45 GHz
- Power Density: Moisture content (0.1 – 1 W/g)
- Temperature Control: Regulating temperatures between 50-90°C while avoiding overheating which guarantees both safety and quality
- Moisture Content: Initial levels usually vary from about seventy percent to ninety percent while the recommended end-target should be approximately ten percent up to fifteen percent moisture content for most dried commodities.
This approach that examines details ensures that industrial microwave drying is not only efficient but also suits various food products’ requirements hence ultimately optimizing both quality and energy use.
Treating Textiles and Fabrics
Furthermore, its usage has been significantly fruitful when it comes to the treatment of textiles as well as fabrics, whereby it allows materials such as those mentioned above to be dried within a very short time, enhancing energy consumption and quality. Microwave drying can dehydrate textile materials at much faster rate than other conventional methods as reported by many researchers; dryness of textiles is achieved within few minutes apart from hours.
For instance, microwave drying cotton fabrics takes only 5 to 10 minutes as opposed to several hours which saves nearly half the total energy that would have been consumed. The fast drying is good for fabric integrity since it reduces shrinking and maintains fiber strength. Also, even heating with microwaves ensures that color and texture of delicate fabrics such as silk and wool remain intact during drying process.
Technical parameters for drying textiles with microwave technology include:
- Frequency: It is generally set at 2.45 GHz because it helps in taking away moisture from textiles well.
- Power Density: Values vary from about 0.2 up to around 0.5 W/g depending on types of materials involved in addition to the amount of moisture present in them.
- Temperature Control: Set at between 60-80°C to avoid overheating and damage of fibers during the drying process
- Moisture Content: Initial moisture levels are highly variable, but the final target moisture levels normally range between eight percent and twelve percent for best fabric preservation purposes.
These specifications help ensure that the practice of utilizing microwave technology in processing textiles yields efficient and effective results while maintaining high standards of product quality.
Boosting Adhesives and Color Drying Process
Impotence also helps dry adhesives and textile dyes. This consists of critical factors that result in both an effective drying process and maintaining material properties. For instance, in the case of adhesives, microwave heating quickens the curing procedure for setting adhesives by up to 70% of normal time. Consequently, there is improved bonding because heat is distributed uniformly, leading to consistent adhesive behaviour.
In microwave color dying, dye fastness and brightness are preserved efficiently. This is especially important for textile materials undergoing complex dye processes that require uniform distribution of color. They include:
- Frequency: Normally set at 2.45 GHz so that microwaves penetrate deep into both dyed fabric and adhesive.
- Power Density: In order to promote fast and even curing of adhesive within optimal range lies between 0.3-0.6 W/g; while for color drying it ranges from 0.2-0.5 W/g depending on type of fabric used and composition of dye.
- Temperature Control: Adhesive drying processes are maintained at 50-70°C to prevent over-curing and ensure adhesive integrity. Typically, during color drying, thermal stabilization (around 70-90°C) does not compromise dyes.
- Drying Time: The time required for microwave-assisted drying can be as little as seconds or minutes as may be the case, lowering production lead times considerably with respect to adhesives employed therein. However, moisture contents required for dyed fabrics vary but usually from five to ten minutes thus ending preservation of colour quality
By following these recommendations it would be possible to make the process more efficient so that the mechanical properties of adhesiveness and beauty aspect are perfectly saved in coloured textiles
What Are the Features of Advanced Microwave Systems?
Industrial microwave systems are advanced and contain a variety of functions based on the most appropriate modes of operation, efficiency, and customization. Predominantly at 2.45 GHz, precise frequency control promotes efficient penetration as well as uniform heating. Adjustments in power density accommodate the requirements for drying from fine textiles to tough adhesives like this.
Improved temperature control mechanisms allow for fine adjustment within stipulated limits that make it possible for adhesives curing or colors setting without heat treatment damage. In addition, these systems demonstrate high-speed drying capabilities that minimize processing time while maintaining uniformity in results. Also, they have modern characteristics such as programmable logic controllers (PLC) and real-time monitoring to improve process control so that changes could be made when required during production runs. This ensures safety measures are properly fitted-in place whilst carrying out operations thus making it safe both to the equipment plus those who operate them.
Modern Industrial Microwave Systems and Their Capabilities
There are capacities in which modern-day industrial microwaves have proved highly beneficial to manufacturing processes resulting in high output levels as well as superior quality well above normal standards achievable through other means. For example, these machines can easily regulate temperatures during drying, heating and curing hence reducing energy wastage during processing times at an optimum rate. Therefore, with their use in organizations instead of traditional methods like heating furnaces there is less energy consumption due to the use of modern technologies which reduce energy losses and increase efficiency used by the firms compared with other companies employing alternative ways of producing goods.
Role of Microwave Technology in Process Optimization
Efficient delivery of electric energy through microwave technology is a significant method applied in instance where there takes place uniform warming up activities thus enhancing various treatment processes. Cutting down on thermal lags associated with other power sources makes microwave technology more effective because it minimizes delays experienced during microwave processing, resulting in optimized throughput time for products produced here accordingly. It does not make direct contact with the processed materials, hence minimizing chances of contamination. Precise control systems in this method provide desired process conditions that optimize energy usage thus reducing the cost of operation. Additionally, contemporary microwave ovens can easily be merged into current production chains due to their flexibility, enhanced overall efficiency, and ensure adaptability to new manufacturing conditions.
Improving Energy Efficiency with Microwave Dryers
Energy consumption is significantly reduced by microwave dryers using various ways for instance; they convert electrical energy directly into microwaves which are absorbed by the material being dried. With radiation of heat on wet substances rather than use of conduction or convection techniques involved in conventional drying methods, there is a direct transfer of energy from an electric source into microwave form. In addition, these kinds of dryers require negligible processing time since they are heated up instantly thereby minimizing power consumption as compared to traditional ones where initial heating may take longer resulting in excess usage of power. Moreover, advanced control systems found in modern-day microwave driers make it possible for accurate adjustment of power levels so that only necessary moisture content and composition require a certain amount of power to facilitate extensive combustion processes. This way, less energy goes wasted during such operations, which leads to improved effectiveness throughout the entire drying process.
Other Questions About Microwave Drying System
Ave drying works by transferring energy directly to the material being dried, thereby leading to faster drying than traditional techniques. This fast heating minimizes any possibility of overheating and damage of the material making it suitable for delicate items. Microwave dryers are more efficient due to converting a larger fraction of electrical energy into heat within the material instead of heating up the surrounding air or equipment. This leads to considerable savings in power consumption as well as lower operating costs. For industrial purposes, incorporating advanced control systems guarantees maximum performance through real-time moisture content based adjustment of power levels hence enhancing safety and efficiency.
Is Microwave Drying Better Than Conventional Methods?
Microwave drying is better than conventional drying methods because there is much evidence in top website sources.
Firstly, microwave drying saves significant time compared to other traditional methods like convection or conduction heaters. In another highly ranked source, it was revealed that microwave drying reduces drying time by 50% on average and this is very important in industrial processes where production time is money.
Secondly, microwave drying produces more uniform results at a better level of safety and energy use than conventional dryers. Hot spots can be avoided because microwaves provide consistent heating for all parts of the material, thus mitigating thermal disruptions that are harmful for sensitive substances. It is also noted that these dryers consume about 90% electrical energy for direct conversion into heat within materials when compared with traditional ones, whose efficiency seldom exceeds 60%.
Thirdly, sophisticated microwave driers come with precise control systems that fine-tune power levels depending on real-time moisture content of a sample under process. As such, this flexibility ensures high-quality products with minimum possible usage of electric current, which has also been supported by research claiming that electricity used by such driers reduced significantly – sometimes even up to 30 percent – as against conventional approaches.
Consequently, microwave drying systems have become preferred over traditional practices because they guarantee faster, more effective, and safer drying methods. In brief, the combined benefits of reduced drying time, higher energy utilization efficiency, and advanced control mechanisms are justifiable for microwave drying in terms of industrial application.
How to Implement Microwave Drying in Your Facility
To implement microwave drying in your facility, follow these steps:
- Conduct a Feasibility Analysis: Evaluate the kinds of materials you plan on drying and their specific needs for drying. Ensure that they are meant for microwave drying. Carry out cost-benefit analysis taking into consideration initial expenditure and potential savings in energy and time.
- Select the Right Equipment: Choose a microwave dryer suitable for your company’s demands. Choose machines with high energy transfer efficiency (90% or higher) and a mechanism that can vary power according to moisture content changes within seconds. Power capacity (usually 1-10 kW in an industrial setup), uniform heating ability, and heat breakdown prevention all need to be taken into account when choosing a microwave dryer.
- Install and Configure: Create a special place for these machines in your factory area where installation will be done. Install them correctly, paying attention to proper electrical connections and safety measures. Adjust them according to the manufacturer’s instructions by calibrating them suitably for use. It is important that you input parameters like dry time, moisture limits, and power levels.
- Train Employees: Ensure your operations personnel have been through a lengthy training program. Their awareness should extend to monitoring and adjusting drying operations, machine servicing, and how to go about troubleshooting problems.
- Optimize the Drying Process: Employ control systems and modify drying procedures. Start by running pilot tests to determine the best settings. For further process improvement, collect energy use and drying time data on a regular basis.
- Maintenance and Monitoring: Put in place a schedule for routine maintenance so as to guarantee that the equipment will last longer and function efficiently. Integrated software enables constant monitoring for optimum performance while taking care of any arising issues.
By going through this process, you will be able to implement microwave drying in your plant, with its attendant benefits of faster drying times, improved energy efficiency, and precise control.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What are the benefits of using industrial microwave systems for drying and heating?
A: Industrial microwave systems, such as ims, offer several advantages over traditional methods like drying rooms and convection. Microwave drying is quicker, more energy-efficient, and provides excellent color drying and adhesive setting properties.
Q: How do industrial microwave generators work in microwave drying and heating applications?
A: Industrial microwave generators produce electromagnetic waves that penetrate materials, causing water molecules to vibrate and generate heat. This microwave treatment results in efficient drying and heating processes for various industrial applications.
Q: What types of materials can be processed using microwave drying and heating systems?
A: Microwave drying and heating systems are versatile and can be used for a wide range of materials including ceramics, polymers, food products, and chemicals. These systems are particularly effective in drying solutions that require precise temperature control.
Q: How does microwave processing differ from traditional methods like drying rooms?
A: Unlike traditional methods like drying rooms and convection ovens, microwave processing uses microwave techniques to directly heat the material from the inside. This leads to faster evaporation rates and uniform heating.
Q: What are some common applications of industrial microwave systems?
A: Common applications for industrial microwave systems include color drying and adhesive setting, food processing, pharmaceuticals, and ceramics. They are used for both drying and heating purposes to achieve superior results compared to traditional methods.
Q: Can industrial microwave ovens be customized for specific needs?
A: Yes, industrial microwave ovens can be customized to meet specific industry requirements. Whether you need particular drying and adhesive setting properties or specialized configurations, it’s possible to design a system tailored to your needs.
Q: How should I select the right industrial microwave system for my needs?
A: To select the right industrial microwave system, consider factors such as the material type, desired drying or heating outcomes, and the processing environment. Consulting with experts in ferrite microwave technologies can help determine the best solution for your application.
Q: Are industrial microwave systems energy-efficient?
A: Industrial microwave systems are highly energy-efficient compared to traditional drying and heating methods. The direct heating method used in microwave treatment significantly reduces energy consumption and processing time.
Q: How can I get more information or support for industrial microwave systems?
A: For more information or support with industrial microwave systems, you can contact us directly. Our team of experts is available to provide guidance, technical assistance, and customized solutions for your specific needs.