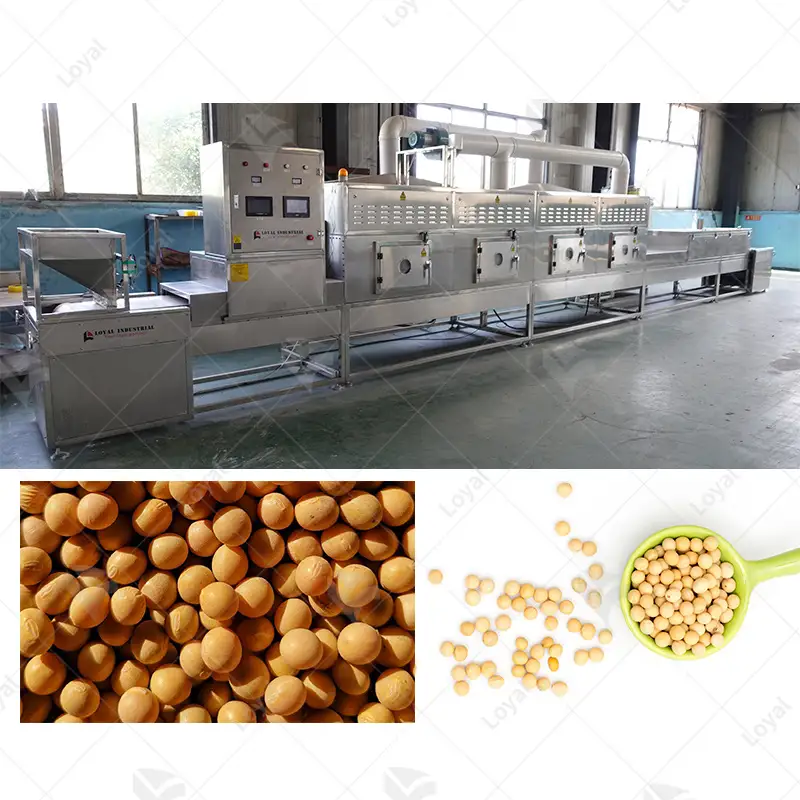
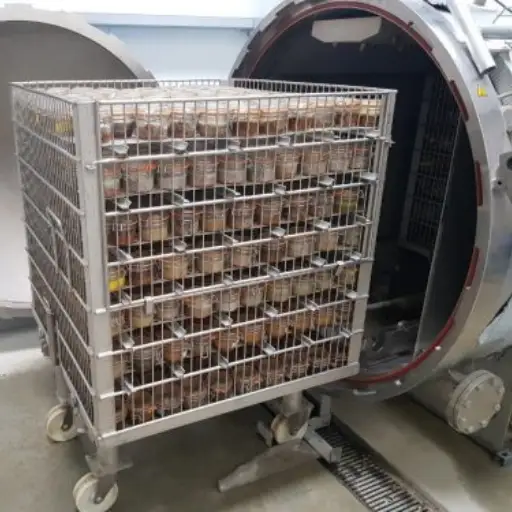
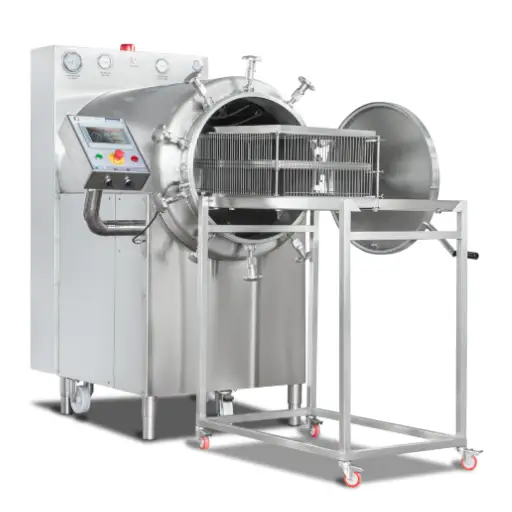
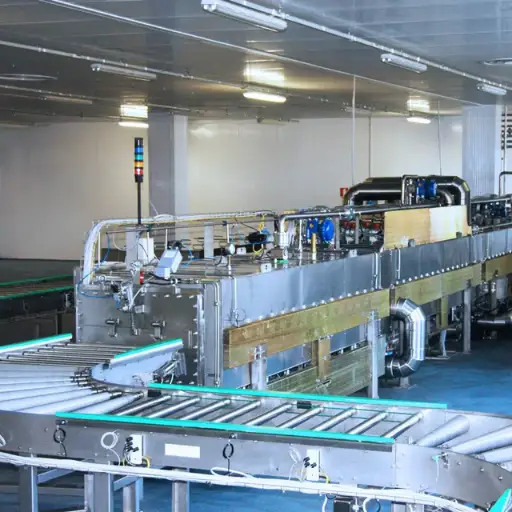
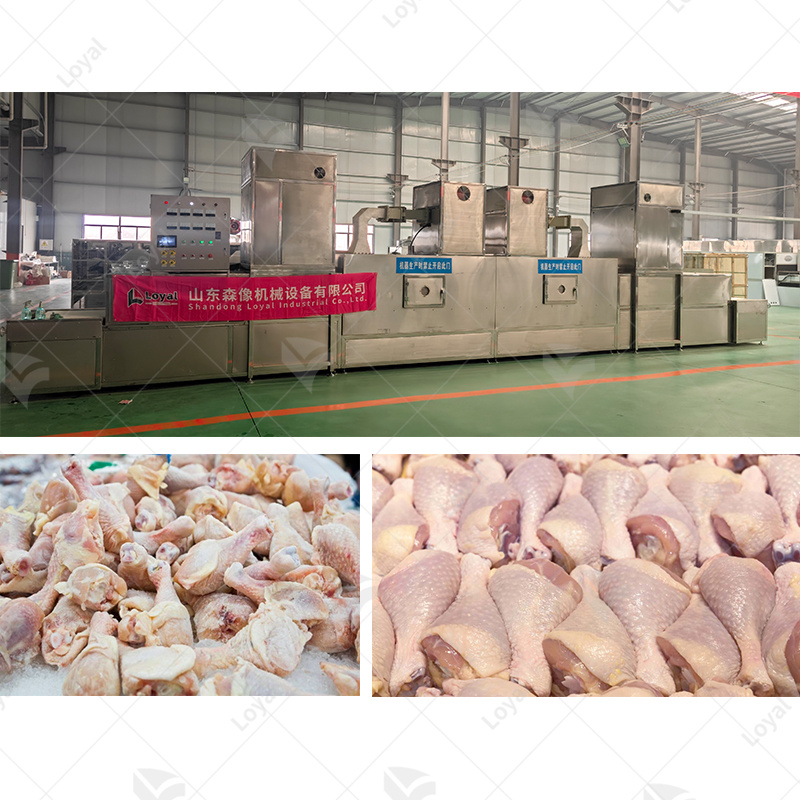
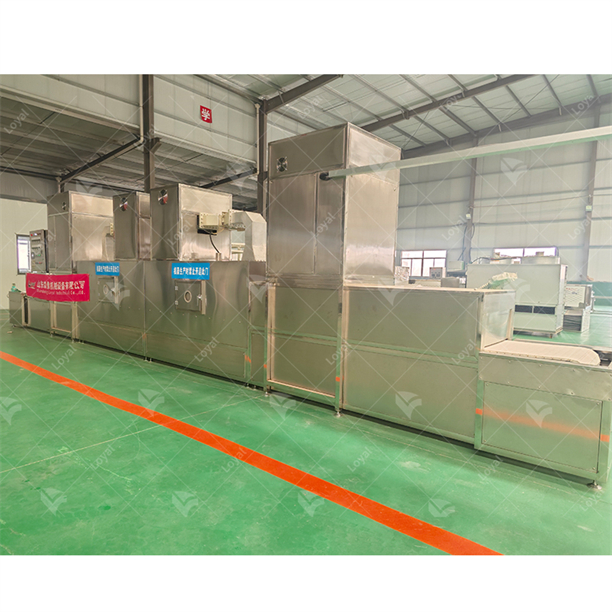
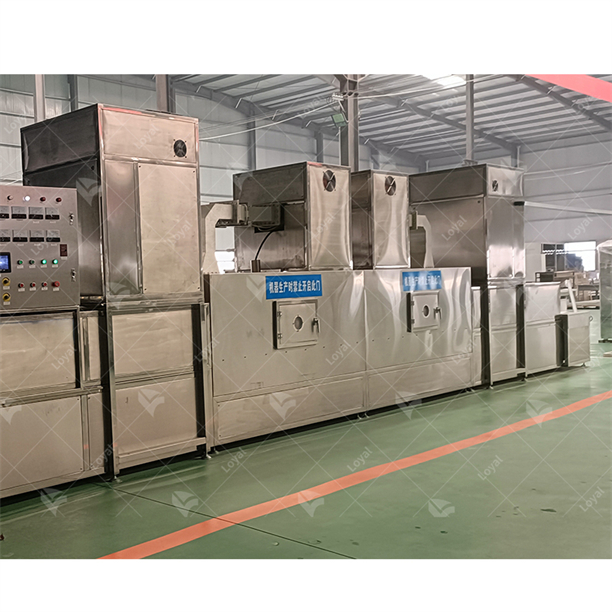
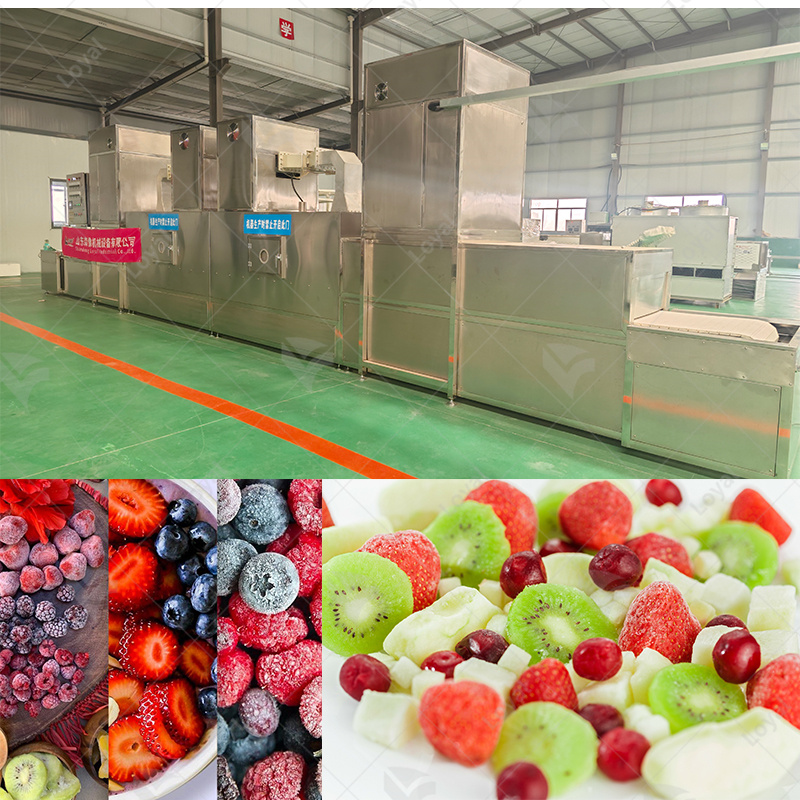
Industrial microwave defrosting machines and tempering systems are considered to be a sophisticated and efficient method of thawing and reheating various types of frozen products. These systems use modern microwave technology which allows for uniform rapid heating so that the product is processed under a controlled and consistent environment. Unlike the traditional ways of defrosting, which might take long hours while leading to uneven heat distribution, microwave defrosting does not damage the product quality and reduces microbial risk.In industries where food safety and quality during thawing is critical such as the pharmaceuticals or food processing sectors, this technology offers an advantage. Microwave heating principles will be covered in this article, including why one should consider using industrial microwave heaters; and how they can be tailored into different industrial backgrounds.
How Does an Industrial Microwave Thawing Machine Work?
The industrial defrosting machine operates on the principle of microwave thawing that uses electromagnetic waves in the microwave frequency range. These microwaves penetrate into the frozen product which causes rapid oscillation of dipolar water molecules in order to generate a lot of internal friction that ultimately produces heat. Incidentally, these microwaves have the ability to penetrate directly into the product, leading to its internal and uniform warming rather than relying on conduction from the outside towards the inside like other traditional methods do. To do this, it is necessary to manage temperature well without resulting in any hotspots or thermal gradients which may cause uneven thawing. They are further kept compliant with health standards through constant surveillance and feedback systems as part of their built-in programs.
Microwave Thawing Basics
Microwave thawing technology relies on dielectric heating principles. The interaction between microwave energy and polar molecules in frozen material results in molecular oscillations that produce internal heat. Important technical parameters for this process include the frequency at which the microwave is used, power density, the composition of the product, and set point temperatures.
- Microwave Frequency: Frequencies usually employed by major commercial microwave systems are 915 MHz or 2450 MHz because they ensure optimal depth penetration and heating performance.
- Power Density: Regarding watts per kilogram (W/kg), power density determines how fast energy will be transferred to products being treated. For gradual steady thawing rates, about 1-2 W/kg would be typical.
- Product Composition: Specific heat capacity, moisture content, and dielectric properties that determine how well microwaves are absorbed and converted into heat by-products differ among various products.
- Temperature Set Points: Precise control over starting and target temperatures helps avoid partial defrosting or overheating. Product temperature within freezing limits, which normally falls between -2°C – 0°C is maintained by most systems so as to enhance quality and safety concerns.
The industrially efficient defrosting process occurs in microwaves, with uniformity and safety of products for food and pharmaceuticals.
Principal Components of Microwave Thawing Machine
A microwave thawing machine is composed of a microwave generator, waveguide, product handling system and control panel as its major components. The microwave generator which operates at 915 MHz or 2450 MHz provides the necessary energy to be used in the form of microwaves while also ensuring that it has an optimal depth penetration and heating performance. Waveguides help to properly direct and distribute microwaves evenly throughout the product under treatment. Product handling systems such as conveyor belts or rotating trays ensure that products pass uniformly through the field formed by microwaves so that they can be thawed uniformly. The control panel gives accurate adjustment for microwave frequencies, power densities as well as temperature set points thereby making sure that this equipment works within predetermined limits for quality assurance purposes.
Various Food Products Applications
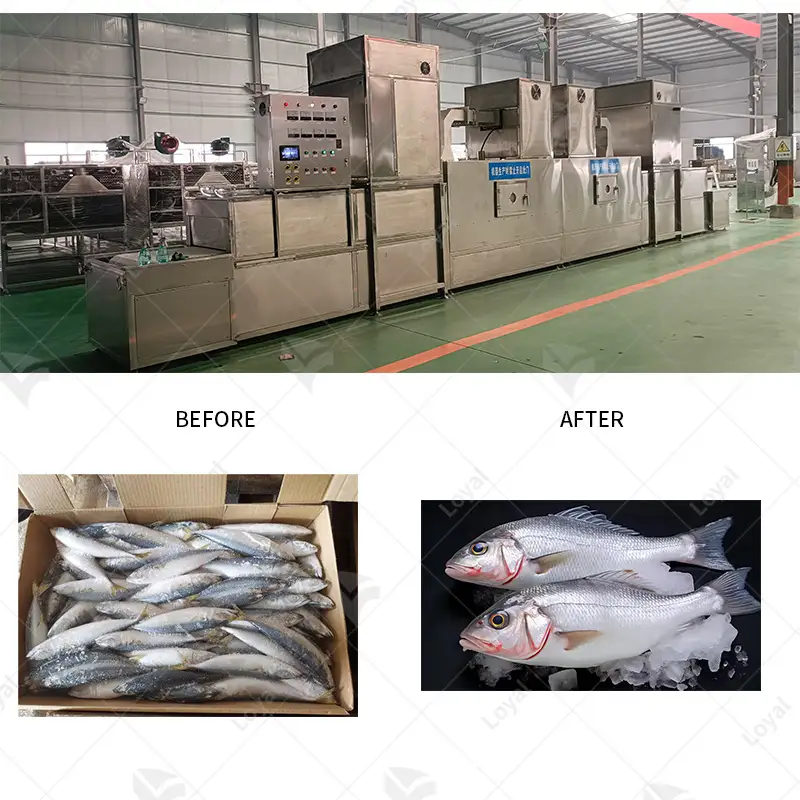
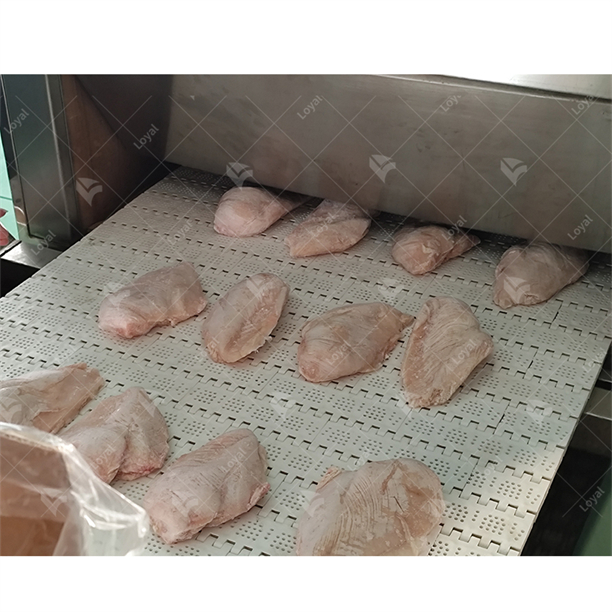
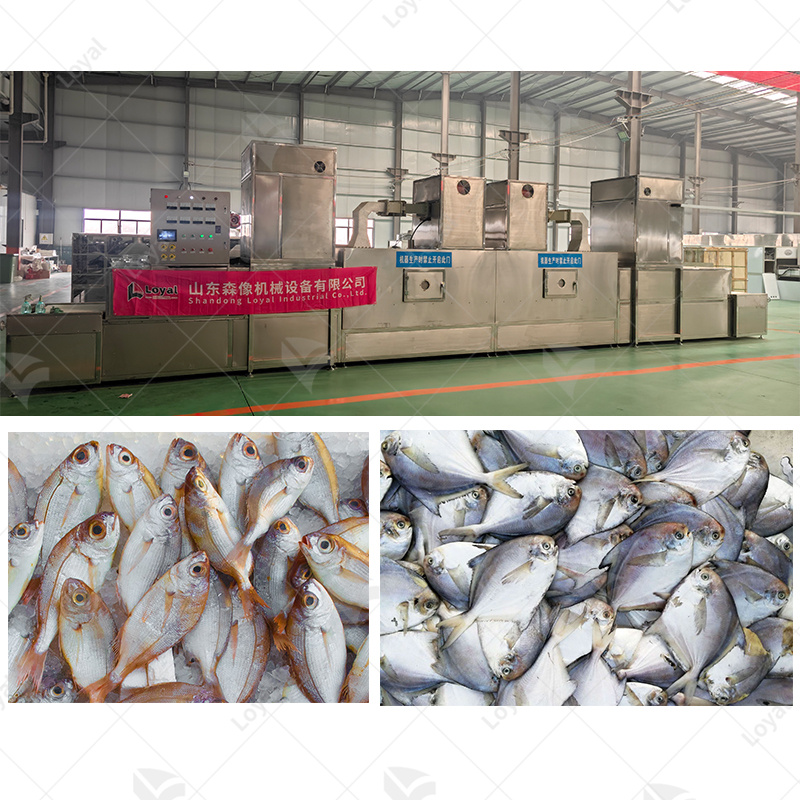
Microwave thawing technology is highly important in many food products since it increases efficiency while maintaining quality. Precise control of such parameters as initial and target temperatures (-2°C to 0°C) is essential when dealing with meat products like beef, pork or poultry, to avoid microbial growth and keep texture. Fish and seafood also benefit from microwave frequencies that are usually set at 2450 MHz so as to ensure a uniform thaw without altering the fragile structure of its flesh. For fruits and vegetables, maintaining specific moisture content levels is critical to prevent cellular damage, thus the microwave power density should be adjusted accordingly. The frequency settings and power modulation depend on dielectric properties and fat content in dairy products such as butter or cheese to avoid uneven thawing and oil separation. In line with strict food safety regulations as well as industry standards, each application needs customized microwave energy parameters that can guarantee the quality, texture and security of foodstuffs.
What Are the Benefits of Using Microwave Defrost and Thaw Systems?
Advantages of the microwave defrost and thaw systems over conventional methods include, reduced time for defrosting, higher efficiency in operation and cost benefits due to low labor needed. Short processing times also reduce microbial growth risk hence better food safety. Secondly, such systems provide even thawing that ensures that the products remain their original structure as well as quality without being partially cooked or melted at the surface. Uniformity is especially important in preserving perishables’ texture, flavor and overall sensory attributes. Lastly, microwave defrost is an energy-saving technology because it directly targets the moisture content of food, resulting in a decrease in energy use compared to traditional thawing practices like air or water bath defrosting techniques, thereby not only reducing operational costs but also promoting sustainability practices in food processing industry.
Fast and Efficient Thawing of Frozen Products
Microwave defrost and thaw systems work by using electromagnetic waves to heat up water molecules inside frozen products thereby causing rapid temperature rise and uniform thawing. This method contrasts sharply with the slower air or water bath method, which are inefficient ways of handling frozen products. According to USDA reports on microwave thawing, this technique can considerably cut down on processing periods often demanding a fraction of time used under conventional methods thereby improving efficiency during operations. The technical parameters like frequency (typically 915 MHz or 2.45 GHz) power density (in Watts per kilogram) are very important here because they have to be carefully set so as not to cause uneven cooking or incomplete thawing through localized over-cooking respectively between different areas within any given product being heated up. Furthermore, studies published by International Journal of Food Science & Technology prove that microwave defrost does not affect texture changes and does maintain food quality by minimizing changes made to moisture content. It does two big things: it preserves energy by targeting the internal moisture of each item, thus placing less pressure on the environment while at the same time fulfilling health requirements since no excess thawing periods are allowed and foodborne bacteria are restricted from multiplying.
Minimizing Drip Loss and Preserving Quality
Microwave defrost and thaw systems are inherently designed to minimize drip loss, thereby maintaining the quality of frozen products. During the process of thawing, a phenomenon known as drip loss occurs which causes water and soluble nutrients to be lost in a food. On one side, compared with traditional methods, microwave thawing results in far less drip loss due to better control over temperature as well as energy distribution. A recent study covered by Journal of Food Engineering showed that the use of optimized parameters such as power level (around 30-50% of total microwave power) and intermittent application (switching on and off) reduces it significantly. Furthermore, operating at certain frequency levels like 915 MHz or 2.45 GHz ensures equal internal heating throughout the foodstuffs thus minimizing excessive moisture evaporation through localized overheating. With this method, not only protein matrix remains intact but essential nutrients stay inside resulting into an improved product quality. Furthermore, rapid thawing limits bacterial growth by reducing exposure to temperatures, favoring their multiplication, hence enhancing safety measures for edibles. In general, this means that precise and efficient parameters used in microwave thawing processes focus on both product quality and safety, hence making it an invaluable technique in the modern food processing industry.
Energy Efficiency and Money Saving
Energy efficiency and cost-effectiveness are significant advantages of microwave defrosting and thawing systems. Water immersion or air thawing compared to conventional methods, microwave systems consume much less energy as a result of their effective heat transfer mechanisms. International Journal of Refrigeration Studies and US Department of Energy have revealed that the energy conversion efficiency in this kind of equipment could be as high as 65-80% while the traditional ways can only achieve 50% at their best. This is because microwaves directly interact with water molecules that quicken the melt process, reducing total power consumption.
Technical parameters influencing energy utilization include specific microwave frequencies (915 MHz or 2.45 GHz) that ensure even energy allocation, minimizing hotspots. Other factors, such as power levels and pulsed power application, are also critical. Running the system at 30-50% power levels and using intermittent microwave applications will optimize the thawing process, thus assisting with product quality maintenance by reducing energy use.
From a cost perspective, this reduces thawing time and consumes less electricity, resulting in direct operating savings. For example, companies report cutting down on their bills by at least one third after transitioning from ordinary approaches to microwave defrosting methods. Additionally, shorter melting duration results in increased throughput coupled with reduced labor costs, which ultimately contribute to overall productivity gains. The adoption of microwave-based thaw systems in food processing industry has therefore enabled operational and economic efficiencies by achieving these benefits
What product categories can benefit from microwave thawing?
For various classes of products, thawing by microwaving can be a significant advantage especially in the food business. This includes categories like frozen poultry, seafood and meat that need quick and even defrosting for quality maintenance and adherence to safety standards. Also, microwave thawing is good for freezing fruits and vegetables that preserve best when thawed using the microwave compared to conventional methods in which they lose their nutritional values as well as texture-wise. Thawing dairy products such as frozen cheese and butter will improve their consistency and thus shorten processing time. It’s therefore concluded that overall, microwave thawing is an adaptable, efficient solution for multiple groups of frozen food improving both quality and operational efficiency.
How does it work for frozen meat and poultry?
Thawing meat or poultry from a freezer with a microwave uses electromagnetic waves, producing heat resulting in the vibration of water molecules within it, causing them to generate some heat energy. The process begins when microwaves enter the outer layers then penetrate further inside the bird or meat; thus allowing for even defrost at a fast pace. Careful control of power selection plus period used in defrosting must be observed so that no part starts cooking. Furthermore, this technique also reduces the amount of time during which bacteria would multiply since it avoids keeping food within temperatures dangerous to health termed “danger zone”. As such, aside from preserving its texture as well as quality; there is compliance with regulations on food safety after thawing through this method.
Is it suitable for frozen food like vegetables and seafood?
Microwave thawing really works well on frozen vegetables, including different sea foods, despite their differences. In case of vegetable items, the process takes less time but maintains more nutrition than if one followed traditional ways of defrosting them. There is minimal loss of vitamins as well as minerals due to microwave thaw such that overall quality does not deteriorate significantly. For fishy products, though, there may appear unevenly cooked fish given that the microwave allows defrosting without overcooking while maintaining their fragile texture and taste. Quality can be a problem if some parts have patches that are partially cooked; hence, it is important to use correct power and timing. Therefore, this technique turns out as an effective approach for both frozen vegetables and seafood altogether since they remain testy and nutritious.
Can it be used for food products with packaging?
It is crucial to ascertain that the packaging is microwave-safe when dealing with microwaving packaged food during thawing. Numerous materials, such as certain types of plastics, glass, and ceramics, are safe for use in ovens. However, those whose packaging contains metals and other materials not intended for microwave heating should be avoided as they cause sparks, which may damage it too. For this reason, before any signage on the package, the user should always go through the instructions about making sure that this process does not put him or her at risk.
How to Choose the Right Industrial Microwave Thawing Machine?
What are the key factors that must be looked at when choosing a suitable industrial microwave defrosting machine? First, consider the capacity and throughput of the machine relative to your production requirements. The ability to handle varying food volumes is different for various machines; hence, select one that matches your operational scale. Secondly, its thawing uniformity has to be put into account. In this regard, some of these advanced devices provide an even and consistent defrosting necessary for maintaining food products’ quality and safety standards. Thirdly, energy efficiency matters because there is huge amount spent on electricity bill. At least look out for those machines with features built in them to save energy. Also, you should think about how easy it will be to maintain this equipment and get technical support for it over time. Such things can impact operational efficiency levels in the long term. Finally, make sure that the device meets all applicable requirements stipulated by regulatory bodies as well as complies with food safety laws so as not to face any legal problems or risk harming consumer’s health.
Important Characteristics
The important thing here is uniform thawing and energy economy when choosing industrial microwave defrosting oven. For example, microwaves from leading manufacturers usually have many-point temperature monitoring systems along with variable power settings, among other things, where multi-point temperature monitoring systems are preferable, thus making models offered by top brands even more attractive in terms of functionality and convenience. Technical parameters like frequency (usually around 915 MHz or 2450 MHz) and power output (from several KW up to more than ten KW) are vital since they affect both speed and consistency during thawing.
Another critical consideration is energy efficiency, whereby some sophisticated ones utilize the inverter technique as well insulation chamber, which helps reduce wastage of power through conduction or radiations into surroundings, thereby lowering their ratings within higher grades achievable by these rated producers. Moreover, process controls can be programmed such as automatic routines that hardly require operators, thereby improving overall efficiency. Similarly, these devices are made of easy-to-clean parts and have a strong construction that meet the stringent hygienic demands usually required. In particular, stainless steel is commonly used due to its resilience and ease of cleaning. Lastly, do not fail to verify machinery compliance with such food regulations as FDA or USDA in the U.S., which will save you from serious legal problems and ensure highest possible quality.
Comparison of Different Product Types
When comparing various types of industrial microwave defrosting machines, there are several factors to consider. First of all, the potential flexibility and low production volumes make batch-type defrosters more suitable for an operation where you can increase or decrease output or change product at any time, as well as utilization of versatile processing conditions, though manual handling may lead to higher labor costs. Conversely, continuous thawing machines are intended for larger-scale operations where it is possible to reach high throughput rates with minimum human intervention required into the process execution. Typically equipped with conveyors and automatic loading systems that improve thawing efficiency by ensuring work consistency.
Microwave hybrid systems employ additional heating means like infrared radiators, blown air, and microwaves so that a uniform temperature can be maintained throughout the product. In this regard hybrid systems would be most useful when dealing with thick materials that may not defrost uniformly just upon application of microwaves alone. Every category has different benefits depending on specific operational requirements including volume and type(s) of items produced.
Therefore, while making a choice, you should consider your own needs alongside the technical specifications mentioned above because they must correspond to the desired performance level together with norms and conformance goals meant for each category.
How does an industrial microwave defrost and thawing machine compare with other tempering systems?
A defrosting machine for industrial microwave is better than other tempering systems in several ways. Firstly, the microwave-based system helps in evenly and quickly heating foods, thus reducing thawing times as compared to traditional air or water-based methods. This hastened process lowers the risk of microbial infection while preserving the taste, texture and nutritional value of product. Secondly, microwave defrosting machines have lower energy consumption and operating costs since they directly transfer energy to food thus requiring less power. Lastly, these systems can be used over a wide range of food products and processing requirements, allowing greater flexibility in temperature control and product integrity maintenance.
Thawing vs Tempering: How Do They Differ?
Even though related, tempering and thawing are different processes with different results depending on how they are carried out.
Defrosting refers to converting a frozen product into an unfrozen one by increasing its temperature above a freezing point, usually 0°C (32°F). Refigeration, immersion in cold water or use of microwaves are common thawing methods used to restore the product to normal usable condition whilst guarantee food safety and quality.
On the other hand, tempering is a more controlled approach in which at least part of a frozen item is brought up to certain temperatures, which might still be below zero degrees Celsius, especially between -3°C (26°F) and 0 °C (32°F). The main objective here is making them soft enough for slicing or grinding without full thrawing. It’s good for industries that want to maintain product texture and moisture content.
Comparison of microwave energy with water thawing
Several technical parameters that influence the effectiveness, safety, and efficiency of these methods need to be considered when comparing microwave energy to water thawing processes:
- Processing Time:
- Microwave Energy: It unfreezes food rapidly within seconds or minutes depending on size of product and microwave power settings.
- Water Thawing takes quite a long time, usually between 30 minutes and several hours, depending on the volume of water and the size of the item under treatment.
- Energy Efficiency:
- Microwave Energy consumes more energy because it heats at high speed but can transform the electric current into heat in the food directly.
- Water Thawing is economical in terms of energy because it uses the transfer of heat energy between water and food, though heating or maintaining temperature may have some potential energy costs.
- Microbial Safety:
- Microwave Energy: This method has a fair risk in case food is not even; since cold spots can facilitate microbial growth, there is, therefore, a need for proper heating.
- Water Thawing: The risks are lower provided this operation is done within controlled temperatures (below 40F or 4C); otherwise, prolonged exposure above this range can lead to contamination increase.
- Product Integrity:
- Microwave Energy: A probable outcome could be irregularly defrosted products leading to partial cookery as well as texture changes thus there is need for turning while constantly monitoring quality during the process,
- Water Thawing: Its advantage lies in ensuring that foods maintain their texture and moisture contents hence best suited for delicacies that require structural integrity.
In summary, microwave energy offers convenience and speed while keeping water-thawed frozen products well preserved only if properly done. Thus, by addressing specific requirements alongside available resources, the choice of appropriate thawing technique considerably influences both product and process optimization.
Efficiency of microwave generator compared to other systems
Several technical parameters must be considered in evaluating the efficiency of microwave generators compared to other systems. Microwave generators, often known as magnetrons, are highly efficient in converting electrical energy directly into microwave energy, achieving efficiencies typically around 50%-75%. This is significantly higher than traditional radiant or convection heating systems, where efficiency commonly hovers between 30%-60% due to heat loss during energy transfer.
Energy Conversion and Heating Efficiency
- Microwave Generators: Achieve direct electricity conversion to microwaves with about 50%-75% efficiency.
- Radiant Heating Systems: Approximately 40%-60% efficient, with significant heat loss to the surrounding environment.
- Convection Heating Systems: About 30%-50% efficient due to prolonged heating times and non-direct heat application.
Environmental and Operational Factors
- Microwave Generators: Offer rapid heating and reduced energy wastage by targeting the food product directly, thus minimizing energy consumption for quick heating or thawing processes.
- Radiant and Convection Systems: Typically require higher energy input and longer operational times, leading to greater overall energy consumption.
Justification of Parameters
- Thermal Conductivity: Microwaves heat food through dielectric heating, where polar molecules align with the microwave field, causing friction and heat generation internally. This process is intrinsically more efficient than surface heating.
- Energy Distribution: Microwaves can penetrate food to varying depths based on frequency, allowing more uniform heating compared to surface-only methods.
In summary, microwave generators provide superior energy efficiency and operational effectiveness for heating applications compared to traditional radiant and convection systems, making them a preferred choice for rapid, targeted heating processes.
What Are Common Issues & Solutions with Microwave Thawing Machines?
Industrial microwave thawing machine faults can involve uneven thawing, excessive fluid loss and partial cooking of the product in question. Inconsistent microwave energy distribution is the leading cause of uneven thawing, resulting in the defrosting of some parts and freezing of others. Hybrid systems could be used to mitigate this challenge by introducing microwaves alongside other heating methods or through continuous rotation during the process.
Excess fluid loss may compromise the texture and quality of the thawed product. To avert this, it is important to manage humidity and temperature within the chamber. Preserving moisture content in products is possible with controlled environments for partial melting that have humidity and temperature settings properly balanced.
Lastly, if microwave energy causes too rapid heating on outer layers of a product, it can partially cook it. This is preventable through altering power levels and defrost times so that thawing proceeds smoothly throughout by taking care not to change its rate suddenly. Partial cooking can also be prevented by employing advanced sensors and control systems that optimize temperature ranges.
Handling Drip Loss During the Thawing Process
Drip loss — while materials are being defrosted –remains a significant problem affecting yield as well as quality. In connection with the topmost contents from reputable sites, management of parameters for thawing is vital to minimizing drip loss. For instance, one approach to take would entail having a thaw chamber that has precise temperature control keeping just above freezing point of the product concerned.The technical parameters show that maintaining it at 1-2°C (34-36°F) significantly reduces drip losses.
Furthermore, using intermittent microwaves during pulsed energy mode aids in reducing the thermal gradient across food items, thus minimizing drip formation. A pulse interval involving turning on microwaves over 15-20 seconds followed by 30-40 seconds off time works best while optimizing such processes, among many other detailed researches.
One more technological solution lies in applying vacuum packaging during thawing process. The water vapor pressure is lowered within the product while under vacuum conditions, thereby keeping moisture inside it. Investigation has shown that drip losses can be efficiently controlled with vacuum pressures of -0.8 bar or more. These methods are combined in such a way that they reduce the rate of drip loss while also preserving the form and state of defrosted food.
Maintaining the Machine for Optimal Performance
Regular maintenance of thawing machines is essential for optimal performance and longevity. First, routine checks should be carried out to ensure all parts are operating properly. This may involve inspecting seals’ integrity, electrical connections, and temperature controls’ accuracy, among other things. Lubrication prevents wear and tear on moving parts, hence prolonging their service life.
Secondly, there is need for hygiene practices. For example, regular cleaning as well as sanitization helps to remove bacterial contamination from the chamber which would otherwise compromise both safety and quality of products in question.Use suitable detergents that are safe for use on food contact surfaces so that no residues remain after cleaning is done.
It is also important to calibrate sensors and control systems regularly to maintain precise temperature settings. With time, adjustments may be needed to account for any deviations in sensor accuracy. This method of maintaining the machine ensures that its thawing rate remains high and product characteristics do not change.
Quality and Food Safety Assurance
During the thawing process, it is necessary to ensure that rigorous control measures are implemented so as to guarantee food safety and quality standards. Hazard Analysis Critical Control Points (HACCP) protocols should also be followed, which help identify potential hazards in the process of thawing. Utilizing well-calibrated thermometers as well as maintaining a constant temperature is very significant in preventing pathogen growth. The entire thawing process, from storage through to final use, must have product traceability systems put in place to meet all regulatory standards, thus ensuring each step complies with legal requirements. Furthermore, keeping the staff regularly trained on hygiene and safety practices is crucial for high food safety levels and quality assurance.
In addition, product traceability systems need to be put up throughout the entire defrosting process, storage up to final usage to certify that every stage brings out compliance with regulations on this aspect. Also, consistent training of personnel on hygiene and safety practices will maintain a high level of food security by means of steady regularity. Additionally, adherence to HACCP protocol is imperative since it assists I recognizing various forms of hazards during defrosting processes.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What are the main benefits of using microwave technology for defrosting and tempering in the food industry?
A: Microwave technology offers several advantages, including rapid defrosting, uniform thawing both inside and outside the product, reduced drip loss, and energy efficiency. These benefits improve the overall quality and safety of frozen food products while enhancing the productivity of food processors.
Q: How does industrial microwave defrosting equipment work?
A: Industrial microwave defrosting equipment works by emitting electromagnetic waves that penetrate the frozen food products. The waves cause the water molecules in the food to vibrate, producing heat and causing the ice to melt more uniformly and quickly. This method allows for efficient and consistent defrosting.
Q: What types of products can be defrosted using industrial microwave defrosting systems?
A: Industrial microwave defrosting systems can be used to defrost frozen meat, fish, poultry, pet food, fruits, vegetables, and various other frozen food products. These systems are versatile and can handle a wide range of food items.
Q: What is the difference between tempering and defrosting in the context of industrial microwave systems?
A: Tempering refers to the process of partially thawing frozen products to a pliable state, suitable for further processing, without completely defrosting them. Defrosting, on the other hand, involves fully thawing the frozen products to a state where they can be cooked or consumed directly. Both processes can be effectively achieved using industrial microwave equipment.
Q: What are the key features of a high-quality industrial microwave oven used for defrosting?
A: A high-quality industrial microwave oven for defrosting typically features a robust microwave cavity, precise control systems for uniform heating, advanced sensors for monitoring product temperature, and durable construction to withstand industrial environments. These features ensure efficient and reliable performance in food processing applications.
Q: How does microwave thawing equipment improve thawing speed compared to traditional methods?
A: Microwave thawing equipment significantly improves thawing speed by generating heat directly within the product, allowing for faster and more uniform thawing. Traditional methods, such as air or water bath thawing, rely on heat transfer from the outside in, which is slower and less efficient.
Q: Can industrial microwave defrosting systems handle continuous processing?
A: Yes, many industrial microwave defrosting systems are designed for continuous processing, allowing for uninterrupted thawing of large quantities of frozen food products. This capability is essential for food production facilities that require consistent and high-volume processing.
Q: What are the benefits of microwave tempering for meat thawing?
A: The benefits of microwave tempering for meat thawing include faster thawing times, reduced risk of bacterial growth, uniform temperature distribution, maintained meat quality, and minimized drip loss. These benefits ultimately result in a more efficient and safe meat processing operation.
Q: How important is the design of the microwave cavity in industrial defrosting equipment?
A: The design of the microwave cavity is crucial in industrial defrosting equipment as it directly impacts the uniformity and efficiency of the defrosting process. A well-designed cavity ensures even distribution of microwave energy, preventing hotspots and cold spots within the product, leading to consistent and high-quality defrosting results.