Safety and quality are of utmost importance in the ever-changing world of food processing. This guide covers the importance of industrial food sterilization machines, especially autoclaves, in keeping food authentic. By comprehending how these appliances function, their advantages, and sound implementation practices, one will learn how to optimize efficiency and improve overall productivity. Whether you are an old horse or a new kid on the block in this line, read through this article to get schooled about handling the complexities of food sterilization.
What is Food Sterilization?

Image source: https://www.smcsrl.net/
Food sterilization aims to increase food products’ safety and shelf life by eliminating or reducing harmful microorganisms such as bacteria, viruses, and fungi. The process usually uses techniques like heat treatment, chemicals, or irradiation. Since it uses high temperatures or specific chemical agents on foods, it frees them from spoilage-causing pathogens and other causes of illness through infections. The result should be a safe product for eating over a long period but maintain its nutritional value.
Understanding the Sterilization Process
The sterilization process proceeds systematically to ensure food safety. Food is initially cleaned to remove any surface contaminants and then put into an autoclave, where it is exposed to high-pressure steam at elevated temperature. This heat and pressure combination kills all microorganisms. How long the exposure lasts, as well as temperature and pressure level, are critical for determining if the sterilization process works or not. Also, proper sealing and packaging of food items after sterilization are essential in preventing recontamination. In conclusion, food manufacturers must comply with regulations and guidelines so that their products undergo improvements while retaining their qualities.
Standard Methods for Sterilization in the Food Industry
- Heat Sterilization: One of the most commonly used methods in the food industry is when high temperatures destroy harmful microorganisms. Examples include pasteurization, whereby foods are heated to a particular temperature over a specific period, and canning, which involves sealing foods into containers before heating them to eliminate pathogens.
- Chemical Sterilization: For instance, chlorine hydrogen peroxide acids may be used to exterminate all microorganisms on food surfaces. This is an effective method of maintaining hygiene, especially on fruits and vegetables, in various food processing plants.
- Irradiation: This technique uses ionizing radiation to kill bacteria, parasites, and other pathogens present in foods consumed by humans. The method enhances the shelf life of the products, minimizing spoilage without significantly affecting their nutritional quality. Gamma rays, X-rays, and electron beams are among these irradiation forms.
Overall, these approaches help maintain safe food supply chains through preservation techniques that guarantee integrity, keeping consumable goods out of danger for people who buy them.
Why Sterilize Food: Benefits and Necessity
Food sterilization is essential for several reasons, with most of them being related to safety and preservation. First, sterilization eliminates all the disease-causing microorganisms, such as bacteria, viruses, and parasites, thus minimizing the chances of foodborne illnesses, which have profound health implications. Secondly, the process helps retain nutritional value and organoleptic properties to ensure safety and consumer appeal. Moreover, sterilization prevents food spoilage by prolonging shelf life. This finally reduces food waste. Sterilization guarantees safe foods that meet industry requirements and allows for trust-building between consumers and manufacturers.
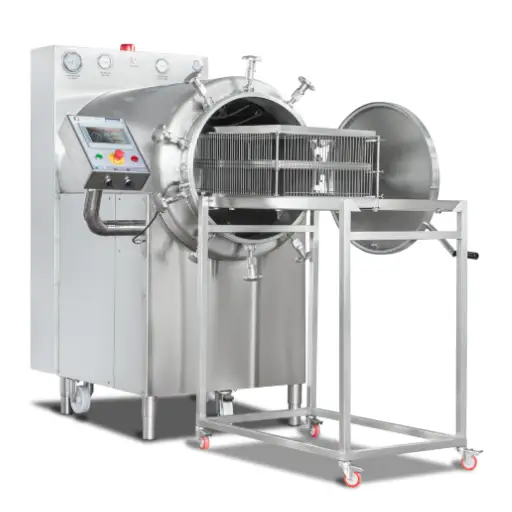
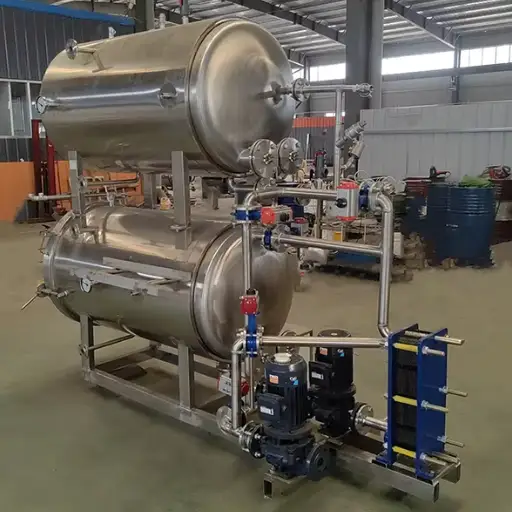
How Do Autoclaves Work in Food Sterilization?

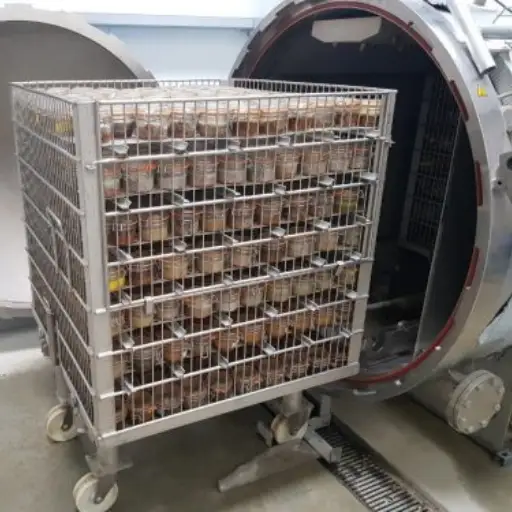
They use high-pressure steam to achieve sterilization, effectively killing bacteria/viruses/spores found in food products. The process begins when the items to be processed are sealed within a chamber. From there, steam is introduced into the chamber while increasing its pressure. In this way, water’s boiling point increases because of elevated pressure, enabling steam to reach a temperature above 100°C (212°F). Therefore, sterilization can only be realized when foods are exposed to these higher temperatures for some set time, usually between fifteen to thirty minutes, depending on what type of food plus how it has been packaged. Once done with their cycle, steam releases from the system, and the chamber is de-pressurized, resulting in sterile food that can sustain extended periods without getting spoilt, thus having a prolonged shelf life.
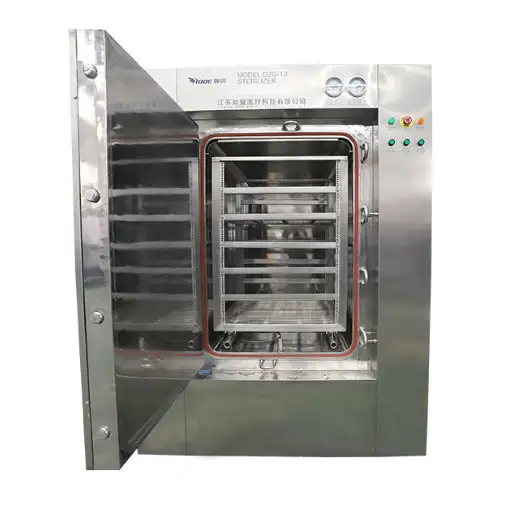
The Mechanics of an Autoclave Sterilizer
The autoclave sterilizers use steam sterilization as a fundamental principle, a process that entails the application of steam under pressure to achieve the high temperatures required for the effective removal of microorganisms. The three main components of an autoclave include:
- Heating Element: It is responsible for heating the chamber’s water, which eventually generates steam. Precise temperature control is crucial to ensure that the steam attains the required parameters for sterilization.
- Pressure Chamber: This sealed compartment allows for the buildup of steam at higher pressures, thereby increasing the water’s boiling point so that it reaches beyond customary boiling points for water, which are typically within 121°C (250°F) and 134°C (273°F), respectively. Thus, full sterilization is achieved.
- Ventilation System: After a sterilization cycle, this system provides an avenue through which pressure and steam can be safely released so that the chamber returns to standard atmospheric conditions without causing burns or exposing one to hot steam.
In practice, pre-vacuum or gravity displacement starts the cycle by removing air from the chamber, thus ensuring greater steam penetration. A drying phase follows after the sterility stage, permitting dryness for subsequent uses. This technique finds wide applications in food processing sectors, medical facilities, and laboratories to promote safety and compliance with health standards.
Autoclave vs Other Sterilization Equipment
Comparatively, autoclaves have distinct advantages and limitations over other sterilization methods such as dry heat, ethylene oxide gas, and chemical sterilization. Autoclaves use steam under pressure to achieve fast and efficient sterilization, making them suitable for heat- and moisture-resistant materials. Conversely, temperature is held high for an extended period in the dry heat sterilization process so that microorganisms are killed. However, it may not be effective against all spores. Ethylene oxide gas is a low-temperature option ideal for heat-sensitive instruments but requires prolonged exposure times and extensive aeration to ensure safety after processing. Chemical sterilization, on the other hand, is good at surface sterilization using solutions like hydrogen peroxide; however, residues can be left behind, which means it is not ideal for porous materials. As such, the choice of the optimal method of sterilizing depends upon whether they are resistant or non-resistant organisms.
Choosing the Right Autoclave for Your Needs
To pick out the perfect autoclave that suits well with you. Taking in mind these points might help:
- Types of Autoclaves: Depending on available space and the number of items to be sterilized, choose between tabletop models and larger floor models. Tabletop versions serve smaller practices, while bigger ones fit hospitals or labs with high throughput demands.
- Size and Capacity: Make sure that your selected option has an internal chamber size that fits the utensils, instrumentation, and materials used in your laboratory.It should be easy to load while preventing overcrowding for efficient operation.
- Features and Options: Look for digital controls, pre-programmed cycles, or validation capability to monitor the effectiveness of these products. Some others come with additional functions, like drying cycles or dual pressure options, enhancing functionality.
Thus, using these criteria, one may choose an autoclave that will satisfy their requirements regarding sterility and optimize operational efficiency in accordance with health standards.
What Are the Main Features of Industrial Sterilization Machines?

Industrial sterilization machines are made to provide reliable and efficient sterilization in various applications. Such features include:
- Advanced Control Systems: Most of these machines are fitted with sophisticated control systems, which allow for accurate temperature and pressure settings and ensure consistent sterilization cycles.
- Robust Construction: Industrial sterilizers are built from solid materials to withstand heavy use and harsh environments, guaranteeing a long life span and reliability in high-demand contexts.
- Automatic Cycle Monitoring: Built-in monitoring systems form part of many models, tracking cycle parameters and producing real-time data to guarantee compliance with sterilization protocols and safety requirements.
- Multi-Sterilization Methods: In an industrial setting, numerous sterilizing methods, such as steam, dry heat, ethylene oxide, or hydrogen peroxide, might be used to treat diverse kinds of materials.
- User-Friendly Interfaces: Intuitive interfaces for easy programming, operating, and maintaining processes are commonly used to improve efficiency amid busy schedules.
Therefore, they enable industrial sterilization machines to effectively meet the stringent demands imposed by healthcare facilities, laboratories, and manufacturing establishments.
High-Temperature Operations and Control
In industrial sterilization machines, high-temperature operations mean using elevated temperatures to eliminate microorganisms effectively. These procedures often require precise temperature control to allow for adequate sterilization without compromising the integrity of the materials being processed. Sterilizers capable of performing at high temperatures, such as autoclaves, typically employ steam with a temperature range of between 121 and 134 °C (250 °F-273°F). Advanced digital control systems and accurate sensing devices are essential in maintaining these temperatures consistently throughout each sterilization cycle. Furthermore, automation reduces human error and improves efficiency, making it necessary for institutions to rely on sterility for safety and effectiveness.
Batch Sterilization vs Continuous Sterilization
Two main methods are used in industrial applications for material sterilization: batch sterilization and continuous sterilization. Batch sterilization involves treating groups of items simultaneously in one cycle. This method is commonly used in facilities with complete control over the sterilizing process because they can confirm that all items within the batch were fully penetrated with enough sterility. However, if you have many products that need quick processing times, this system may not be viable.
Continuous sterilization systems conversely function continuously, allowing new items to be introduced while materials undergo sterilization. This method is highly applicable in large-scale manufacturing where production volumes per unit time must be very high (throughput). Continuous operation cycles are frequently reduced, leading to increased efficiency. Still, they may necessitate more advanced controls than required by batch processes or might not provide the same level of confidence about homogeneous sterilizations. Ultimately, choosing between these two methods depends on what specific requirements a facility has.
Key Components and Specifications
When one considers sterilization systems, essential components and specifications are needed to ensure the sterilization is effective.
- Sterilization Chamber: This is actually the most crucial part in all batch and continuous sterilization systems. It needs to be designed to take up the required volume and types of materials to be sterilized while ensuring uniform exposure of these items to the sterilant.
- Temperature and Pressure Control: These values greatly influence the efficiency of the sterilization process; therefore, controlling them accurately is vital. Hence, reliable sensors and regulators should be equipped on such a system to maintain optimum conditions.
- Safety Mechanisms: Pressure relief valves, alarms, and automatic shut-off mechanisms are some examples of solid safety features necessary for personnel protection during operations.
- Monitoring and Data Logging: Many current systems have advanced monitoring functions that log critical parameters for verifying a successful sterilization cycle. This information is crucial for regulatory compliance and process improvement.
- User Interface: An intuitive user interface makes setting adjustments easier, assuring easy operation and boosting overall productivity.
The above components determine how effective, efficient, and safe sterility processes are in various operational environments.
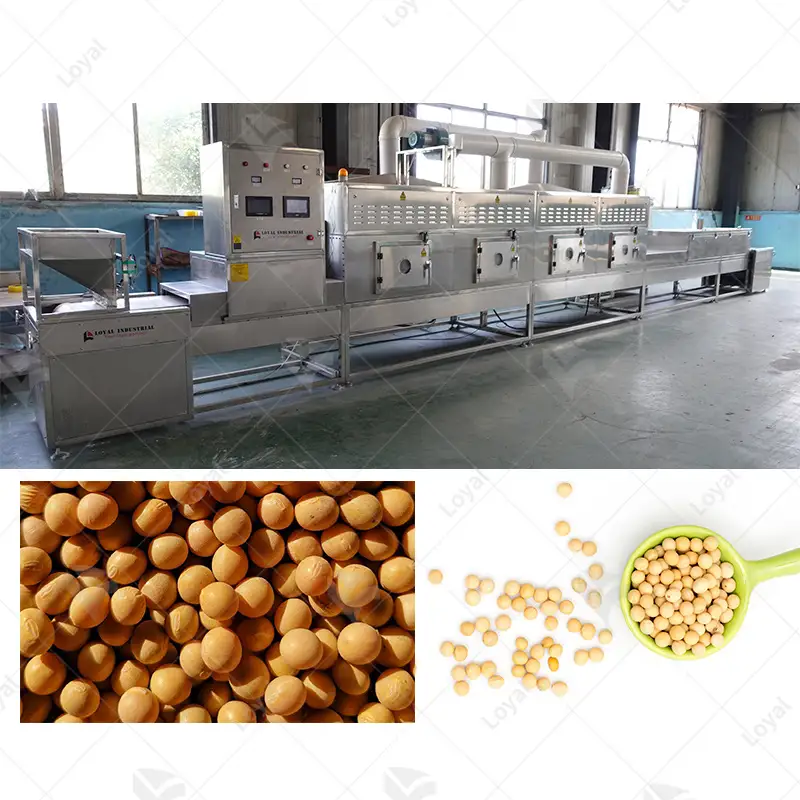
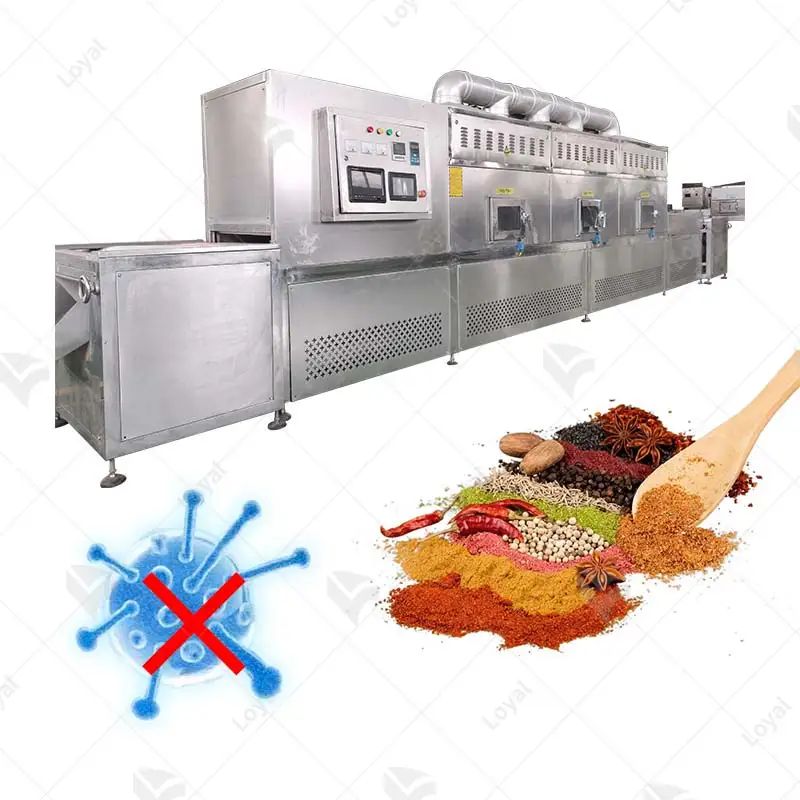
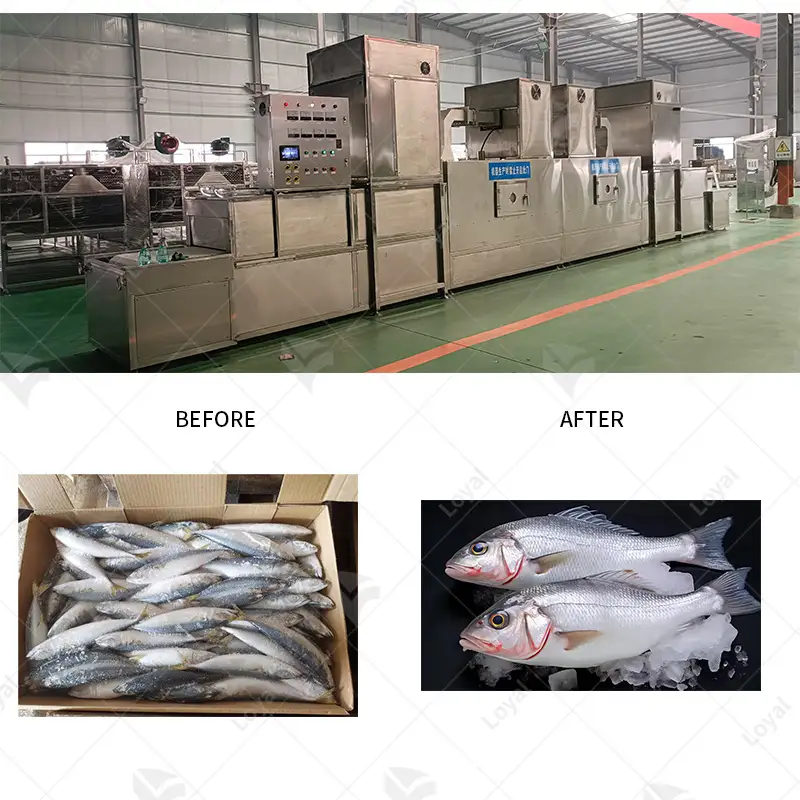
What Are the Applications of Sterilization Machines in Food Processing?

Food processing relies on using sterile machines to make food safe for long periods. Such devices may be used to pasteurize liquids like juices or milk, thereby preserving taste characteristics and all nutrients contained therein. Canning also utilizes this equipment by sealing containers, thus eliminating pathogens or spoilage organisms and extending shelf life. Another application involves sanitizing surfaces, tools, or equipment within food production areas where sanitation standards help ensure against cross-contamination among food products being prepared. Overall, such appliances improve food safety levels along with quality assurance measures required across different industries engaged in providing eatables around the globe.
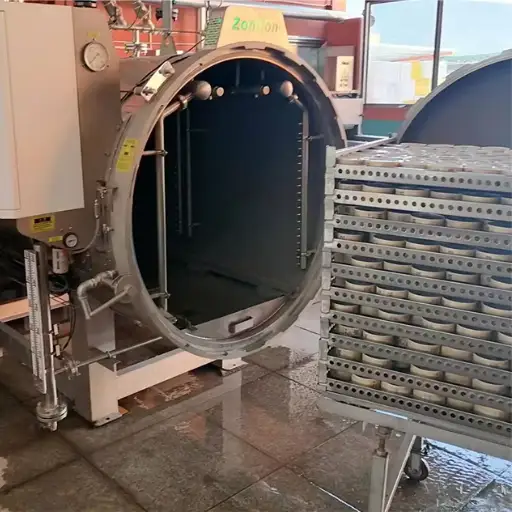
Using Retorts for Preserves and Ready Meals
In the food processing industry, a retort is a specialized pressure vessel for sterilizing jars, cans, and pouches of ready meals and preserves. In this case, steam or hot water at high pressure is used to destroy microorganisms and enzymes that could cause spoilage of food materials. This, in turn, ensures that those products’ nutritional values and flavors are maintained. By being efficient at what they do, retorts help manufacturers to produce large quantities within a short period of time, thereby meeting the high demands of consumers who want fast meal options while extending shelf life. Other advantages associated with retort packaging, including its lightweight, contribute towards reduced transportation costs, making it an environmentally friendly choice in foodstuff.
Food Autoclaves in Baby Food Processing
Food autoclaves are essential in manufacturing baby food, ensuring the product remains free from harmful microorganisms while maintaining its nutritional integrity. When filled with pressurized steam, these equipments are able to sterilize containers, including their contents, hence safeguarding infant nutrition safely. It’s worth mentioning that autoclaves ensure the safety of baby food by subjecting it to intensive processes, purporting its long-term preservation without spoilage, and extending its shelf life. More so, autoclaves assist in retaining essential nutrients, flavors, and textures necessary for developing taste preferences among children during the infancy stage. Manufacturers can, therefore, use autoclave technology to make safe quality baby foods that meet health standards, making parents feel secure about what their babies eat all day.
Batch Sterilization for Various Food Products
Batch sterilization is one way of ensuring the safety and long life of different types of foods. In this regard, a specific collection of food is subjected to a predetermined time during which it is exposed to controlled temperature and pressure levels. This ensures that harmful microorganisms are killed while maintaining food quality. The main areas where batch sterilization can be applied include canned vegetables, sauces, and dairy products.
This approach allows food processors to comply with safety guidelines and boost product longevity. Through accurate temperature and time management, lot sterilization helps lower nutrient degradation and maintains sensory properties like flavor feel and natural color. The method not only guarantees consumer protection but also minimizes wastage in the food sector, thus promoting sustainability activities in this industry.
How to Choose the Best Food Sterilization Equipment?

Several factors must be considered when choosing the best food sterilization equipment. The first one is examining your production process’s particular needs, including the types and volumes of foodstuffs you will be disinfecting. Also, check whether the technology supports your current systems so that there is no major disturbance during the machinery’s integration.
You should also go for machines with exact control temperature and pressure settings because they will maintain nutritional value and food quality. Besides, reliability and longevity are essential; purchasing superior quality materials and designs will prolong the equipment’s lifespan, reducing its maintenance cost. Moreover, it examines whether the product consumes energy efficiently and whether any safety measures installed can lead to long-term savings and compliance with health rules. Finally, see how other stakeholders in this sector rate various brands through user reviews or recommendations to enable you to choose which manufacturer to buy from.
Factors to Consider Before Purchase
Various factors affect efficiency and quality when selecting the food sterilization machines. Here are some key aspects to evaluate:
- Food Compatibility: Ensure that the equipment you use is suitable for the product you want to sterilize. Different products may require specific settings or steps.
- Capacity and Throughput: Consider demand to determine the volume of production required. Choose equipment with an appreciable throughput that will not be a processing bottleneck against your projected output.
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensuring the equipment conforms to industry regulations and safety standards; this is crucial in protecting consumer health and securing market access.
- Ease of Use and Maintenance: Choose user-friendly equipment that requires minimal maintenance, thereby helping you streamline operations and reduce downtime.
- Customer Support and Warranty: The companies to be considered should offer good customer support services and warranties so that help can be easily obtained if mechanical breakdowns or technical hitches occur.
- Cost of Ownership: When analyzing the total cost of ownership, other costs such as energy consumption, routine maintenance, and parts replacement over time should be considered in addition to the initial purchase price.
Through these considerations, one can make an informed decision aligned with one’s production objectives while considering sustainability issues.
Top Brands and Models in the Market
When searching for the best food sterilization equipment, a few well-known brands come to mind because of their reliability and advanced technology. Below are three top brands to consider:
- Hobart: Hobart is famous for its high-class food processing and sterilizing devices, such as the HCS series, which offers flexible sterilizing options for different types of foods, thus maintaining efficiency while ensuring conformity to safety regulations.
- Tetra Pak: As a leading player in food processing technology, Tetra Pak offers an innovative line of aseptic processing systems, such as its Tetra Therm® systems, which are suitable for large-volume production and are known for their energy-saving properties and ease of use.
- Steris: Specialising in sterilization and infection prevention solutions, Steris provides robust systems like the Reliance® 2, which is effective for various applications. Their equipment enjoys a good reputation due to its dependability, sophisticated monitoring functions, and user-friendly interfaces.
Examining these brands will enable you to find equipment that will meet your operational needs while keeping in mind safety practices in food processing.
Reading Customer Reviews and User Feedback
Regarding food sterilization equipment, customer reviews and user feedback should be analyzed as they offer insights into how products perform under real-life conditions. Websites like Capterra, G2, or Trustpilot are important forums where customers can share their experiences with various brands and models.
- Capterra: This site presents detailed feedback from verified users about sterilization equipment. Prospective buyers can compare different product performances according to performance capacity, dependable characteristics, and ease of handling, among other factors. Many users comment about effectiveness during sterilization processes and other issues related to the quality of service delivery by different brands.
- G2: On G2, there is extensive user feedback, including pros and cons, on specific models. Users often mention whether certain machines seamlessly adopt themselves into existing workflow processes, the time-saving nature associated with such machines at work, overall effectiveness, and the return on investment.
- Trustpilot: Trustpilot is a customer satisfaction-focused platform that gathers reviews from different brands to give potential buyers a glimpse into what any brand might be like in terms of reputation and trust. The overall sentiment of reviews can point out similar problems or features that users enjoy, helping you make better choices.
By integrating information from these platforms, one can choose an ideal sterilization equipment based on the operational requirements.
What Does the Future Hold for the Food Sterilization Equipment Market?

The food sterilization equipment market will have a bright future, driven by technological advancements and increased food safety regulations. Innovative technology, such as automated sterilization processes and eco-friendly substitutes, is becoming more popular, demonstrating an increasing commitment to sustainability and efficiency. On the other hand, the need for efficient sterilization solutions may be reinforced by health-conscious consumers’ demand for high-quality, safe food products. Moreover, the growth of emerging markets and expansion of the food processing industry will lead to further developments in the market, making manufacturers need to develop more innovative technologies that conform to consumer needs.
Market Trends and Innovations
Recent research on leading industry websites shows several key trends and innovations that determine the course of development in the global food sterilization equipment market.
- Digital transformation: Websites like FoodProcessing.com promote digital integration into sterilization processes, showing several real-time monitoring tools used for data collection purposes. This change increases not only work efficiency but also compliance with strict safety standards.
- Green practices: Articles from PackagingStrategies.com reveal growing efforts concerning environmentally friendly packaging methods, such as using steam or chemical-free processes. These techniques not only minimize harm to nature but also appeal to an increasingly larger group of consumers who consider environmental issues essential.
- Advanced Automation: According to the Food Industry Association’s findings, there has been a rise in automation within sterilization machines today. The reason behind this trend is maintaining quality control uniformly through reduced labor expense rates while scaling up production with no human interference.
Taken together, these trends suggest a dynamic marketplace where technologies and consumer preferences are closely interlinked, enabling future advances in food sterilization.
Growth Opportunities in Various Regions
Significant industry websites have noted that the food sterilization equipment market has potential for growth in different regions.
- North America: This part of the world looks set to emerge as a vibrant center characterized by strict rules about food hygiene and an increase in the number of people consuming processed foods. A detailed report on FoodProcessing.com points out that the continuous development of technology and focus on digital transformation have been boosting this market.
- Europe: According to articles posted on PackagingStrategies.com, Europe is starting to embrace sustainability in its production practices, with an emphasis on eco-friendly sterilization methods. This has not only been necessitated by European Union regulations but also meets the consumer’s demand for sustainable development.
- Asia-Pacific: According to insights from The Food Industry Association, the Asia-Pacific region will soon experience remarkable expansion because of factors such as rapid urbanization, increased disposable income, and changes in eating habits. Consequently, there has been a rising demand for sophisticated automation systems used in the sterilization process, indicating a promising future for those involved in this region.
In conclusion, these findings indicate that global firms should invest in technologies and adapt their strategies to continuously align with shifts in consumers’ choices if they want to take advantage of these opportunities offered within the global food sterilization equipment market.
Forecast for Commercial and Industrial Use
The commercial and industrial sectors’ forecasts indicate a continuous upward movement for such products as everyone now wants more secure food products and better technology. Furthermore, according to ResearchAndMarkets.com’s forecast, it is anticipated that this market could grow at a CAGR of over 7% over the next five years, which indicates automation is growing more extensive over time. Simultaneously, another news article published by FoodProcessing.com suggests that manufacturers are coming up with complex sterilizing machines, including high-pressure processing (HPP), which extends shelf life while retaining quality among other applications like microwave-assisted thermal sterilization (MATS). A recent study from Grand View Research further demonstrates the growing trend among food manufacturers to adopt sustainable practices, fueling demand for eco-friendly sterilization technologies. All in all, these findings project the sturdy growth of the industry, which is driven by innovation and a focus on safety and sustainability.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What are the main applications of an autoclave steam sterilizer in the food industry?
A: The primary applications of an autoclave steam sterilizer in the food industry include eliminating microorganisms in food and preserving perishable items. These machines sterilize food and packaging materials, ensuring products are safe for consumption and have an extended shelf life.
Q: How does a food sterilization machine help maximize efficiency in production lines?
A: Food sterilization machines, such as the autoclave steam sterilizer, help maximize efficiency by streamlining the sterilization process. This reduces the need for manual intervention, ensures consistent sterilization, and accelerates the production line, thereby increasing productivity and operational efficiency.
Q: What is the difference between a benchtop autoclave and larger retort sterilizers?
A: Benchtop autoclaves are smaller units designed for laboratory or small-scale use, ideal for research and development (R&D) purposes. In contrast, larger retort sterilizers, capable of sterilizing large quantities of food and packaging simultaneously, are used in industrial settings to handle bulk processing for food processing manufacturers.
Q: Why is the demand for food sterilization equipment on the rise?
A: The demand for food sterilization equipment is increasing due to heightened awareness of food safety standards, the need to eliminate all viable microorganisms, and the growing market for processed and packaged foods. Consumers and regulatory bodies are placing more emphasis on food hygiene, driving the adoption of sterilization solutions.
Q: How do companies like Allpax and JBT Corporation fit into the food sterilization segment?
A: Companies like Allpax and JBT Corporation are significant players in the food sterilization segment, providing advanced sterilization equipment and technology solutions. They offer a range of products designed to meet the stringent requirements of food safety and production efficiency, catering to various sizes and types of food processing operations.
Q: What role does a steam sterilizer play in eliminating microorganisms in food?
A: A steam sterilizer uses high-pressure steam to eliminate all viable microorganisms in food. This process effectively destroys bacteria, viruses, spores, and other harmful pathogens, ensuring that the food products are safe for consumption and have a longer shelf life.
Q: Where can you buy a wholesale food sterilization machine?
A: You can buy a wholesale food sterilization machine from online platforms such as alibaba.com. These sites offer a range of options from different manufacturers and suppliers, allowing buyers to find the sterilization equipment that best suits their needs and budget.
Q: What are some examples of devices sterilized by autoclaves other than food?
A: Besides food, autoclaves are used to sterilize medical devices, laboratory instruments, and other tools requiring stringent sterilization. This helps prevent contamination and ensures the safety and reliability of these devices, whether used in healthcare, research, or industrial settings.
Q: How does the use of tray arrangements improve the efficiency of autoclave steam sterilizers?
A: Using tray arrangements in autoclave steam sterilizers improves efficiency by allowing better organization and maximizing the space within the sterilizer. This ensures even steam distribution, reduces cycle time, and enhances the overall throughput of the sterilization process.
Q: How important is it to stay informed about advances in food sterilization technology?
A: Staying informed about advances in food sterilization technology is critical for maintaining competitive advantage and complying with regulatory standards. Ongoing innovation, driven by companies like Steriflow and Terra food-tech®, brings more efficient, reliable, and cost-effective solutions to food sterilization, ensuring healthier food production and improved operational efficiency.