The last few years have seen a surge in interest in black soldier fly (BSF) larvae due to their incredible nutritional content and the possibility of using them as a sustainable protein source for animal and fish food. With an increasing need for alternative proteins, it is important to know how to properly dry the BSF larvae so that they can be stored and transported easily and their shelf life extended by reducing humidity levels within them. This paper discusses different methods used in drying BSF larvae, highlighting the advantages and disadvantages of each technique employed in this process. The article will help readers understand these practices better, thus enabling us to optimize such resources, leading to more sustainable food systems.
What are the Benefits of Using Black Soldier Fly Larvae?

Image source: https://www.pinterest.com/
There are many important benefits to using black soldier fly larvae in various industries. For starters, they contain an abundance of protein and essential amino acids, making them ideal feed for livestock, poultry, and aquaculture. Secondly, these insects can convert organic waste into high-quality protein, efficiently reducing waste and promoting environmental sustainability. BSF larvae also supply good fats, vitamins, and minerals that can boost animal health and growth. Moreover, compared with traditional animal protein sources such as beef or chicken eggs, their farming requires less land space plus water usage, hence creating more sustainable alternatives within food production systems.
Why are BSF Larvae a Sustainable Source of Protein?
The black soldier fly (BSF) larvae are seen as a sustainable protein source for various reasons. First, they can efficiently convert organic waste materials like food scraps and agricultural by-products into high-quality protein, thus reducing waste going to landfills. This process not only reduces environmental impact but also encourages a circular economy. Second, BSF larvae have lower carbon footprints than conventional livestock because their raising takes much less land and water, which makes them suitable for resource-constrained areas. In addition, their fast growth cycle and high feed conversion efficiency make them more attractive as a protein source. Altogether, these reasons give hope that BSF larvae can be used in global food security efforts while supporting sustainable agriculture practices.
How is the Nutritional Value of BSF Larvae Beneficial to Animal Feed?
Black soldier fly larvae (BSF) have a nutritional profile that benefits animal feed. These larvae are rich in protein, containing 40-45% crude protein necessary for the growth and development of livestock and aquaculture species. BSF larvae also have high levels of essential amino acids, thus providing a complete protein supply that can improve animals’ overall welfare and productivity. Their fat content comprises about 30% lipids, so they contain valuable fatty acids that boost energy and make feeds more palatable. What’s more, vitamins and minerals found in BSF larvae enhance immunity and other health benefits in pets, making them ideal components for different types of pet food formulations. Studies show livestock fed with black soldier flies grow faster while consuming less feed, resulting in sustainable animal farming practices.
What is the Role of BSF Larvae in Food Waste Management?
The black soldier fly (BSF) larvae are a critical component in managing food waste through organic waste conversion. They can eat many different organic materials, such as fruits and vegetables, that are unfit for human consumption. Therefore, this decreases landfill waste and reduces greenhouse gas emissions linked to decomposition. In breaking down food waste, BSF larvae turn it into valuable biomass, which can be used as animal feed or organic fertilizer. These insects help create a sustainable circular economy by converting food scraps into protein-rich larvae and nutrient-dense soil improvers while tackling agricultural resource recovery and modern waste management problems. Additionally, their rapid lifecycle and prolific reproduction make them an affordable option for companies and local governments wanting to improve their trash disposal methods.
How Do You Prepare Black Soldier Fly Larvae for Drying?

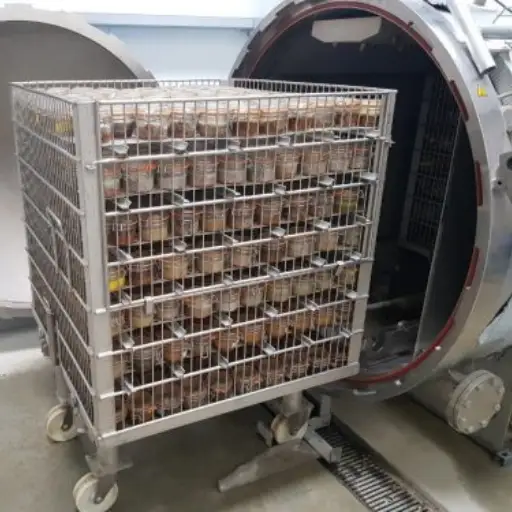
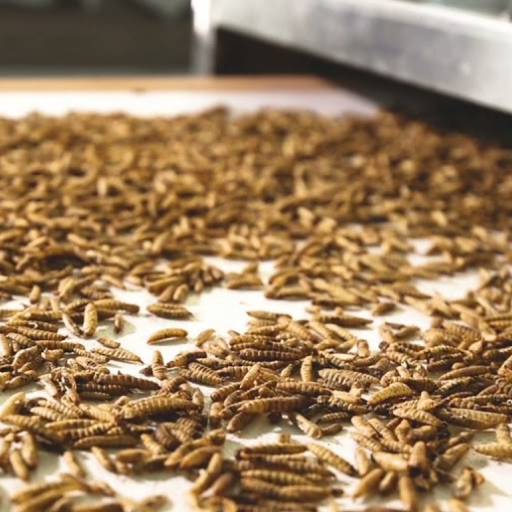
To ensure quality and safety, there are several key steps to follow when preparing black soldier fly larvae for drying. The first step is to harvest the larvae at the right growth stage, which is normally just before they enter their prepupal stage so that you can get maximum fat content. Then, rinse harvested larvae thoroughly to remove contaminants or residual substrate. Following this, blanching with boiling water should take place for a few minutes, as this helps kill pathogens while preserving the color and texture of the insects. After draining them, spread them evenly on trays used for drying purposes, then use either a dehydrator or an oven set at low temperatures until all moisture has been obliterated from the product. For storage purposes, keep dried ones in airtight containers to maintain freshness and prevent spoilage.
What Steps Are Involved in Cleaning BSF Larvae?
Cleaning black soldier fly (BSF) larvae is vital in ensuring their safety and readiness for use. Here are the key steps for cleaning BSF larvae:
- Harvesting: Gently collect the larvae, not harming their bodies.
- Rinsing: To cleanse the harvested larvae, place them in a colander or sieve and wash them thoroughly under running water. This removes debris, waste material, and residue from their substrate.
- Soaking: For an extra cleaning step, soak rinsed larvae in saline solution (salt water) for about 10-15 minutes. This may help eliminate remaining contaminants.
- Final Rinse: After soaking, perform one last rinse under fresh running water to remove any salt and ensure the larvae are clean.
- Drain: Before blanching or drying, let the cleaned larvae drain in the colander for several minutes.
By following these instructions, you will have clean, safe Black Soldier Fly Larvae that can be used later or prepared immediately.
Do You Need to Use an Acid Solution Before Hot-Air Drying?
Using an acid solution before hot-air drying isn’t strictly necessary, but it does improve the preservation of some food items. Acid solutions such as lemon juice or vinegar can prevent browning and promote quality enhancement; however, this practice is more common with fruits/vegetables than with protein sources like black soldier flies (BSFs). When dealing with BSFs, the focus should be placed on proper washing procedures because they are sufficient enough to guarantee safety while maintaining quality standards during storage/drying processes after blanching has been done already. Whether you want to use an acid depends solely on your objectives regarding dried products made from BSFs as well as personal preference during cooking times involving different types of dry snacks containing high protein content obtained from these insects grown commercially around the world today where legal regulations permit such activities without any restrictions whatsoever!
What equipment is required to Prepare BSF Larvae?
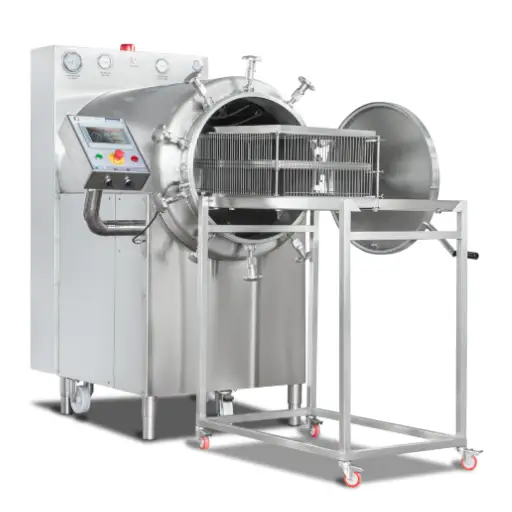
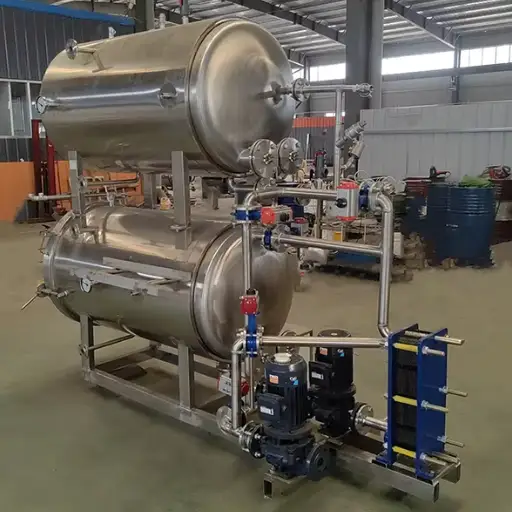
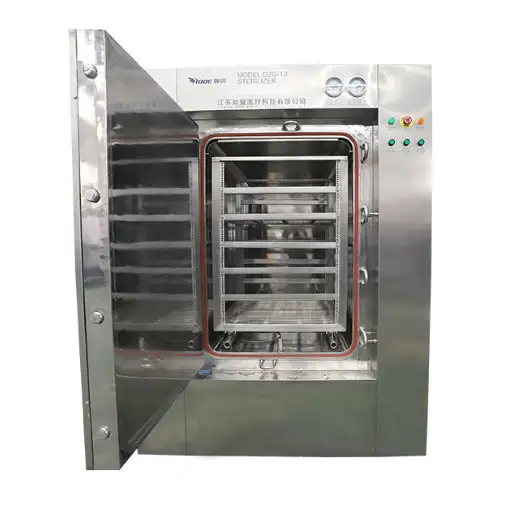
If you want to prepare black soldier fly (BSF) larvae properly, certain pieces of equipment will make the process easier. First, you’ll need a colander to wash and drain the larvae after cleaning them. To ensure safety, you should also have a big pot or boiler for blanching the larvae in hot water. Use a thermometer to check whether your water has reached its ideal temperature during blanching. It is best to use a dehydrator or hot-air drying machine for drying purposes as these devices provide controlled heat and airflow, effectively removing moisture from the product. Lastly, storage containers are necessary for keeping dried larvae fresh until they are used.
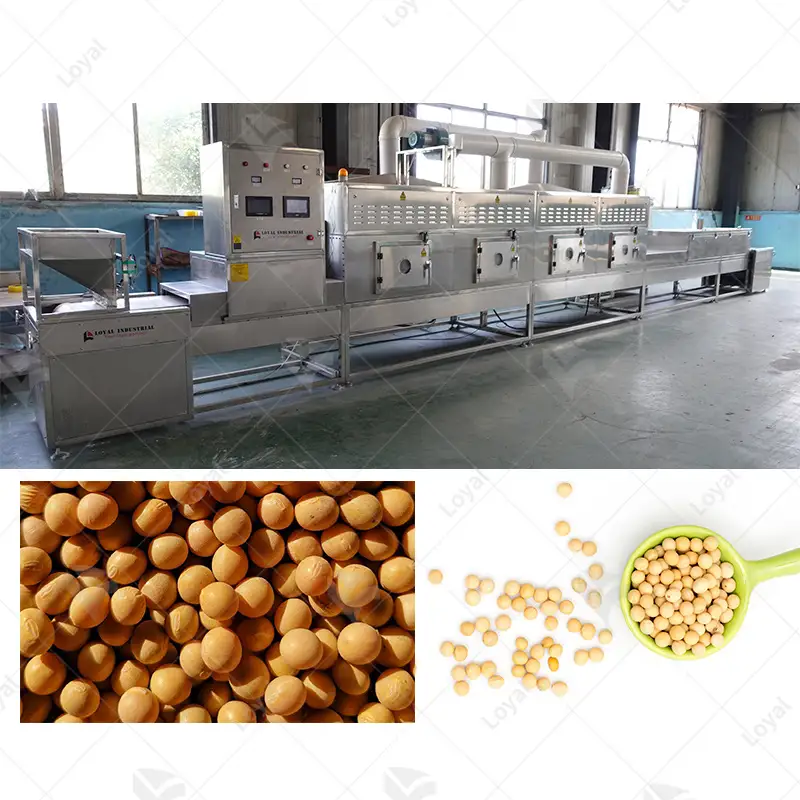
What are Different Methods for Drying Black Soldier Fly Larvae?

There are many ways of drying black soldier fly (BSF) larvae, depending on available equipment and the desired end product. Each method has its own advantages.
- Hot-Air Drying: This method utilizes either dehydrators or ovens, where heated air is circulated around the larvae, causing evaporation of moisture content within them. It is efficient while allowing for maintaining quality by controlling temperature accurately.
- Sun Drying: In warmer regions where there’s plenty of sunshine throughout the year, this traditional approach involves spreading cleaned insects out under direct sunlight exposure so as to dry them up at lower energy costs, but it may take longer since it needs consistent sunny weather conditions
- Freeze Drying: This technique uses specialized equipment because freezing the larva followed by reducing surrounding pressure allows ice particles change directly from solid state into vapor without passing through the liquid stage, thus retaining more nutrients compared to other methods though expensive due
- Microwave Drying: Small quantities can be dried using microwaves, as this method uses microwave energy to remove moisture quickly. However, uneven cooking/drying may occur if not carefully monitored, making it less ideal for large batches.
Choosing one over another usually depends on balancing efficiency against preservation quality and what resources are available.
How Does Microwave Drying Work for BSF Larvae?
Microwaves produce heat from the inside out to dry black soldier fly larvae, which drives moisture away. The process starts by uniformly placing the cleaned larvae into a microwave-safe container and ensuring equal exposure. Water molecules within the larvae absorb this energy as microwaves pass through them before rapidly converting it into steam that escapes, thereby achieving effective drying results. One of its main advantages is speed since drying time can be drastically reduced through microwave use compared to conventional methods. However, it is important to monitor very closely so as not to cause overheating or uneven drying that may affect the quality and nutritional value of the insects. Moreover, due to size limitations associated with standard microwaves, such a method might be best suited for smaller batches.
What are the Advantages of Hot-Air Drying for Larvae?
The hot-air drying technique for processing larvae, especially black soldier fly (BSF) larvae, has several advantages. Firstly, this method allows large volumes to be dried at once and is thus very efficient in commercial settings. Secondly, because hot-air drying works at controlled temperatures, it reduces the risk of overheating, which can affect the nutritional value of these insects. Furthermore, compared to freeze drying, this process is less complicated and requires fewer specialized tools, making it easier for small-scale farmers to use. Last but most importantly, moist content is effectively removed by hot air drying, therefore improving shelf life and storage stability, which are necessary in different ways when using them over an extended period.
Can You Use Solar Drying Methods for BSF Larvae?
Indeed, black soldier fly (BSF) larvae can be effectively dried using solar methods. This technique is environmentally friendly and low-cost because it uses the sun to dry the larvae. Leading experts cite that regions with lots of sunshine benefit most from solar drying since it lowers energy costs significantly, which would have been used in conventional drying methods. In addition, designing solar dryers to maintain controlled temperatures helps keep the nutritional quality of the larvae intact. Nevertheless, some limitations should be considered; these include being weather-dependent and needing proper ventilation to avoid mold formation. When done right, BSF larvae processing can use this method sustainably while encouraging sustainable practices in society.
What are the Effects of Different Drying Methods on Black Soldier Fly Larvae?

Different drying techniques may significantly affect the nutritional quality, texture, and shelf life of black soldier fly (BSF) larvae. Freeze drying is a conventional method that preserves most of the nutrients in larvae and produces light, crispy textures for high-quality applications. On the other hand, higher temperatures during hot air drying can degrade some nutrients; however, this process efficiently reduces moisture levels, improving shelf-life. Environmental conditions make solar drying variable from one region to another, but when done correctly, it can still be cost-effective while maintaining reasonable nutrition profiles. In summary, selecting a drying technique must correspond with what you want to use these bugs for and their desired characteristics after being processed into food products.
How Does the Drying Process Impact Nutritional Value?
The drying process can greatly affect the nutritional value of black soldier fly (BSF) larvae. Different methods of drying can result in varying levels of nutrient retention. Research shows that freeze drying usually retains more proteins and essential fatty acids than any other method because it uses low temperatures, which do not cause thermal degradation. Conversely, hot-air drying may destroy specific vitamins and amino acids due to prolonged exposure to high temperatures. Solar drying is inexpensive and energy efficient but may lead to inconsistent nutritional retention based on environmental factors like temperature or humidity. Thus, choosing a suitable drying technique becomes important for maximizing the nutrient profile content in BSF larvae.
What is the Effect of Drying on Digestibility?
Drying methods can significantly influence the digestibility of black soldier fly (BSF) larvae. Research shows that different drying techniques can increase or decrease digestibility depending on how they modify the structure of BSF larvae. For instance, freeze-drying usually preserves proteins and other nutrients, thus enhancing their absorption in the gut. On the flip side, hot-air drying might cause protein denaturation, which makes it more challenging for digestive enzymes to act upon these molecules. The efficacy of solar drying varies with its specific conditions; if temperatures are not consistent throughout the process, this will either protect or destroy BSF digestibility. Therefore, when selecting a drying method, it is important to consider what will result in maximum BDF suitability for use as feed in animal or fish farming systems.
How Do Different Methods Affect the Utilization of Black Soldier Fly Larvae?
The nutritional value of black soldier fly (BSF) larvae is greatly affected by how they are processed. By retaining more essential amino acids and fats, freeze-drying maintains the nutritional profile, ensuring better feed quality for livestock. On the other hand, hot-air drying can destroy heat-sensitive nutrients, leading to poor larvae’s feeding efficiency. Moreover, anaerobic digestion used on BSF larvae gives them a better nutrient profile due to microbial fermentation, making it easy for animals’ health to benefit from their consumption. Suitable drying and processing methods must be used to maximize the culinary potential and efficacy of BSF larvae in feed applications.
Best Practices for Using Dried Black Soldier Fly Larvae in Poultry Feed

Several guidelines must be followed to get the best results from dried black soldier fly larvae (BSF) in poultry feed. The first is to have a correct incorporation rate, which usually ranges between 5% and 20%. This will depend on the specific nutritional needs of the poultry. The second point concerns monitoring the quality of larvae. You need to ensure that they are not contaminated and dried using methods such as freeze drying that preserve their nutrients. It’s also important to gradually introduce these into diets to allow a smooth transition while observing birds’ acceptance and general health status. Lastly, consider conducting periodic nutritional analysis for evaluation; this will help you determine if any adjustments should be made based on growth performance or egg production rates.
How can we efficiently incorporate dried BSF Larvae into poultry feed?
Nutritional experts recommend determining the optimal inclusion rate, which usually ranges from 5% to 15% of the overall diet based on birds’ specific ages and production stages. The second strategy is to introduce it gradually so that it can acclimatize the poultry gradually, starting with a small percentage of total feed and increasing it over time to avoid digestive problems. Also, there is a need to combine BSF larvae with other dietary components whose nutrient profiles complement each other, thus ensuring a balanced diet. Finally, continuous monitoring should be done on health and performance indicators among birds kept under these conditions, just as needed when assessing their inclusion efficacy or making necessary adjustments toward meeting flock nutritional requirements.
What are the Recommended Proportions for Mixing Dried Larvae in Feed?
The ideal ratio for incorporating dried black soldier fly (BSF) larvae into poultry feed is generally determined by the birds’ specific dietary requirements.
- Growing pullets can be fed about 10% of total feed, ensuring they get enough protein and energy needed for growth.
- It is advised to use between 5% and 15% on average, but this may vary with poultry age, breed, or production stage.
- Experts recommend beginning at around five percent and gradually increasing it to fifteen percent as the birds become accustomed, allowing better digestion and nutrient absorption.
These proportions must be tailored to meet individual flock needs and continually monitored to ensure optimal health results.
What are the Observed Benefits of Using Dried BSF Larvae in Poultry Farming?
Poultry farming has seen the introduction of dried black soldier fly larvae, which come with many benefits.
- Better Nutrition: Dried BSF larvae are rich in necessary amino acids, proteins, and good fats, greatly enhancing the nutritional value of poultry feed. Including these feeds helps chickens meet their protein requirements, thus improving growth rates, egg production, and general health among flocks.
- Cost Effectiveness: Protein sources like BSF larvae can help lower feeding costs since they can be produced sustainably and efficiently. They add economic value because they can convert organic waste into quality, high-protein products, leading to a more sustainable poultry farming model.
- Environmental Impact: Waste management is supported by using BSF larvae to recycle organic wastes that would otherwise pollute the environment. Such practices reduce carbon footprints from poultry farms and conform to sustainable agriculture standards.
The practicalities and sustainability of using dried BSF larvae for chicken farming should make it an option for all bird producers.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What are the main methods for drying Black Soldier Fly Larvae (BSFL)?
A: The main methods for drying BSFL include hot air, freeze, and microwave drying. Each method has unique benefits in terms of nutrient retention and processing efficiency.
Q: How does the hot air drying method work for BSFL?
A: The hot air drying method involves placing BSFL in a drying chamber where heated air circulates to remove moisture content. This method is effective and widely used due to its simplicity and relatively low cost.
Q: What are the benefits of using BSFL as a feed ingredient in aquaculture?
A: BSFLs are highly nutritious, rich in protein and fat, and have been shown to enhance growth rates and nutrient utilization in aquaculture species. They serve as a sustainable and efficient alternative to traditional feed ingredients.
Q: How does freeze-drying affect the nutrient composition of BSFL compared with other methods?
A: Freeze drying preserves the nutrient content, including crucial vitamins and proteins, more effectively than hot air drying or microwave drying. This method retains higher levels of crude protein and other essential nutrients.
Q: What impacts do different drying methods have on the effects of drying methods on nutrient digestibility of BSFL?
A: Drying methods substantially influence the nutrient digestibility of BSFL. Studies based on in vitro assays have shown that freeze-dried larvae often maintain higher nutrient digestibility than hot-air or microwave-dried larvae.
Q: Why is BSFL considered a valuable feed ingredient?
A: BSFL, or Hermetia Illucens, provides high crude protein and essential fats, making it an excellent feed ingredient. It also contributes to enhanced growth rates and nutrient utilization of animals, making it highly valued in animal science.
Q: How does drying time affect the quality of BSFL meals?
A: Prolonged drying time generally lowers moisture content, which can preserve the larvae better and enhance storage life. However, excessive drying can degrade some nutrients, potentially reducing the feed quality of the black soldier fly larva meals.
Q: How does the moisture content of BSFL affect their use as feed?
A: The moisture content is crucial for both black soldiers’ storage stability and nutrient utilization. Lower moisture levels typically prevent microbial growth and spoilage, making the feed safer and more effective.
Q: What are the advantages of using a citric acid solution before hot-air drying of BSFL?
A: Treating BSFL with a citric acid solution before hot-air drying can help preserve nutrients and reduce microbial contamination. This pre-treatment method can also improve the overall quality and safety of the dried product.
Q: How does BSFL compare with mealworm in terms of use as a feed ingredient?
A: Both BSFL and mealworms are excellent feed ingredients high in protein and fat. However, BSFLs, particularly Hermetia Illucens L., are often more sustainable and more accessible to produce on a mass scale, making them a more efficient alternative.