A critical role of these machines is to ensure the safety and preservation of food and act as a vital defense against various micro-organisms that cause food spoiling or infections like those related to foodborne diseases. In this final manual, we shall look into multiple types of food sterilization machines, how they work, and the primary considerations while choosing the suitable machine for you. This article will provide you with ideas on selecting a suitable sterilization method for your food if you work in the food industry or are just someone who likes cooking at home so that you can decide which one is most suitable for your requirements. Our journey starts by venturing into a realm of eating security devices made to safeguard our daily meals.
How does a sterilization machine work?

Image source: https://reads.alibaba.com/
Sterilizing machines employ different operational techniques to eliminate or deactivate dangerous microorganisms living in foods. Some standard methods include heating, where bacteria and spoilage organisms are killed through high temperatures, and chemicals could be utilized, such as hydrogen peroxide or ozone, to disrupt microbial cell function during chemical sterilization. Radiation may also be used by other tools like ultraviolet light to target and kill pathogens within them. Several factors, including temperature, exposure time, and type of microorganism, determine the efficiency of these machines so that after treatment, food remains healthy and fine.
Understanding the sterilization process
Food sterilization has several stages that make it possible to be effectively treated and made safe. Initially, the foods are made ready for sterilization, which may entail cleaning and sorting out any contaminants. Once prepared, the sterilization machine applies one proven method—heat, chemical, or radiation—to kill the harmful microorganisms. After this treatment, most food products are either cooled down or packaged under sterile conditions to avoid chances of recontamination. Finally, we can determine how effective sterilization has been through testing for pathogen reduction, ensuring food safety and quality preservation. This systematic approach protects public health and lengthens product shelf life.
Critical components of a sterilization machine
The sterilization systems are composed of these parts:
- Heating Element: In heat sterilizers, a heating element helps generate high temperatures required to kill dangerous microorganisms.
- Control System: This regulates temperature, exposure time, and the way of eliminating harmful bacteria so that it functions accurately and according to safety rules.
- Chamber: The area at which food products are placed for treatment is called a sterilizing chamber. It is designed to withstand high pressures and temperatures while preventing contamination during the process.
- Circulation Fan: Some machines have a circulation fan that ensures equal distribution of heat or other agents used to intensify effectivity throughout their chambers.
- Cooling System: After being made sterile by an autoclave, rapid cooling keeps their temperature low, thus maintaining their quality and not giving them any chance to get polluted again.
These components act together as a reliable and efficient means of killing germs, leading to better public health and longer use dates for foodstuffs.
The role of high temperature and high-pressure
In sterilization, high temperature and high pressure kill bacteria, viruses, or other germs that may make food unhealthy. Microbial destruction is obtained when proteins are denatured by applying high temperatures, which leads to cell dysfunction in the microorganism. Specifically, pressure steam sterilization requires a temperature beyond 121oC (250°F) to make the heat more effective. In this way, food products can be heated evenly because the substances that facilitate heating move in quickly due to increased pressure. Together, both factors enable sterility to be reached, preserve nutrients, and extend shelf life, thus making it a fundamental part of food processing and safety protocols.
What types of food sterilization machines are available?

Some types of food sterilization machines have been developed, each designed for specific operations. The primary examples include;
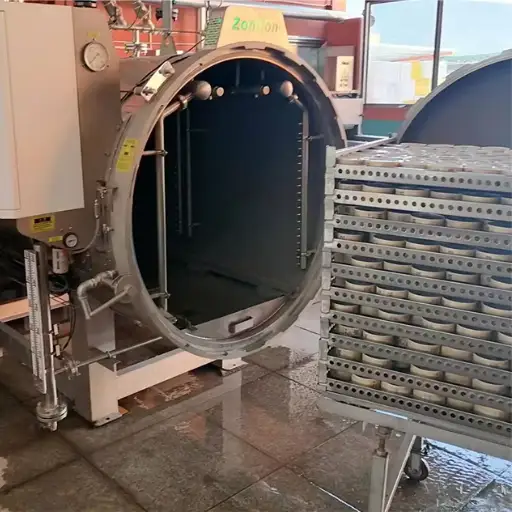
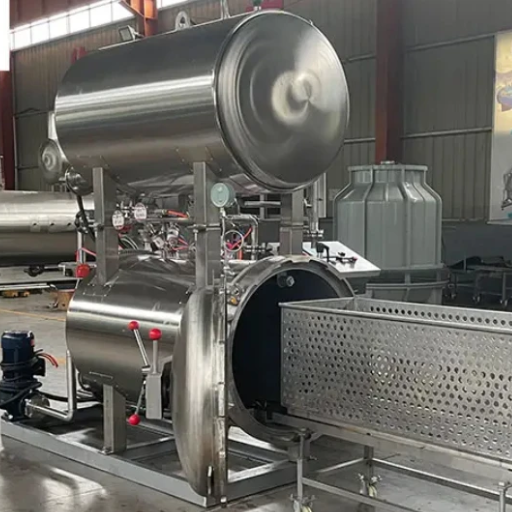
- Autoclaves: These are sterilizing units that use steam under pressure to eliminate harmful microorganisms while conserving food quality.
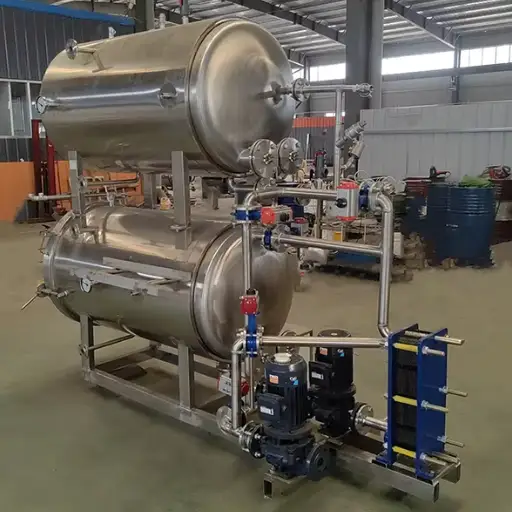
- Retorts: They rely on both heat and pressure to achieve total sterilization for extended storage life, mostly in canned foods.
- Pasteurizers: This type of equipment usually heats liquid products to a certain temperature at a predetermined time period to minimize the microbial load without changing flavor or content.
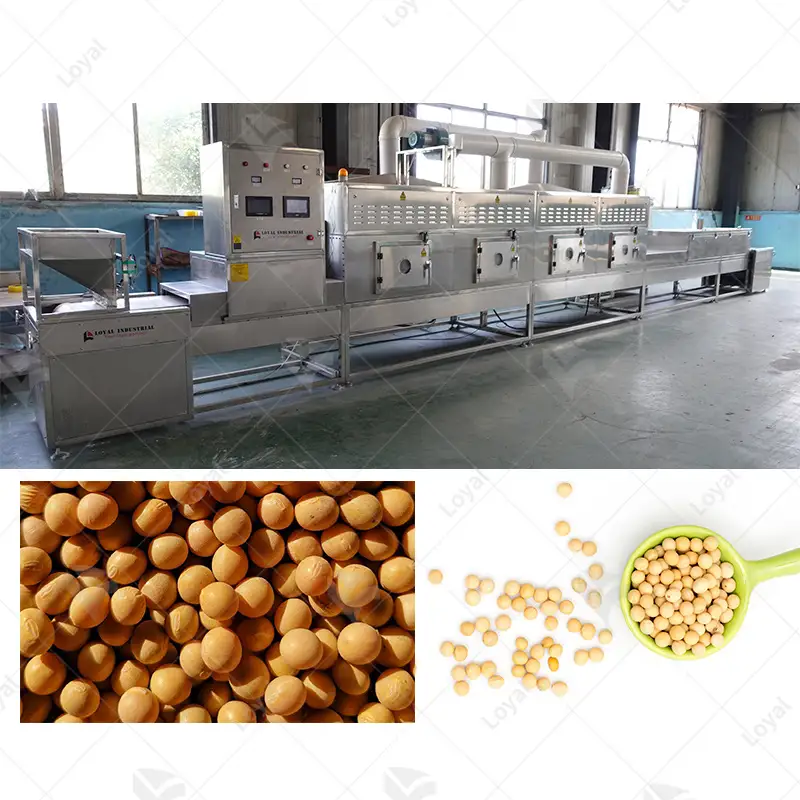
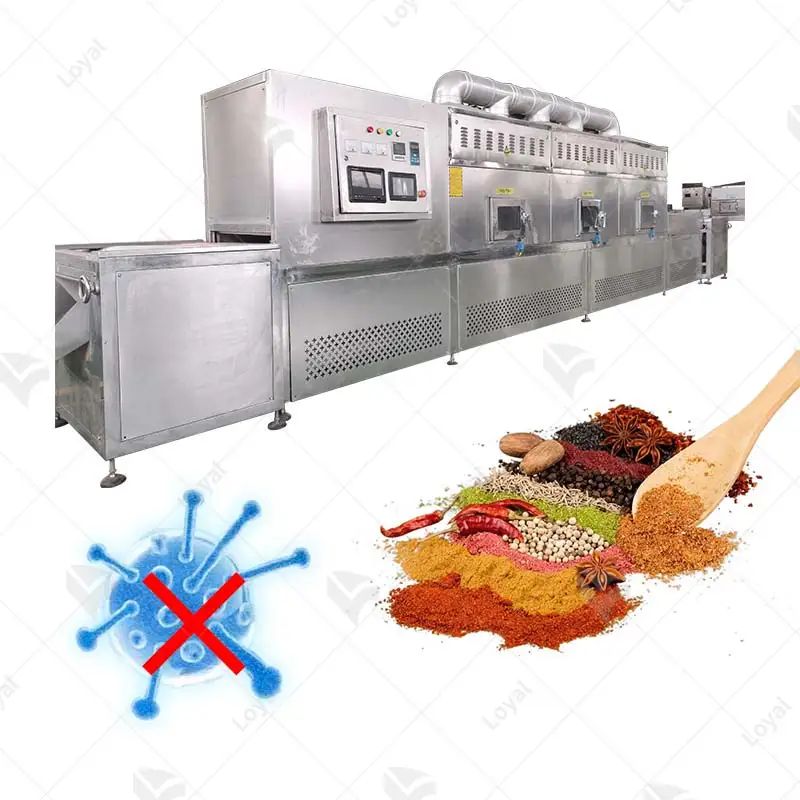
- Microwave Sterilizers: These machines employ microwave energy to swiftly heat food during sterilization, consuming less energy and reducing processing durations.
- Chemical Sterilizers: Unlike the above-mentioned methods, some machines use chemicals like hydrogen peroxide or ozone, which makes them suitable for low-temperature treatments of such products.
Each machine’s design aims to safeguard health while ensuring good nutrient preservation and excellence.
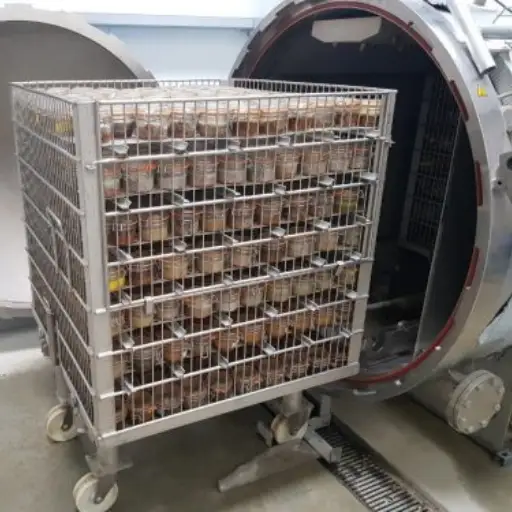
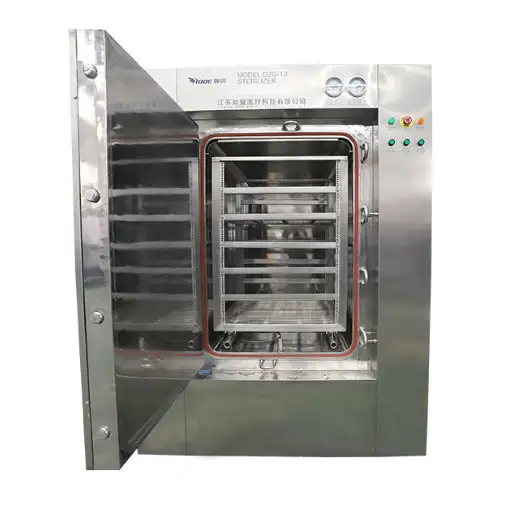
Overview of autoclave sterilizer
Food processing requires autoclaves to sterilize products and extend their shelf life. On the principle of steam under pressure, they create conditions in which temperatures exceed boiling point, effectively killing bacteria, yeasts, and molds. In this way, foods are put into a sealed chamber, and afterward, steam is added, which increases the temperature for a given period. This ensures that there is no room for any kind of bacterial contamination other than maintaining food quality and nutrition content. Autoclaves are preferred in many manufacturing sectors because they are dependable, efficient, and can handle several products, hence indispensable in food safety systems.
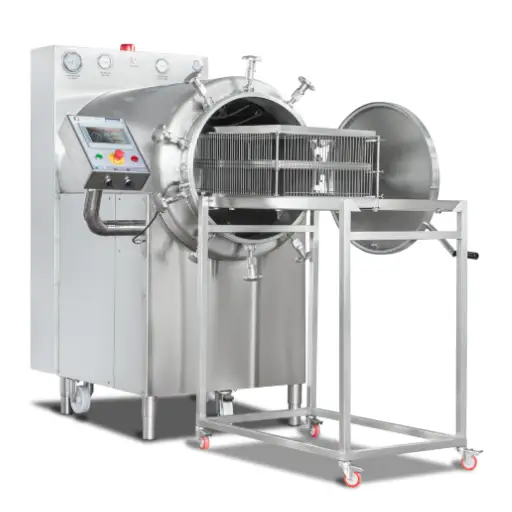
The benefits of a retort sterilizer
Retort sterilizers have many advantages when used for food processing, particularly in guaranteeing food safety and extending shelf life. First, they provide even heat distribution essential for proper sterilization thus reducing the risk of under-processing. Moreover, uniform heating maintains different food varieties’ palatability, consistency, and nutritional composition. Secondly, retort sterilizers come in adaptable designs since they accommodate various packaging materials or sizes and are suitable for diverse foods on market shelves. Additionally, large quantities can be processed quickly, enhancing productivity and lowering operational costs simultaneously. Lastly, recent retort technologies also feature sophisticated monitoring mechanisms to ensure compliance with safety standards, improving the final product’s quality assurance level.
New technologies: UV sterilization and pasteurization
The use of UV sterilization and pasteurization methods has been a recent important development in food safety. Both are vital for improving food safety and extending shelf life. Unlike heat, ultraviolet light used in UV sterilization gets rid of harmful microorganisms on food surfaces. It is a highly effective method for preserving the sensory qualities and nutritional value of foods because it doesn’t require heating processes.
Among fruits and vegetables, this technology is most beneficial to those who are sensitive to high temperatures.
On the other hand, heating food products at a given temperature within a specific time limit is an old traditional technique called pasteurization that remains relevant today. The process helps reduce the number of disease-causing microorganisms, ensuring the safety of dairy products and juices. Modern pasteurization techniques have introduced continuous flow systems, while others have adopted high-temperature short-time (HTST) strategies, all aimed at improving efficiency and maintaining food quality. This indicates a transformational shift in food processing that enhances both sustainability and safe production practices adopted.
Why is food sterilization important in the food industry?

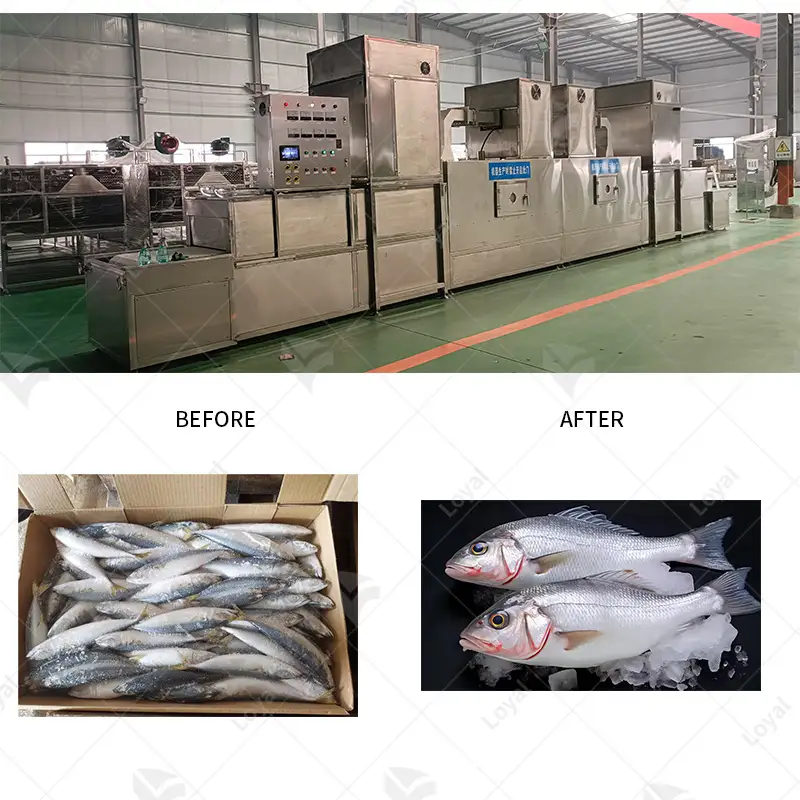
In the food industry, food sterilization is essential as it ensures the safety and longer life of foods by killing disease-causing microorganisms that can cause food poisoning. Sterilization upholds public trust in food safety and keeps consumers healthy by effectively reducing or killing pathogens such as bacteria, viruses, and fungi. Moreover, it helps reduce food losses by prolonging shelf-life, particularly considering that the world is grappling with achieving food security. In addition, sterile processing methods could lead to better quality and taste and enhance the product’s nutritional composition, thus matching consumer demands for safe and healthier choices.
Ensuring the safety and quality of canned food
Consumers’ health should be prioritized when dealing with canned foods. This process begins with choosing high-quality raw materials, followed by strict hygiene during preparation. Canning includes sealing food in containers that will not allow air inside them before exposing them to high temperatures that destroy germs responsible for diseases and spoilage (canned). Also important, therefore, is monitoring the canning process to ensure correct temperature and pressure settings are used (Pectin). Continuous quality checks and adherence to safety standards prevent contamination, ensuring that canned goods remain palatable and maintain their texture while still supplying enough nutrients, making them a reliable source of nourishment. Additionally, people should examine preserved products for bulging or other signs of spoilage before they consume them because this may indicate damaged packaging or the presence of harmful substances inside such cans.
Extending the shelf life of food products
Extending the shelf life of food products is crucial to minimize wastage and ensure food safety. Several approaches can be utilized to achieve this objective. Firstly, refrigeration and freezing are effective methods that can retard bacteria and enzyme deterioration. Additionally, vacuum sealing eradicates packaging air, significantly reducing oxidation and maintaining freshness. Thirdly, preservation methods such as canning, pickling, drying, etc., can help extend shelf life by restraining microbial growth. Furthermore, proper storage conditions like maintaining correct temperatures and humidity levels are essential in improving the longevity of foodstuffs. By following these guidelines, safekeeping of the item prevents spoilage while making sure it’s healthy over time.
Addressing microbial contamination in baby food and pet food
Contrasting baby foods and pet foods with microorganisms needs utmost attention because children and animals are more likely to suffer from illnesses caused by contaminated food. For example, during production, it is necessary to have a very stringent quality check approach, which includes conducting routine pathogenic examinations for bacteria such as Salmonella or Listeria spp, among others, at all times. To identify risks and act on them at every level of processing, manufacturers should follow GMP (Good Manufacturing Practices) and HACCP (Hazard Analysis Critical Control Points). Moreover, high-pressure processing and pasteurization could remove harmful bacteria without destroying nutritional value; therefore, they may be applied in practice. Consumers also need to check for expiry dates on products they buy before using them; when purchasing goods, one should ensure that packages are not broken or damaged; and lastly, keep things under temperature control to prevent disease transmission between goods that consumers acquire from market links before they enter households.
How do you choose the right food sterilization equipment?

There are a few things that should be taken into consideration when selecting the appropriate food sterilization equipment. One of these things is to assess the kind of foods you want to sterilize because different products may require specific methods such as steam, dry heat, or chemical processes for sterilizations. Secondly, look at the scale of your operations; it may be better for large plants to use more automated systems, while smaller ones can use manual or semi-automated equipment. It is also necessary to evaluate whether it is compatible with existing production lines, energy efficiency, and maintenance requirements. Compliance with health and safety regulations and industry standards must also be considered if product quality has to be protected and consumer safety maintained. Lastly, identify suppliers with an excellent reputation for being dependable and offering after-sales support services when implementing a new system.
Comparing different sterilization methods
When comparing sterilization methods, three primary techniques are often considered: steam sterilization, dry heat sterilization, and chemical sterilization.
- Steam Sterilization: This method utilizes saturated steam under pressure to accomplish sterilization by killing microorganisms at lower temperatures. It is, therefore, very reliable and efficient. It is particularly effective for heat-resistant instruments and can typically achieve sterility in less than 30 minutes.
- Dry Heat Sterilization: This technique employs high temperatures over long periods, which makes it suitable for moist-sensitive materials. Unlike steam, it operates through oxidation but can be used on powders, oils, or metal instruments.
- Chemical Sterilization: Another way, called chemical sterilization, is to use gases or liquids to disinfect objects that cannot tolerate hotness from other sources since such items contain gaseous or liquid chemicals inside them instead of being heated up as others. For instance, ethylene oxide gas is commonly employed because it does not destroy delicate medical devices but still ensures their integrity as sterile goods; however, some precautions should be taken against its toxic effects.
Each method has advantages and limitations, and the choice is dependent upon the specific requirements of the food production process and the types of products being sterilized.
Factors to consider: energy saving and batch sterilization
Energy efficiency is crucial in selecting a sterilization method, especially in large-scale operations. Usually, steam sterilization has shorter cycle times than dry heat methods, thus making it more energy efficient. Further energy optimization can be achieved by batch sterilization, which combines several items into one load, thereby reducing the overall processing time and energy use. Implementing equipment and technologies that are energy efficient will enhance savings, which come with both environmental and economic gains. It is, therefore, essential to evaluate the specific requirements of the production process while considering the efficiency of sterilization techniques.
What are the challenges in implementing sterilization equipment?

Implementing sterilization equipment has various challenges that can affect its efficacy and efficiency. One such challenge is the initial capital needed to purchase and install advanced sterilizers, which may be significant, especially for small businesses. Therefore, staff training is integral because when used unsuitable, it may lead to ineffective disinfection and jeopardize product safety. Calibration and maintenance of these equipment must also be done regularly, or else they might break down, posing contamination risks due to their inability to work as expected. Besides, meeting regulatory compliance and safety standards adds another layer of complexity since the industry guidelines need to be observed by all centers operating in this field. Careful planning is necessary for addressing these issues through appropriate resource allocation during successful implementation processes.
Meeting industry standards and regulations
For effective sterilization procedures, it is essential to meet industry standards and regulations. The FDA (Food and Drug Administration) and CDC (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention) have set guidelines that sterilization techniques must follow as provided by regulatory bodies. Conformance involves periodical validation of sterilization equipment and processes through exhaustive testing with supporting documents to establish their efficacy and safety. Also, centers must be vigilant about the changes in laws regarding this aspect of medical care, and employees should be trained accordingly. Regular audits or checks by appropriate authorities will ensure that there is a continuing effort to make improvements in the process, thereby ensuring public health safety is maintained while at the same time maintaining product integrity. Engagement with industry-standard organizations can help navigate these hurdles effectively.
Training and safety precautions for operators
To maintain the proper functioning of sterilizing processes and ensure public safety, operators must undergo appropriate training programs to guarantee their security. Operators should be given extensive knowledge on how to use and maintain sterilization equipment, including a discussion of operating principles, potential hazards, and emergency procedures. Therefore, Their competencies must be enhanced via refresher courses and on-job training to conform to these standards.
Strict observance of safety precautions is also necessary. Protective gear such as gloves, goggles, and gowns should be available for operators so that they are not exposed much to hazardous substances, if any, in those areas where the procedure occurs. This can also reduce risks associated with handling such devices by developing standard operating procedures (SOPs). Moreover, a culture of safety that enables workers to feel encouraged enough when raising issues will make it a safer place for them to work. Periodic drills on protection measures can allow the identification of training deficiencies, hence moving towards prevention rather than reaction in terms of sterilizing outcomes.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What is a food sterilizer, and how does it work?
A: A food sterilizer is a machine used to sterilize food products by eliminating microorganisms in food that can cause spoilage or health hazards. It typically works through steam sterilization, heat sterilization, or microwave sterilization.
Q: How does an autoclave sterilization machine function in food processing?
A: An autoclave sterilization machine functions in food processing by using high-pressure steam to sterilize food products. This method ensures that the food is thoroughly sterilized, effectively killing harmful microorganisms and preserving the food.
Q: What are the different types of food sterilization techniques?
A: Different food sterilization techniques include heat sterilization, steam sterilization, and microwave sterilization. Each technique uses different processes to eliminate microorganisms and sterilize food products, making them safe for consumption and extending their shelf life.
Q: What role does a pasteurizer machine play in food sterilization?
A: A pasteurizer machine plays a crucial role in food sterilization. It uses controlled heat treatment to reduce the number of microorganisms in food and beverages. This ensures the food is safe to consume while maintaining its nutritional value and flavor.
Q: How is the food sterilization equipment market evolving?
A: The food sterilization equipment market is evolving due to technological advancements and the increasing demand for safe, long-lasting food products. Innovations in sterilizer machines, improved control systems, and more efficient sterilization techniques drive this market forward.
Q: What is the importance of sterilization time in food processing?
A: Sterilization time is crucial in food processing as it determines how long food is exposed to sterilizing agents such as heat or steam. Proper sterilization time ensures that all harmful microorganisms are eliminated without compromising the food’s quality and nutritional content.
Q: Can I get wholesale food sterilization equipment for industrial use?
A: Yes, you can get wholesale food sterilization equipment for industrial use, including industrial autoclaves, continuous sterilization systems, and other robust machinery designed to handle large-scale food processing operations. Wholesale options often provide cost savings and customization to meet specific requirements.
Q: What are the benefits of using a steam sterilizer in the food industry?
A: Steam sterilizers are beneficial in the food industry because they effectively eliminate harmful microorganisms, preserve food quality and taste, and comply with health regulations. They are also energy-efficient and suitable for various types of food products.
Q: How does heat treatment in a pasteurizer help preserve your food?
A: Heat treatment in a pasteurizer helps preserve food by reducing the microbial load. This prolongs the shelf life and ensures the food remains safe to consume. The heat treatment is controlled to maintain the food’s sensory and nutritional properties.
Q: Why is an exchanger used in some food sterilization equipment?
A: An exchanger is used in some food sterilization equipment to transfer heat efficiently during the sterilization process. It helps maintain consistent temperatures, reduce energy consumption, and ensure even heat distribution, essential for effectively sterilizing food products.