For ordinary individuals and experts in food safety, it is necessary to comprehend how to microwave food safely. The present article explores if microwave ovens can be used to kill bacteria; explaining the heating mechanism of microwave ovens and its effects on microbial organisms. We expect to give full details about microwave food safety by examining scientific facts and expert’s viewpoints. Readers will learn about the mechanisms of microwaves, the conditions for killing bacteria, as well as how to use them safely to ensure food is safe. Without this basic information, it would be impossible for consumers of food or cooks to come up with reasonable choices concerning their health when they handle food.
How Does a Microwave Eliminate Bacteria?
Microwaves emit electromagnetic waves that act on the water molecules in the food, causing them to oscillate and generate heat through friction rapidly. Most pathogens will be killed if the food temperature rises enough to break down bacterial cell structure (165°F or 74°C). This is how microwaves kill bacteria and make food safe for eating – it works because of a thermal effect. However, it is important to ensure even heating because cold spots may exist where surviving bacteria may be found, which may cause food-borne illnesses. Proper technique and careful stirring can mitigate this risk.
Understanding Microwave Radiation and its effects on Food
In the Non-ionizing part of the Electromagnetic Spectrum, microwave radiation operates at a frequency of about 2.45 GHz. For this reason, microwave radiation has less energy than is necessary to dislodge tightly bound electrons or cause ionization, making it safe for food preparation. These fields induce dipoles rotation in polar molecules like water creating thermic effects.. The penetration depth for microwaves into food depends on composition and density ranges from 1-3 cm typically.The energy absorption rate is determined by dielectric properties which depend on materials such as water.
Key technical parameters include specific heat capacity, which determines how much energy is required to raise the food’s temperature, and thermal conductivity, which governs the distribution of heat in foods. To achieve homogeneous heating, we can use microwave stirrers or turntables to prevent cold spots resulting from uneven dispersion of microwave energy. To ensure safety, these parameters should always be adhered to when using microwaves for cooking.
How does a microwave oven produce enough heat to kill bacteria?
Heating, known as dielectric heating, occurs during microwave cooking. Placing a meal within a microwave machine generates electromagnetic radiation at approximately 2.45GHz frequency range. This involves causing polar molecules, especially water, within the meal to rotate very quickly. Because it constantly moves around, molecules rub against each other, resulting in higher temperatures. The heat produced raises the internal temperature of the food, disrupting bacterial cell membranes and denaturing proteins, thereby effectively killing bacteria.
This heating process uniformity depends on a number of factors including the composition size and shape of food. This is because foods with high water contents tend to warm more quickly because many more individual molecules are available for dipole rotation. Moreover, turntables are used to improve distribution of microwave energy as well as stirrers which make sure all parts are heated up evenly without cold spots where surviving bacteria may reside. It is important that food reaches 165°F (74°C) internally since most common pathogens will be eliminated at or above this temperature level.
Electromagnetic waves and microwave heating
Microwave ovens cannot work without electromagnetic waves which become essential in heating. Basically, microwaves function at a frequency of 2.45 GHz that matches the resonant frequency of water molecules hence providing effective energy transfer between the two. Polar molecules like water, sugars, fats among others experience quick oscillation as these microwaves penetrate through the food. This results into frictional forces that are converted into heat.
These technical parameters include:
- Frequency: 2.45 GHz – Most effective for interaction with water molecules.
- Wavelength: 12.24 centimeters- they ensure deep penetration into the food.
- Power output: Typically between 600 to 1200 watts – this controls how fast it will cook.
These parameters aid in effective dielectric heating, leading to even temperature distribution.Microwaves keep food’s internal temperatures above 165°F (74°C), thus ensuring complete sterilization by denaturing bacterial proteins and destroying microbial cell structures effectively.
What Types of Bacteria Can Microwaves Kill?
Most common foodborne bacteria can be destroyed by microwave heat. The pathogen Salmonella, often linked to poultry, eggs, and meat dishes, can be effectively eliminated when its food content is heated sufficiently using a microwave. Similarly, the presence of Listeria monocytogenes in dairy products, deli meats or smoked fish can be influenced by microwave radiation if proper heating guidelines are adhered to. This includes E.coli found in raw vegetables and undercooked beef that can also be done away with by heating it in a microwave to necessary temperature levels. The recommended cooking times and power settings are strictly followed to ensure comprehensive bacterial destruction.
Can Microwaves kill Pathogen Like Salmonella?
Yes microwaves are capable of killing Salmonella provided the food gets to an internal temperature of 165°F (74°C). The primary cause for eliminating this pathogenic organism is by making sure that all parts of the food being cooked are uniformly warmed. Non-uniform heating which is usually associated with microwave cooking could allow areas with bacteria in them to remain alive even though microwaves are one way of effectively destroying Salmonella if all needed conditions for heating had been met. It therefore becomes important to make certain that during the time they cook one has followed instructions given by the makers so as to achieve uniform warming such as covering up foods or stirring or rotating during cooking thereby ensuring every part attains enough temperatures that will exterminate Salmonella.
Do Microwaves Destroy Dangerous Bacteria?
Yes, microwaves kill dangerous bacteria, but it depends on how well heat penetrates the whole meal evenly. For this reason, these germs, including salmonella, listeria, and E.coli, have their lives rounded up if they get the proper internal temperature on average around 165°F (74°C). Sometimes, microwaving heat without consistency might lead to uneven distribution where there can still be some cooler spots with bacteria in them. Therefore, before you microwave, cover your food and stir or rotate it during the cooking process so that it is uniformly heated all over; this will allow for complete killing of Salmonella, hence following recommended durations and power ratios.
Are there Bacteria that Microwaves Don’t Kill?
Microwaves kill many harmful bacteria, but microwaves do not eradicate some. Some bacterial spores, for instance, those from Clostridium perfringens and Bacillus cereus, defy the effect of heating in a microwave cooker, especially when food has not been cooked uniformly to a high temperature enough. Meanwhile,, these spores can survive even during cooking if the temperature inside does not reach the level at which they die because they resist heat greatly.
- Clostridium perfringens: If uniform internal food temperature does not reach 212°F (100°C), its spores can withstand microwave heating process.
- Bacillus cereus: Like Clostridium perfringens, Bacillus cereus develops resistant spores during misheating. To ensure complete deactivation of such spores, it is important to boil all food portions in like manner.
To minimize these risks observe the following practices while using a microwave oven:
- Thoroughly covering foods as they cook in a microwave to create steam pockets that distribute heat evenly.
- Stirring and rotating foods as they heat in order to prevent cold spots where bacteria may be present.
- Checking temperatures for thoroughness through use of a thermometer on various parts of the meal being heated up until proper levels are reached
Thus, adhering to these principles will enable microwaving become more effective in eliminating bacteria and spores.
Can Microwaving Food Lead to a Salmonella Outbreak?
Yes, not heating food well during microwaving can cause a Salmonella outbreak. Salmonella bacteria are only killed by thorough cooking because microwave ovens tend to heat food unevenly. The most important hazards revolve around non-uniform heating and areas with cool temperatures that allow the survival of Salmonella. Therefore, ensure that while cooking, you cover it with lid, stir and rotate the food properly during the period of warming. Moreover, it is crucial to take the product’s internal temperature to at least 165°F (74°C) with a food thermometer for risk abatement against salmonellosis.
How to keep off salmonella from your food
For Salmonella-free foods several steps must be taken effectively and consistently from sources’ perspective as follows:
- Cooking Temperature: Ensure poultry is cooked internally at 165°F (or 74°C). To ascertain uniformity in heating, use a meat thermometer inserted into the thickest part of the flesh but not touching the bone.
- Cross-Contamination: Avoid contact between other foods and raw meats including poultry or seafood; for cutting boards use separate ones for raw foods and ready-to-eat.
- Produce Washing: Wash all fruits thoroughly with running water so that they have even skins. If some parts are peeled before consumption, they might contain bacteria on their skin after peeling or cutting.
- Sanitize Surfaces Used For Cooking: Regularly cleanse kitchen surfaces such as cutting boards and utensils which have come into contact with raw materials using an efficacious disinfectant bleach solution (1 tablespoon in one gallon of water).
- Rapid Cooling Of Food Items: Refrigerate perishables within two hours after preparing or within one hour if the ambient temperature is above 90° F. A suitable environment lacks the nutritional content needed for bacteria growth, like Salmonella.
- Hand Hygiene: Wash hands thoroughly using soap and water for at least 20 seconds before touching raw meat, seafood, and poultry, as well as after defecating, changing diapers, or contacting bodily fluids with pets.
Adhering to these directives will significantly reduce the risks of Salmonella soiling and multiplying in food, enhancing food safety and public health.
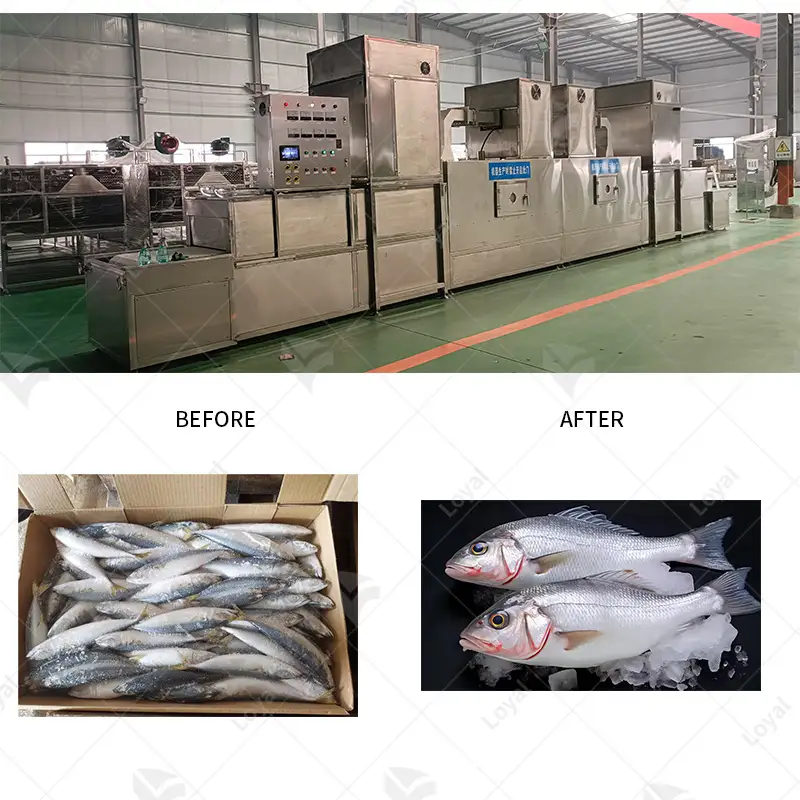
Can Industrial Microwave Sterilization Equipment Be Used to Sterilize Food?
Thus, food can be sterilized by industrial microwave sterilization equipment. This technology uses microwaves that emit heat, killing or deactivating bacteria, viruses, and molds. It is always good to use this method of sterilization since it helps to heat the entire product in an even manner so as to enable the necessary temperature to reach all corners of the food for effective sterilization. Moreover, these rays are capable of penetrating deep inside a meal, enabling them to reach areas that normal means may fail to get to. Yet, power and exposure time must be strictly regulated otherwise uneven heating, over-processing and deleterious nutritional effect on the food can happen. Recent studies have also shown that industrial microwave sterilization is quickly becoming a reliable tool for ensuring safe and clean processed foods.
What are Industrial Microwave Sterilization Equipment?
Industrial microwave sterilization equipment is specialized technology for rapid and efficient processing of food products concerning their safety aspects. The equipment operates by generating microwave energy at 915 MHz or 2450 MHz frequencies, which is mainly absorbed by food and vibrates water molecules within it, which in turn generates heat. As a result of this heat, harmful microorganisms such as bacteria, viruses, or fungi are destroyed, causing no harm when eaten.
- Frequency: Preferred operating frequencies are 915 MHz or 2450 MHz as water molecules absorb energy efficiently at such conditions
- Power Output: Varying applications dictate different outputs, but for big industrial machines, they range from a few kilowatts (kW) to a megawatt (MW).
- Temperature Control: Accurate temperature ranges between 70°C – 120°C need monitoring systems installed so practical work should go on accordingly.
- Penetration Depth: Foods heated under conventional surface methods may have cold spots, whereas microwaves spread through the product, providing uniform heating and eliminating any cool patches throughout.
- Exposure Time: Power changes alongside exposure periods must be cautiously done; otherwise they will lead to over-processing and degradation of food value.
The disadvantages of using industrial microwave sterilization equipment are even heating, reduced processing time, and energy savings. However, extensive research and real-life implementation have observed the immense effects of this technique on the safety of food products.
How Effective is Industrial Microve Sterilization?
This shows that food can be easily sterilized with the use of industrial microwave sterilizing devices. Microwaves use heat to kill or inactivate bacteria, viruses and fungi such as molds. This method is the best because it heats all parts of the product evenly, thus maintaining the required temperature throughout the meal. Furthermore, they penetrate into meals at much greater depths than other means do; hence reaching areas typically missed by conventional methods. However, it is critical to avoid uneven heating or over-treating caused by improper management of power levels or exposure times which could impact nutritional value and overall quality. Empirical studies confirm that industrial microwave sterilization has become a widely used tool in guaranteeing pathogen free processed foods.
Another source IFT that highlights the importance of temperature control and exposure time states that bacterial destruction must be made keeping in mind thermal ranges between 70°C – 120°C with an appropriate time for cooking foods until they are no longer harmful. Additionally, deep penetration by microwaves ensures uniformity while dealing with large quantities of food thereby enabling perfect disinfection.
Nevertheless, Food Safety Magazine industry reviews point out that efficient energy absorption occurs during operations involving industrial microwave systems operating at either 915 MHz or 2450 MHz frequencies. The correct level of power output classifies these systems according to different types of foods resulting into ideal sterilization processes alongside maintenance of nutritional elements together with organoleptic attributes in them.
In summary, this method’s efficiency is demonstrated by its technical parameters including:
- Waveband: 915MHz or 2450MHz
- Rated Power: Some kilowatts (kW) to megawatts (MW)
- Temperature Limits: 70°C to 120°C
- Exposure Time: Accurately regulated for better food safety and quality
These parameters reveal that the method has capacity for uniform heating, fast treatment rates and high energy savings thus making it a dependable choice in contemporary food safety practices.
Can Microwave Sterilization Equipment Enhance Food Safety?
With microwave sterilization equipment, food safety can be greatly enhanced as they help reduce pathogens efficiently. The technology works by breaking down the bacterial cell structure through both thermal and non-thermal effects – a process which ensures proper deactivation of microorganisms. In addition, scientific articles have shown that its efficiency surpasses traditional methods by reducing processing times and keeping the quality of foods. Again, the leaders in this sector have agreed that microwave sterilization does not affect nutritional content and sensorial attributes of these products thus upholding their safety and consumer appeal.
Advantages of Industrial Microwave Sterilization Equipment
Industrial microwave sterilization equipment has a number of advantages supported by major sources on food safety and related technologies:
Efficiency and Speed: As revealed by leading food safety websites, microwave sterilization is much faster than conventional heat treatment techniques. In other words, it takes minutes to heat rather than hours thereby reducing energy usage and associated costs.
- Enhanced Food Quality and Nutrient Retention: Publications indicate that this method preserves more nutritionally sound and sensory healthier foods compared to traditiona tempering methods. To maintain texture, flavor and nutritive values for different products; temperatures are kept at 70°C-120°C over reduced duration under accurate temperature controls.
- Uniform Heating: Numerous technical resources emphasize that all parts of a product are heated evenly with microwave heating method. Since each part attains effective sterilizing temperatures uniformity is achieved across all parts thus eliminating any chance of cold spots where pathogen could hang on.
Technical Parameters:
- Frequency: For compatibility with industrial norms for food sterilisation purposes, consistent operational standards involve 915 MHz or 2450 MHz frequency operation ensuring compatibility with established industrial standards for food sterilization processes.
- Power Output: Depending on your specific scale-up needs, you have several kilowatts (kW) to megawatts (MW) options to choose from.
- Temperature Range: The use of narrow temperature control ranges of 70°C to 120°C has optimized microorganism inactivation efficacy while maintaining good-quality food.
In conclusion, the benefits of industrial microwave sterilization equipment are established in widely available data and technical validations from reputable sources, emphasizing its efficiency in addressing food safety needs.
How Microwave Sterilization Equipment works to kill bacteria
Microwave sterilization equipment utilizes dielectric heating to kill any bacteria and pathogens found in food products. When exposed to microwaves, food substances like water align themselves due to the oscillating electromagnetic fields created. Such movements cause friction inside the liquid molecules leading to heat creation within the heated product. This fast rise in temperature uniformly and efficiently reaches microbial inactivation temperatures required typically ranging between 70°C and 120°C.
As a result, specific technical parameters need consideration for this process to be effective. The frequency used, either 915 MHz or 2450 MHz, is based on water molecule resonance frequencies, ensuring optimal energy adsorption rates. Thus, the power output range can be set finely from a few kilowatts (kW) up to megawatts (MW) so that it fulfills various applications at an industrial scale. Precise maintenance of temperatures within this given range is directly linked with microorganism destruction/loss rate as well as overall quality preservation within processed foods.
The uniformity of heat distribution occurs during microwave sterilization, therefore eliminating any cold areas where pathogens could survive, as observed with other methods using conventional heat. According to reliable industry and technical sources, these data signify how effective microwaving technology remains consistent for operational purposes with proven outcomes on food quality assurance.
How Effective Are Microwaves at Eliminating Harmful Bacteria?
Recent studies and data from leading sources indicate that microwaves can significantly effectively eliminate harmful bacteria, provided certain conditions are met. According to scientists, heating with a microwave oven can kill up to 99.9% of all pathogens when the food reaches internal temperatures that are required for cooking it properly. The most important part is to make sure that heat spreads uniformly through the entire product, which is achieved by molecular agitation quickly and consistently done by microwaves. Apart from this, comprehensive industrial research has shown that maintaining and attaining temperatures between 70°C and 120°C are crucial in order to effectively kill microorganisms. Also, it is crucial to know that how effective microwaves perform depends on its power output and the specific resonance frequency which ensures optimum energy absorption along with uniform distribution heat.
The temperature needed to ensure harmful bacteria are killed
Between 70°C and 120°C stands the temperature range within which harmful bacteria can be eliminated. In particular, FDA suggests food should be cooked until it reaches an internal temperature of 74°C (165°F) or higher to destroy common germs associated with food poisoning. Regarding microwave sterilization process this would include:
- Power Output: A typical power output for a microwave ideally is between 500-1000 watts.
- Resonance Frequency: Microwaves usually operate at a frequency of about 2.45 GHz so as to absorb energy optimally; hence vibrating water molecules uniformly cause heat generation.
- Temperature Control: Precise temperature control measures must also be put in place to keep internal temperatures constant within the range of 70 –120ºC, which enables complete microbial death.
These parameters are very important for ensuring effective sterilization during food processing using microwaves.
The role of water molecules in the microwave heating process
Water molecules play a crucial role during microwave heating due to their polarity which makes them responsive to electromagnetic fields. When water molecules are subjected to microwave radiation, usually at a frequency of 2.45 GHz, they oscillate rapidly. As a result of this oscillation, friction occurs leading to the generation of heat that raises food temperature. To ensure efficient heating, the dipole moment of water aligns and realigns itself with an alternating electromagnetic field. Important technical parameters are:
- Frequency: Microwaves typically resonate at 2.45 GHz, which allows water molecules to absorb energy at their maximum capacity.
- Dielectric Properties: Water’s dielectric properties significantly affect how efficiently it heats up in a microwave oven; hence, its high dielectric constant maximizes the absorption of microwave energy.
- Uniformity of Heat Distribution: A good design should ensure even distribution throughout the space being heated in order to prevent occurrence hot spots and make sure that all foods or sterilizations projects will be done properly.
These parameters are necessary for comprehending and optimizing the mechanism used in microwave cooking, implying that the food under consideration should receive effective and uniform thermal treatment.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: Does using microwave sterilization equipment ensure food safety?
A: Using microwave sterilization equipment can contribute to food safety by helping to kill bacteria and keep food safe. It is important to make sure your microwave operates efficiently and heats food evenly to avoid cold spots where harmful bacteria can survive.
Q: How do microwaves kill bacteria in food?
A: Microwaves kill bacteria by generating heat. When food in a microwave is heated to a safe internal temperature, typically 165 degrees Fahrenheit, the heat can effectively destroy bacteria and other foodborne pathogens.
Q: Is food in the microwave safe to eat if it is not evenly heated?
A: Food in a microwave can cook unevenly and may leave cold spots. These cold spots can harbor bad bacteria, making the food unsafe to eat. To ensure food safety, always stir, rotate, or cover food while heating to promote even cooking.
Q: What precautions should I take when using my microwave for food safety?
A: When using your microwave, it is essential to follow proper safety guidelines: cover food to steam and promote even cooking, periodically stir or rotate items, and use a food thermometer to check that the food has reached a safe internal temperature of 165 degrees Fahrenheit.
Q: Can reheating food in a microwave kill bacteria?
A: Yes, reheating food in a microwave can kill bacteria if the food is heated to a safe internal temperature of 165 degrees Fahrenheit. The heat generated by the microwave is effective in killing most foodborne pathogens if the food is thoroughly heated.
Q: Why does food sometimes not get hot enough to kill bacteria in a microwave?
A: Food may not reach a safe temperature in a microwave because microwaves can sometimes heat food unevenly. This uneven heating can leave cold spots that allow bacteria to survive. Ensuring the food is covered, stirred, and rotated can help achieve more even heating.
Q: What role does the food industry play in microwave food safety?
A: The food industry follows regulations and guidelines set by food safety and inspection services to ensure that food products are safe for consumers. This includes providing instructions for proper reheating and using microwave-safe containers to help kill bacteria and keep food safe.
Q: Can all types of food be safely heated in a microwave?
A: Most foods can be safely heated in a microwave if proper guidelines are followed. However, some foods, especially those with uneven shapes or varying densities, may require extra caution to ensure they are heated to a safe internal temperature and do not leave cold spots.
Q: What are common mistakes to avoid when using a microwave to kill bacteria?
A: Common mistakes include not covering the food, failing to stir or rotate the food during heating, and not checking the internal temperature with a food thermometer. These mistakes can prevent the food from reaching the necessary safe temperature to kill bacteria and keep food safe.
Q: Is there a standard safe temperature for microwaving food?
A: Yes, the standard safe temperature for microwaving food is 165 degrees Fahrenheit. Heating food to this temperature can effectively kill bacteria and foodborne pathogens, ensuring the food is safe to eat.