The industrial drying process has historically been monopolized by conventional means, which, though effective, are often deficient in efficiency and homogeneity. Continuous microwave dryers have revolutionized the traditional drying method using microwaves for better results. This article discusses how continuous microwave dryers are positioned to reshape the face of industrial drying through fast drying times, low energy consumption, and the manufacture of better-quality products. This article aims to thoroughly explain why continuous microwave dryers will become the standard of industrial drying for a long time by examining what it takes to use them effectively juxtaposed with other techniques involved in traditional ways of doing things. It will also provide readers with knowledge of practical applications and possible benefits for different industries.
What is a Continuous Microwave Dryer?

Image source: https://www.tshs-dryer.com/
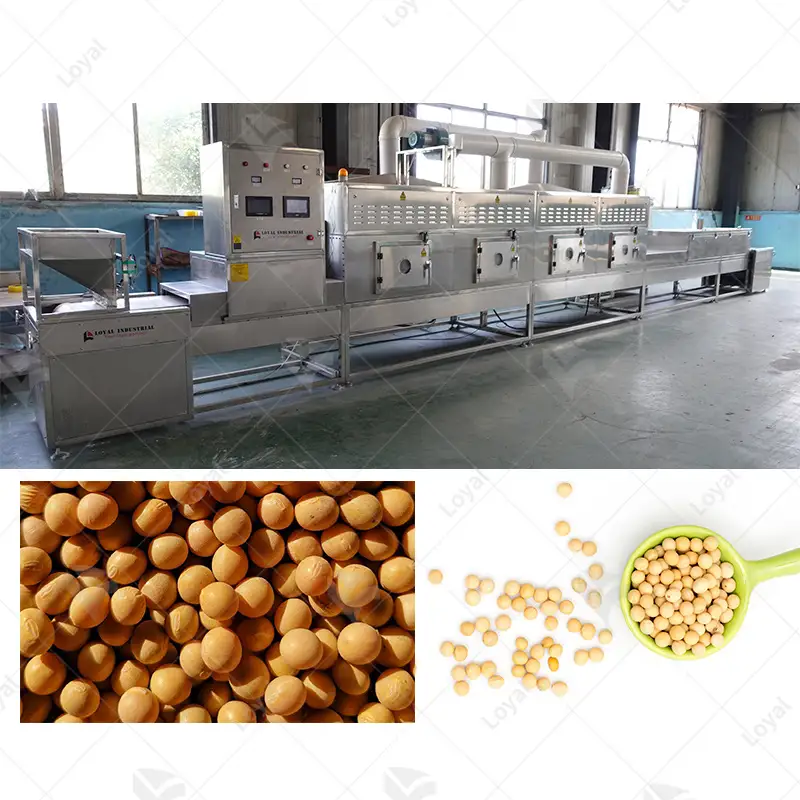
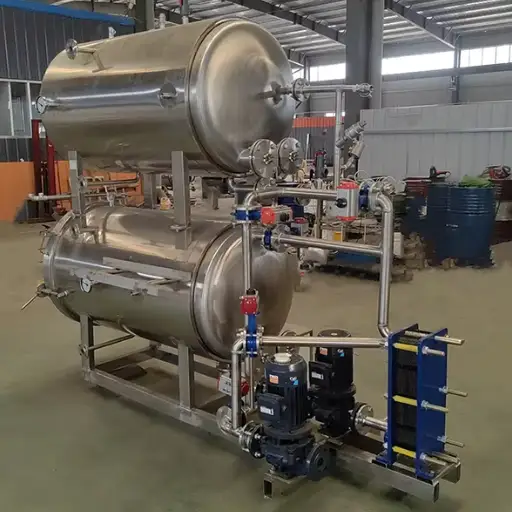
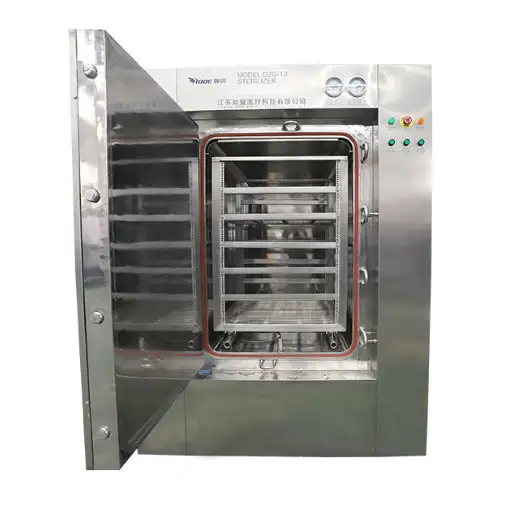
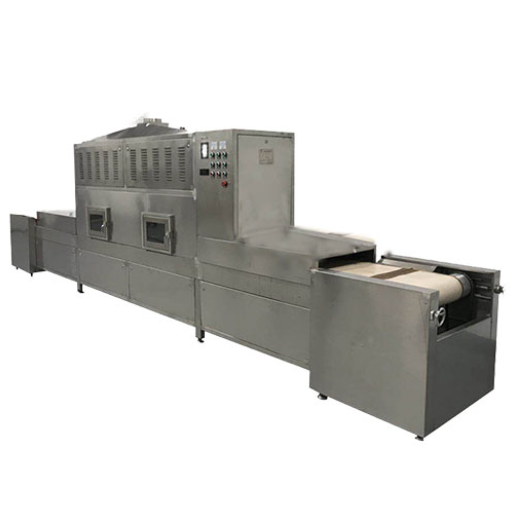
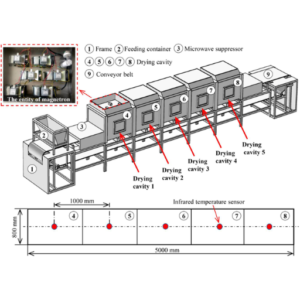
An advanced drying apparatus is a continuous microwave dryer that moves materials continuously through the dryer using microwave energy to heat and evaporate their moisture. The difference between the conventional method of batch drying and continuous microwave drying is the conveyor system, which ensures a constant flow of material to facilitate more even and efficient drying stages. Microwaves go deep into the material, heating water molecules very fast, causing them to evaporate from within, thus resulting in reduced drying time and energy conservation. This technology is most useful for industries that demand accurate humidity control and high-quality final products like chemical production, pharmacy, or food processing.
How does microwave drying work?
Microwave drying is based on the principle of dielectric heating, in which microwave energy is absorbed by polar molecules such as water within the material. Once these microwaves go through the substance, water molecules vibrate quickly, producing heat through friction between molecules. This inside warming facilitates moisture moving from the inside out, making drying even more effective. Some of the benefits of this approach include less drying time and energy usage than traditional drying methods because microwaves directly heat material internally, leading to quicker evaporation of moisture. This focused dehydration procedure is beneficial for materials that quickly get damaged by heat since it guarantees product quality and accurate control over its wetness.
What are the components of a continuous microwave dryer?
A continuous microwave dryer consists of several key elements that work together to ensure successful drying, which is also cost-effective and equal:
- Microwave Generator: This generates the necessary heat energy for drying. This part is essential in yielding electromagnetic waves that infiltrate the material.
- Conveyor System: This moves the material through the drying chamber. It allows for a constant flow and uniform exposure to the microwave energy, leading to consistent drying results.
- Drying Chamber: This section encloses where microwaves are used to dry materials. Microwaves are retained within it to create optimum conditions for drying purposes.
- Water Vapor Removal System: This system removes air full of moisture from the space used for drying products or materials. It usually includes fans, ducts, and sometimes condensers to remove evaporated water.
- Control System: These keep track of variables such as microwave power, conveyor velocity or speed, and temperature, among others. Through this system, efficiency in controlling the process of getting dry becomes more accurate as desired.
-
Safety Features: These filters and interlocks prevent spillage into operating rooms and guarantee client well-being. Due to its nature and intensity, microwave radiation poses a threat; hence, safety is vital.
What industries benefit from microwave dryer technology?
Its efficiency and adaptability make microwave drying valuable technology in various sectors. In the food industry, this technology is used in applications such as fruit and vegetable drying, pasta manufacturing, and snack production, where it helps retain nutritional value and reduce processing time. It is also used for drying heat-sensitive drugs/compounds in pharmaceuticals so that they remain stable and their effectiveness can be guaranteed. Chemical firms are also using this technology to dry polymers and resins, among other chemical substances, which allows for exact moisture content regulation, thus leading to better end-product quality.
How to Improve Efficiency with a Microwave Dryer?

- Optimize microwave oven power levels: Set the microwave power to corresponding moisture content and material properties to prevent it from being over-dried or under-dried.
- Control the speed of the conveyor: adjust this to ensure that materials spend an optimal time in the drying chamber, which leads to uniform drying.
- Implement Moisture Sensors: Use real-time moisture sensors to monitor the dryness process, thus making possible changes in microwave power level and conveyor speed concerning the current water content ratio.
- Improve Airflow Management: Accelerate the removal of the water vapor system by introducing efficient fans and ducting for fast evacuation of moist air that would be reabsorbed, slowing down the drying process, too.
- Carry out routine maintenance: It is essential to check some components, such as magnetrons and conveyor belts, for cleanliness regularly. They must function properly and efficiently.
-
Apply Pre-Drying Techniques: Some pre-drying techniques, such as air drying and centrifugation, can be adopted to reduce the initial moisture content, minimizing the time and energy required during microwave drying.
Tips for optimizing microwave heating settings
- Know Your Materials: Different materials have different dielectric properties, determining their ability to absorb microwave energy. Make sure your settings match the attributes of the material you will heat; this will always lead to effective energy transfer.
- Set Power Appropriately: Wrong power levels can cause overheating and ineffective drying. Start with low power and monitor the item before gradually increasing it. This helps ensure even heating by searching for the best setting.
- Change Heating Time: Microwave exposure duration heavily affects the output. Optimize heating time by making small tests with increments to prevent under- or over-processing of stuff.
- Use Intermittent Heating: Sometimes, constant warming causes uneven drying and hotspots. Introducing intermittent warming cycles into this setup ensures uniform heat distribution, allowing a better outcome.
- Also, Monitor Moisture Levels and Temperature: Drive for feedback should be given through real-time temperature and moisture monitors during the process. Change microwave settings depending on this information to uphold optimal conditions throughout the drying cycle.
- Maintain and Test Equipment Regularly: Maintenance and calibration of microwave equipment are necessary. This includes cleaning parts and checking whether the power output is actual or whether sensors are accurate enough so that the equipment runs smoothly without fail.
The tips above can improve how efficiently your materials dry using microwaves, enabling you to get superior results every time.
Maintenance practices for industrial microwave systems
These guidelines ensure that industrial microwave systems last longer and perform consistently. The following are some of the best practices:
- Keep Clean: Check the interior and exterior parts of a microwave system for dust, dirt, or residue. Regular cleaning minimizes the chances of blockage and overheating, thereby reducing system efficiency.
- Frequent Inspection: Check crucial components like cooling systems, magnetrons, and waveguides. Inspect for signs of wear out, corrosion, or wrong alignment, affecting functioning and safety measures in place.
- Calibration Assessments: To maintain accuracy, periodically calibrate power output, timers, and sensors. This ensures that equipment operates according to its intended function, thus minimizing risks of under- or overprocessing material.
- Component Replacements: Preemptively replace all components with a predefined lifespan, such as magnetrons, to avoid unexpected downtimes. To enhance responsiveness in maintenance requirements, keep some essential spare parts.
- Performance Monitoring: Use performance monitoring tools and software to track how your system is operating. This information is valuable in recognizing deviations from average performance and will be used to plan proactive maintenance.
Compliance with these care procedures guarantees reliability and efficiency during the operation of your industrial microwave systems, thereby reducing downtime while increasing overall productivity.
Common issues and solutions in microwave drying
1. Uneven Drying: When using a microwave to dry, the dry material’s moisture does not dry evenly. This leads to some parts of the product being over-dried while others are too wet.
Solution: To solve this issue, ensure the material is spread homogeneously across the microwave. Turntables or rotating mechanisms can help distribute microwave energy more evenly. Adjusting power levels and including intermittent heating cycles may also improve uniformity.
2. Overheating and Burning: High-intensity microwave energy can cause the material to overheat or burn, especially at its edges or thinner regions, which results in quality degradation.
Solution: This can be controlled and minimized by adjusting the microwave power levels and more accurately managing the heating process. Also, integrating moisture detectors and feedback control units will enable real-time adjustment to avoid excessive heat.
3. Equipment Malfunction: Equipment malfunction, such as arcing or magnetron burnout, can interrupt drying activity, leading to expensive downtime.
Solution: Regular maintenance and inspection are necessary to avoid equipment malfunctions. Consequently, planning a preventive maintenance schedule entails checking for loose connections, cleaning components, and ensuring proper ventilation, among other things. This elongates equipment life span, and investing in high-quality spare parts in readiness during repairs minimizes repair duration remarkably.
Comparing Microwave Drying to Traditional Methods
Microwave drying has various advantages compared to conventional drying techniques. One significant advantage is speed, which drastically cuts down on drying duration because microwave energy targets moisture in materials, thus enabling evaporation at a higher pace. This technique also leads to better energy efficiency since heat is only produced when required, which differs from other methods that heat the entire environment. Furthermore, more product properties such as color, texture, and nutritional content can be maintained through microwave drying.
On the other hand, traditional methods like sun drying or drying using an oven are characterized by long processing times and limited energy efficiency. These methods usually employ high temperatures for prolonged periods, leading to heating damage or uneven dryness. Conventional drying may also involve bigger spaces and more equipment, raising operating expenses.
In summary, although traditional drying processes have been used for a long time now, microwave drying brings a more modern alternative that can be both effective and potentially of superior quality. However, the selection of the appropriate method of drying will depend on specific material requirements, production scales, and available technologies.
Differences between microwave and hot air drying
As regards their mechanisms and efficiencies, microwave drying fundamentally contrasts with hot air drying. Microwave drying uses electromagnetic waves to directly heat the water content in the material, resulting in faster drying time and reduced energy consumption. Generally, this process achieves better quality products through higher retention of color, texture, and nutritional components than hot air.
On the other hand, hot air drying entails flowing heated air over the material, slowly evaporating moisture. This means that it can take a long time before materials are dry, leading to high energy consumption due to heat dissipation throughout the chamber rather than on the material alone. Besides, the hot air method tends to cause non-uniformity in drying or overheating, which may harm the final product’s quality.
In conclusion, while microwave drying offers quicker and more energy-efficient results with higher product quality, hot air drying remains widely used but may incur longer drying periods and potentially lower output quality. Specific requirements for the drying process, operational constraints, and desired characteristics of end products should guide one’s choice between these two methods.
Advantages of using an industrial microwave for drying
- Speed and Efficiency: Industrial microwave drying is speedy compared to traditional methods. Microwaves pass through materials, heating water from within it and, as a result, reducing the time taken to dry.
- Energy Savings: Microwaves can reduce energy consumption because they directly act on moisture in a material. Thus, power bills can be cut down, enabling better business operations.
- Superior Product Quality: The gentle uniform heat utilized in microwave drying helps retain original material properties such as color, texture, and nutrition content. It minimizes thermal damage and produces superior-quality end products.
- Environmental Benefits: Microwave drying reduces greenhouse gas emissions compared to other technologies due to its higher energy efficiency. It also often takes up less space and requires less infrastructure, hence reducing its environmental footprint.
- Flexibility and Control: Industrial microwaves have more control over process parameters using precise power level adjustments that lead to optimal drying conditions for different materials. This makes results more uniform and reproducible.
In conclusion, industrial microwave drying has many advantages, making it a preferred option across various applications. These include speed, energy efficiency, high-quality products, environmental friendliness, and versatility, which explain why modern dryers are adopting them at an increasing rate.
Impacts on product quality and drying time
The usefulness of microwave drying for product quality and processing time is significant and helpful. Initially, microwave drying significantly reduces the drying time as it directly heats moisture inside the material, thus leading to a faster evaporation rate and increased overall processing speed. For example, what may take hours through conventional drying techniques can be affected only in some hours with microwaves.
Moreover, the quality of products is often better when using microwave drying. This method preserves the original properties of materials, such as color, smell, and nutritional value, by using mild, even heat. As a result, high-quality and minimal thermal damage end-products are produced, unlike traditional drying methods.
Lastly, energy efficiency has also been significantly improved. This way, less energy is lost in heating the surrounding environment since microwave power specifically targets water molecules, reducing total energy consumption and lowering operational expenses. In addition to being faster and ensuring that product quality is good enough, it ensures that it’s environmentally friendly, too.
What are the Technical Specifications of an Industrial Microwave Oven?

When looking at industrial microwave ovens, the following crucial technical specifications have to be considered:
- Power Output: Typically ranges from 2 kW to 100 kW, depending on the application and size of the oven.
- Frequency: Industrial and food processing users prefer a standard 915 MHz or 2.45 GHz frequency.
- Chamber Size: Variations in dimension are familiar with bigger chambers facilitating the processing of more significant quantities or largeness.
- Control System: Advanced models have programmable logic controllers (PLC) that offer user-friendly interfaces for controlling temperature, time, and power settings.
- Energy Efficiency: Many models are designed to optimize energy usage, often incorporating reflective materials and insulation to minimize heat loss.
- Construction Material: Normally made of stainless steel to ensure strength, ease of sanitation, and adherence to food safety norms.
- Safety Features: Includes interlocks, over-temperature protection, and fail-safes to ensure safe operation.
- Cooling System: Fans or water cooling are examples of integrated cooling mechanisms used in these ovens to manage heat dissipation for optimal operations.
This way, industrial microwave ovens comply with stringent requirements set by various industries, thus guaranteeing efficiency, reliability, and high performance.
Understanding 6kw and other microwave power ratings
Microwave wattages, for example, 6 kW, significantly affect how well an industrial microwave oven works and its efficiency. This rating shows the energy the stove consumes, thus determining how fast materials can be processed.
- On the other hand, this article will discuss 6 kW microwaves, considered mid-range for industrial uses, as they strike a balance between power consumption and throughput. This type provides sound processing for moderate-sized operations with no wastage of extra power.
- Further, microwave ovens with ratings above 20 kW are designed according to the demands of large-scale manufacturers. These heavy-duty appliances rapidly heat huge volumes of substances in high-demand settings, providing consistent outcomes.
- Meanwhile, microwaves that use power below 6 kW are meant for small-scale applications and more controlled heating while undertaking various tasks. Such devices are perfect for processes that do not require much energy at all.
In summary, when choosing the microwave power rating, one should consider certain aspects, including the production batch’s size, processing speed requirements, and energy-saving objectives that should fit into the given application.
Overview of microwave generator configurations
Microwave generator configurations depend on the application and performance desired. The following are the main types of configurations that you will usually find in industrial settings:
- Single-Mode Generators: Uniform field generators create an even microwave field where materials can be heated consistently. When precise control is vital, single-mode generators become essential, especially during the processing of unique materials that require energy distribution to be even.
- Multi-Mode Generators: These generators produce many modes of microwaves, generating a more dispersed microwave field, making them suitable for bulk processing. This type of generator is common in larger-scale industrial operations where the possibility of uniformly processing large quantities of material is necessary.
- Variable Power Generators: With adjustable power outputs, these systems enable operators to fine-tune microwave frequencies for particular processes. They offer great flexibility and can thus be applied in different applications, ranging from gentle heating requirements to demanding processing tasks.
Optimal performance and energy efficiency are obtained by choosing the right configuration for your microwave generator based on the nature of the material being processed and the specific operational requirements.
Role of the microwave cavity in the drying process
In addition, the microwave cavity performs drying purposes by serving as an enclosure where microwave energy is efficiently turned into heat. By this means, they interact with the moisture content of materials, leading to accelerated heating and evaporation of water. The manufacturing technique adopted in the cavity allows for uniform distribution of microwaves that eventually facilitates homogeneous drying without hot spots or uneven treatment. Furthermore, the glossy interior parts of the cavity go a long way in maximizing energy transfer efficiency, minimizing power usage, and improving the overall performance of the drying process. Consequently, better management of over-drying is realized via optimization of size, shape, and material type, necessitating high standards and energy-saving results.
Applications of Continuous Microwave Drying

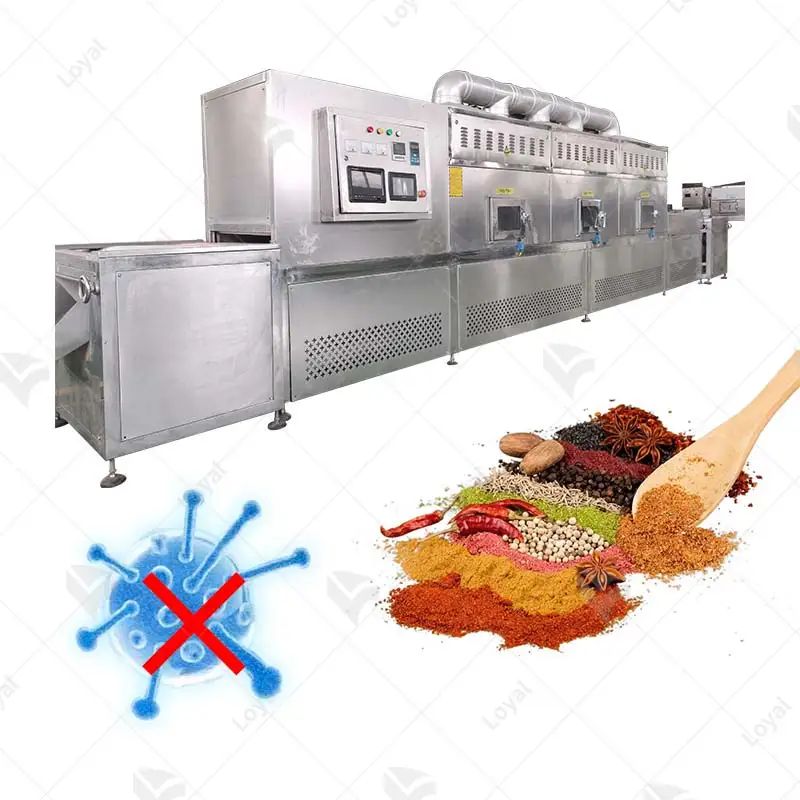
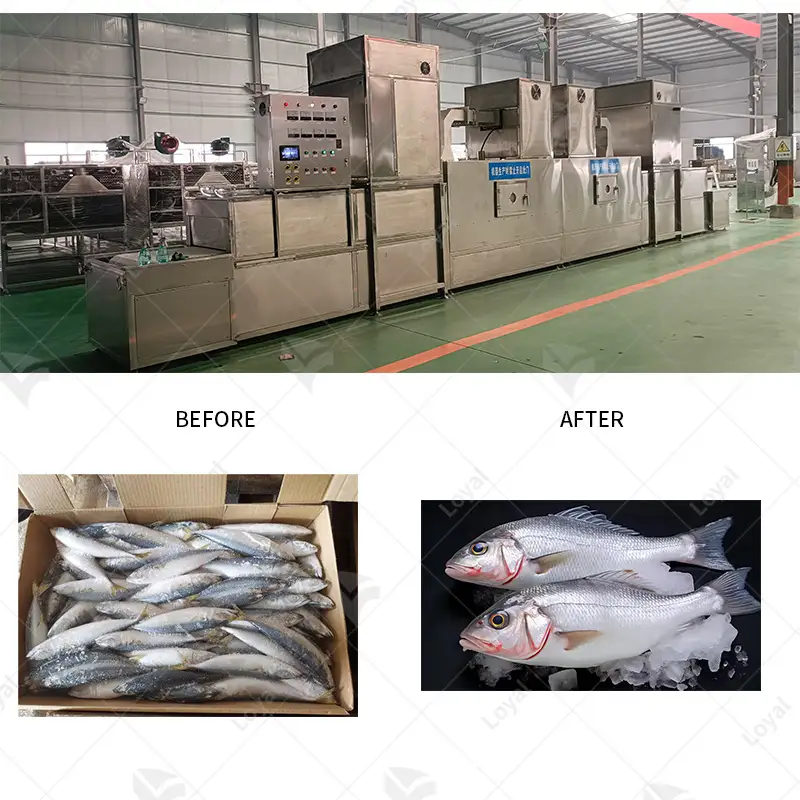
Continuous microwave drying is helpful in many industries as it is highly efficient and effective. In the food industry, it is used to dry fruits, vegetables, and other perishables to retain nutrients and stay on the shelves longer. This process benefits the pharmaceutical sector because it allows for accurate drying of active ingredients and formulations without affecting their medical properties. Continuous microwave drying finds application in the chemical industry, where it processes powders, granules, etc., thus leading to uniform moisture extraction from different materials. Besides, this technology has advantages for paper-making or textile sectors where fibers or fabrics must be consistently kept dry. Continuous microwave drying saves time, enhances energy efficiency, and improves the quality of finished products; therefore, it can be applied anywhere else.
Food processing and mealworm drying
Adopting continuous microwave drying in food processing, specifically for mealworms, ensures they are dried quickly and evenly. This is due to the internal water molecules of the mealworms, which absorb microwave energy and heat up, resulting in fast evaporation that maintains the product’s nutritional content. Such technology drastically reduces drying times compared to conventional methods, increasing efficiency and throughput. Another important aspect of this technique is minimizing thermal degradation, thus preserving mealworm protein levels and quality. Quick drying with continuous microwave drying also supports food safety by reducing microbial growth risk. It is an ecological method of producing worms as food that allows for meeting industry requirements for high-quality and nutrient-rich products.
Pharmaceutical and chemical industries
The pharmaceutical and chemical industries find this valuable technology because it can remove moisture from samples without causing detrimental effects. APIS and excipients are dried using microwaves without losing their bioactivity and therapeutic efficacy in the pharmaceutical industry. Therefore, continuous microwave drying works perfectly on chemicals such as powders and granules, thus ensuring consistency and homogeneity. This technique enhances productivity while reducing drying durations and minimizing power requirements, making manufacturing environmentally friendly and cost-effective.
Drying of sensitive materials using low-temperature methods
Preserving the integrity and quality of delicate materials such as pharmaceuticals, foods, and botanicals demands low-temperature drying methods. To get rid of moisture in these materials without exposing them to severe heat, vacuum drying, lyophilization (freeze drying), and air drying at low temperatures are employed. By reducing the boiling point for water, vacuum drying allows evaporation at lower temperatures by lowering it. Freeze-drying involves freezing a product then subliming ice into vapor in a vacuum where it maintains its structure and essential nutrients. Low-temperature air drying relies on dehumidified air that slowly extracts moisture, safeguarding active ingredients and precluding thermal degradation. These procedures are beneficial for fragile compounds that need to retain their effectiveness, strength, and general eminence throughout periods of loss of water content.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What are continuous microwave dryers?
A: Continuous microwave dryers are advanced drying systems that utilize microwave energy to dry materials uniformly, making the process more efficient and effective than conventional drying methods.
Q: How does microwave energy work in drying machines?
A: Microwave energy interacts with water molecules in the material, causing them to vibrate, which generates heat. This heat evaporates the moisture content, effectively drying the material.
Q: What is the advantage of using microwave technology in industrial drying?
A: Microwave technology offers faster drying times, uniform heating, and energy efficiency. It also reduces the risk of product degradation and enhances the quality of the finished product.
Q: Can a microwave tunnel drying system be used to dry food?
A: Yes, microwave tunnel drying systems are highly effective for drying food. They offer uniform drying and can preserve the food products’ nutritional value, color, and flavor.
Q: What industrial applications benefit the most from continuous microwave dryers?
A: Food processing, pharmaceuticals, and chemicals benefit significantly from continuous microwave dryers’ efficiency, uniform drying, and enhanced product quality.
Q: How does a microwave drying machine ensure uniform drying?
A: Microwave drying machines uniformly distribute microwave energy throughout the material, ensuring that all parts receive consistent heating, leading to uniform drying.
Q: Are there any safety concerns with microwave leakage in these drying systems?
A: Modern continuous microwave drying systems have built-in safety features to prevent microwave leakage, ensuring safe operation and compliance with industry standards.
Q: What is the role of the conveyor in a continuous microwave dryer?
A: The conveyor in a continuous microwave dryer moves the material through the drying unit uniformly, ensuring that it is exposed to consistent microwave energy throughout the process, enhancing drying efficiency.
Q: How does microwave heating and drying compare to traditional heating systems?
A: Microwave heating and drying are faster and more energy efficient than traditional heating systems. They provide uniform heat distribution and better control over the drying process.
Q: What does “microwave treatment” mean in industrial drying?
A: Microwave treatment uses microwave energy to heat and dry materials. It is an effective method for reducing moisture content and achieving uniform drying in various industrial applications.