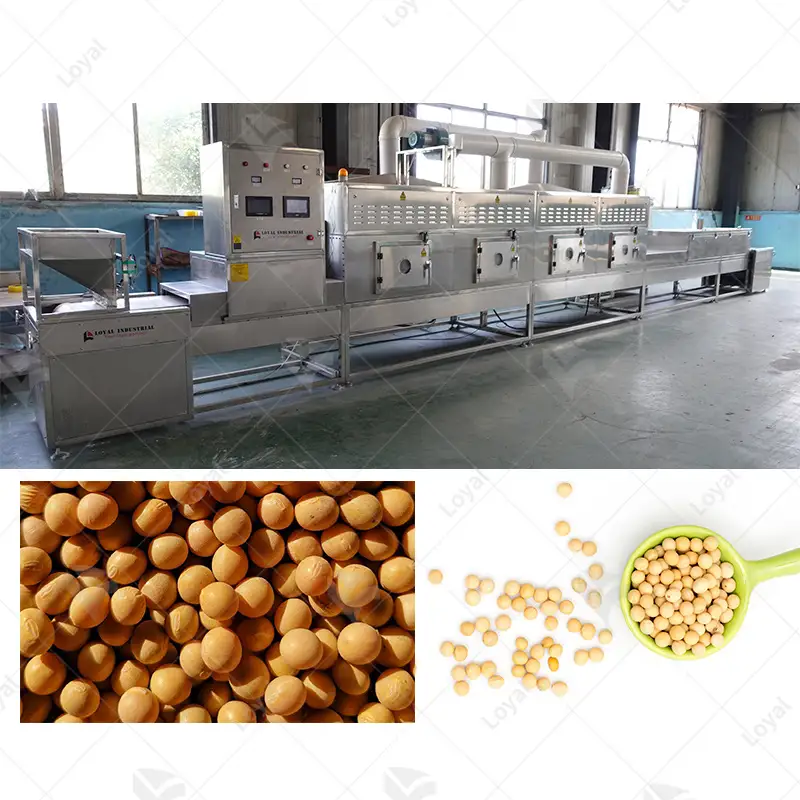
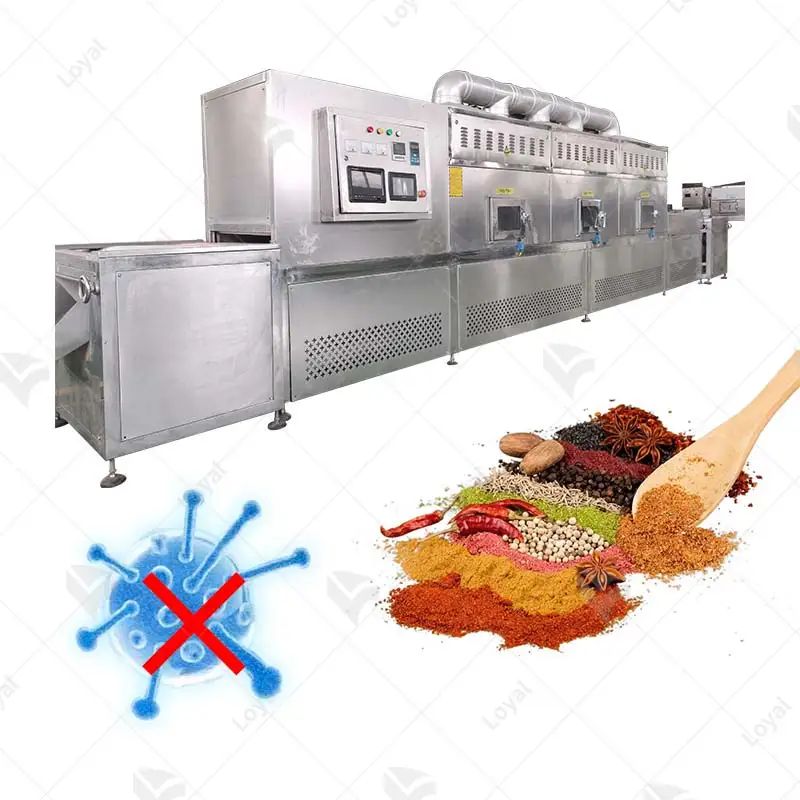
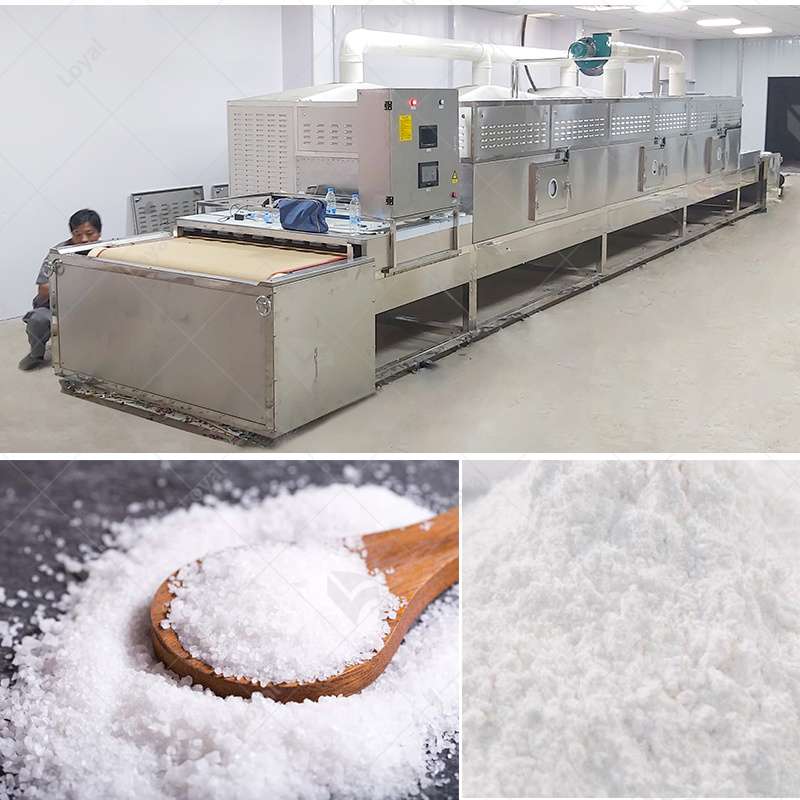
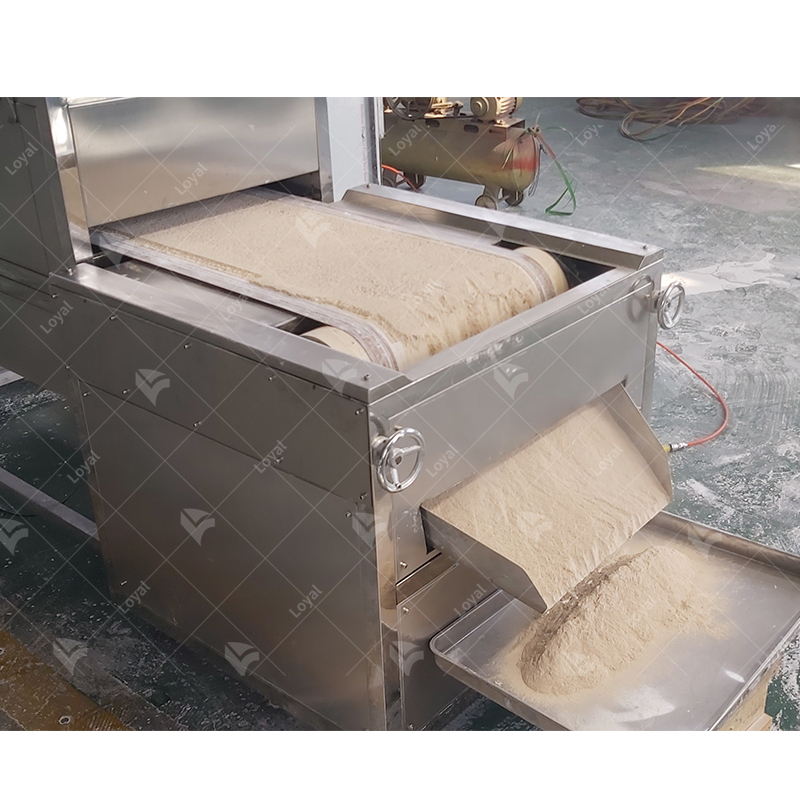
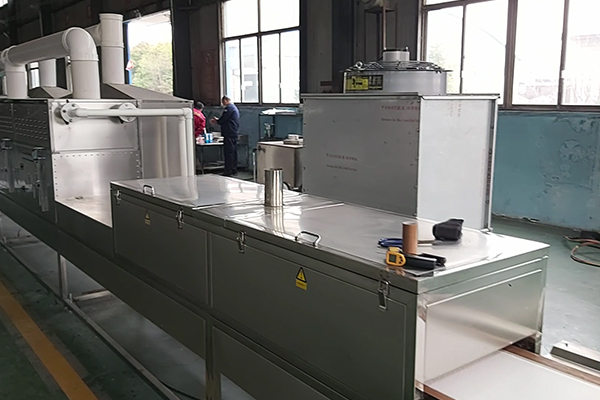
Microwave drying equipment for chemical powders is a significant leap in handling materials. This equipment directs heat through microwaves, thus speeding up the process of drying chemical powders more than it is usually done in traditional ways. The most important merit of microwave drying is that it ensures all parts of the substance being dried have equal temperature, shortening the time spent on drying and improving quality. Additionally, this method can be adjusted to suit various types of chemical powders with different rates or requirements for drying them. In this article, we will discuss the underlying principles behind microwave technology and probe into its advantages and limitations as well as examine its uses across different industries. After undertaking this discussion, I hope readers will have an understanding of how microwave dryer operates toward enhancing efficiency and effectiveness in processing chemical powder by the end of the exploration herein. We will analyze the principles behind microwave drying technology critically and look at its pros and cons while giving examples of where it has been used in various industries.
What is Microwave Drying and How Does It Work?
Microwave drying is a process that employs electromagnetic waves, specifically in the microwave frequency range, to heat and drive out moisture from chemical powders. This approach functions by transmitting warmth internally into the compound by interacting its microwave radiation with polar molecules like water. Microwaves are absorbed by the material, resulting in polar molecule vibrations that generate evenly distributed thermal energy. Even heating throughout eliminates thermal gradients, minimizing potential overheating and degradation of powder. Consequently, microwave drying allows for faster drying times, better energy utilization and uniformity of product quality when compared to conventional methods.
Understanding Microwave Drying Technology
Microwave drying technology is mainly interested in understanding how microwaves interact with powders’ dielectric properties. One very important parameter is the frequency of microwaves, which is usually 2.45 GHz; this has been found to be optimal for absorbing water molecules, which are heated as a result. This frequency is used for efficient energy absorption and conversion into heat within the material’s moisture content.
The power output of microwave dryers should also be mentioned here, although it varies between 500 W and several kilowatts depending on the required drying rate and the nature of the chemicals. It is important to control power levels accurately so that we can avoid non-uniformity during drying and prevent damage to materials due to high temperatures.
On the other hand, penetration depth (δ) refers to how far electromagnetic waves can travel inside a material before they are fully absorbed or scattered away by its bulk properties.Otherwise, there will not be heating if δ does not match the material thickness needed for perfect drying. If we are talking about water in chemical powders, then it penetrates approximately 1-3 cm deep inside them.
Regarding temperature regulation, many microwave dryers have sensors that monitor both surface and internal temperatures to prevent overheating while ensuring product quality. Setting the ambient temperature up to 150°C may work for some thermally stable chemical powders.
By tuning these parameters; frequency, power output, penetration depth and temperature control microwave drying apparatus can be made to suit the specific needs for different powders thereby improving its effectiveness and product values.
The Science Behind Microwave Drying Systems
In essence, microwave drying systems work by using microwaves radiation to interact with water in the powders. The exact frequency of 2.45 GHz has been chosen so as to allow maximum energy transfer to water molecules promoting rapid heating and evaporation. For this reason setting of the required rate of drying is done through power output adjustment which does not compromise thermal stability. Penetration depth is basically a function of dielectric properties of a material that determines uniform heat distribution while sophisticated temperature control measures ensures there are no overheating.The relationship between these factors means that their joint contribution towards an efficient dryer is not mutually exclusive but rather makes it possible for one parameter’s weakness to be made up by another’s strength.
Benefits of Using Microwave Drying Equipment
Microwave drying equipment offers several advantages over traditional dryers, mainly owing to its better efficiency and accuracy in process control. To begin with, as direct energy transfer to the water molecule allows uniform moisture removal, microwave drying significantly reduces drying time. This process is fast enough that fewer risks related to degradation or loss in product quality occur, and hence, applications in industries may be found more effectively.
To bring about these advantages, the following technical factors are important: 2.45 GHz frequency that ensures optimum absorption of energy by water molecules and variable power output from 500 W to several kilowatts to dry at particular rates. The penetration depth is typically within the range between 1 to 3 cm, thus resulting in even heating of different materials. This ensures that there is always a constant temperature, which prevents overheating, thereby maintaining adequate quality of chemical powder. Hence, including these parameters in microwave drying machines leads to increased efficiency during drying as well as helps in maintaining product integrity and quality.
How Does a Microwave Drying Machine for Chemicals Work?
Microwave drying machines for chemicals work under the principle of dielectric heating. When microwaves reach chemicals, they move through objects and cause polar molecules, primarily water to oscillate. The heat that is generated by this movement because of molecular friction evaporates moisture rapidly and uniformly. This process starts with the material being placed in a drying chamber where waveguides evenly distribute microwave energy. As water molecules absorb microwave energy; they become hot and change into vapor which is then blown away using an efficient air system. Advanced control systems monitor the temperature and moisture levels constantly in real-time while adjusting the power output to give precise drying conditions thus avoiding thermal runaway or non-uniform drying. This technique speeds up drying besides preserving chemical integrity and properties.
Microwave Energy as Applied In Chemical Materials
When microwaves are applied to chemical materials, they have several significant effects that contribute to the efficiency of the drying process. Firstly, rapid heating takes place as microwave radiation penetrates deeply into the material, facilitating uniform temperature distribution inside it since all parts attain desired dryness at once.
The frequency of microwave energy is one key parameter with 2.45 GHz being the typical operational frequency used for inducing heat within polar molecules like water in general terms. Additionally, another important factor here is the power of microwaving, which can range from 500 watts up to multiple kilowatts depending on the scale or specific requirements of the drying process.
Moreover, high dielectric constant substances have been found relevant in accelerating rates due to enhanced heating under microwave energy over conventional processes making them more suitable for many chemical compounds during their processing.
Additionally, humidity and temperature control systems are set accordingly to enable fine-tuning of process parameters, guaranteeing consistent quality throughout without degrading chemicals thermally. Microwave systems also have advanced thermal monitoring, which automatically responds to maintain optimal drying conditions, making them very effective ways of conserving chemical integrity while still reducing time spent drying.
Step-by-Step Drying Process in Industrial Microwave Dryers
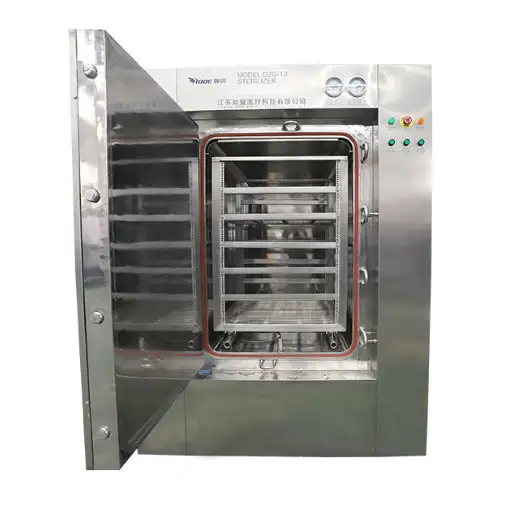
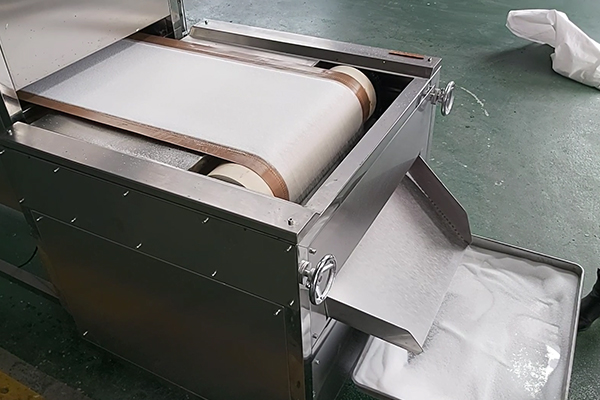
- Materials Loading: Within the industrial microwave dryer, you will load the conveyor belt or trays with chemical compounds or materials to be dried. Ensure that the materials are evenly scattered to ensure homogeneity of exposure to microwave radiation.
- First Stage of Warming Up: Turn on the microwave system. At this stage, the material’s temperature is quickly raised using microwaves at frequency 2.45 GHz which is optimal for this purpose. During this period continuous control of temperature and humidity levels should be observed.
- Uniform Temperature Distribution: Microwave energy promotes uniform heating as it penetrates the materials. With advanced surveillance systems adjusting power consumption and maintaining optimum environmental parameters throughout, hot spots may never arise, assuring consistent drying.
- Drying and Moisture Removal: Microwaves cause polar molecules such as water to vibrate, resulting in heat for moisture removal. This condition is maintained until the dryness level is attained. Materials’ dielectric properties enhance the efficiency of absorption during the drying process.
- Final Cooling Phase: After the target dryness is reached, the materials are permitted to cool and stabilize their chemical structures by setting within the drying chamber or controlled environment to avoid any thermal degradation.
- Unloading and Quality Control: This involves taking dried materials from dryers. In this case, a quality check must be done to ensure that all the required specifications are met. It may involve checking for moisture content and carrying out visual inspections, among other relevant quality assurance tests.
Control Systems of Microwave Drying Machines
Microwave drier control systems guarantee effective and precise operation of microwaves. Such systems encompass a combination of detectors, regulators and software that maintain optimum conditions during drying process. Temperature sensors keep an eye on heat levels in the dryer’s chamber whereas moisture sensors follow the level of humidity in substances being dried. These advanced control algorithms use data from these sensors’ real-time feed-backs to regulate microwave power output, ensuring uniform heating without hot spots. Furthermore, feedback control systems dynamically adapt operating parameters for various material properties changes during drying, thus improving efficiency and product quality. Some of these modern systems also have user-friendly interfaces with automation capabilities enabling operators easily set parameters, initiate drying cycles and remotely monitor process performance.
Why Use Microwave Drying Machines in the Chemical Industry?
The chemical industry has grown to depend on microwave drying machines as they are very efficient and accurate. They have rapid drying times, thus reducing the processing time compared to conventional methods. Throughput is elevated by this efficiency hence increasing the production rates. Furthermore, microwave drying ensures even moisture removal and temperature distributions that are vital in maintaining the quality of chemicals produced. The controlled environment provided by these machines minimizes thermal degradation and allows for precise control over drying parameters leading to higher product quality. In addition, microwave drying systems typically have lower energy consumption which helps save cost and reduces environmental footprint.
Advantages Over Traditional Drying Methods
Microwave dryers offer several benefits if compared to traditional ways such as convection or conduction or infrared dryings. Firstly, microwaves directly interact with the material at a molecular level, making it suitable for quicker processing times than any other way of drying, thus being drastically faster. This results in high drying rates thus reducing the overall processing time by 50-75% relative to conventional methods.
Secondly, microwave drying eliminates unevenness in temperatures during operation, which often results in incomplete dryness and, hence, substandard products before and after collection, respectively, among traditional techniques used. In contrast, there is consistency in terms of power distribution while dough condition remains intact within this contemporary mode of doing things.
Finally , microwave driers consume less power than their traditional counterparts because they tend to lose lesser heat in a more enclosed system thereby taking shorter time when working. Unlike other forms of dries used today, these ones operate on low levels of energy since electrical energy is transformed much better into internal heat within materials they handle . As such their operational costs are low besides having minimal effect on nature . Technical parameters such as specific energy consumption (kWh/kg of water removed) for microwave systems are generally lower compared to conventional drying methods, highlighting their superior efficiency.
Industrial Applications of Microwave Dryers
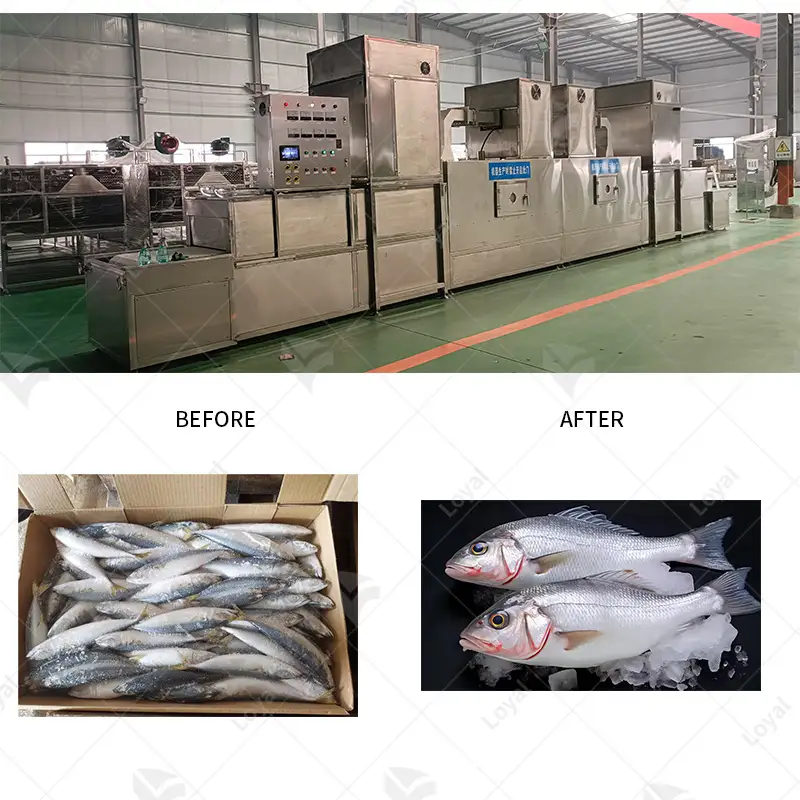
Efficient and effective microwave dryers have been widely used in many industrial sectors. Industrial applications of microwave dryers encompass food industry, where it is used for dehydration of fruits, vegetables and spices among other things like preservation of their nutrients and extending the shelf life. In the pharmaceutical industry, microwave drying ensures uniform drying for active ingredients (APIs) and excipients to maintain efficacy and stability. Microwave dryers’ application cuts across chemical manufacturing as well as materials industries for processing polymers, ceramics, composites with accurate control over moisture content and shorter processing times. Additionally, textile industry uses microwave drying technology to rapidly dry fabrics or clothing without damaging its physical properties such as feel or texture. To ensure an efficient and uniform removal of moisture from any item that requires this process at a high standard.
Efficiency and Cost-effectiveness of Microwave Drying Machines
Microwave drying machines are known for being highly efficient and cost-effective due to rapid heat generation and targeted energy application. The specific energy consumption has been reported as the most important performance parameter by top sources which usually ranges between 0.6 – 1.5 kWh/kg; much lower than that of traditional driers which often exceed 2.5 kWh/kg. This means that the machines consume lesser amounts of electricity hence reducing costs considerably . Also, these devices can cut down on the drying time by half, thereby enhancing more productivity and facilitating savings through reduced labor man-hours or use of equipment during operation compared to using conventional methods alone .
In addition, these machines also have high rates of moisture removal and equal heating characteristics that prevent the occurrence of product defects and promote high-quality production. Current industrial appraisals suggest that drying with microwaves results in constant performance levels thereby leading to optimum manufacturing cycles. Therefore, microwave dryers are cost-effective and practically advantageous for industries since they consume less energy, process within shorter durations and have better quality items.
What Are the Key Features of Microwave Chemical Powder Drying Equipment?
To ensure that these devices are effective and easy to use in manufacturing, several notable features have been incorporated into the design of microwave chemical powder dryers. Frequently, they include state-of-the-art temperature control systems that are indispensable for accurately determining how long the drying process will last and for preventing overheating or underheating. Additionally, their energy-efficient design often incorporates variable frequency drives (VFD) which allows for adjustable power levels and more efficient energy use.
More so, these dryers also have an integrated moisture sensor that checks live conditions to accurately regulate moisture content. This sensor ensures uniformity during the drying process by reducing the chances of excessive drying, maintaining the identity of chemicals. Another advantage is that it occupies limited space in industrial plants.
Moreover, most models come with a programmable logic controller (PLC) complemented by intuitive human machine interfaces (HMIs). These facilitate automation of the entire drying procedure thereby ensuring consistency while at the same time minimizing manual effort. Moreover, they have safety measures incorporated into them such as electromagnetic screening and automatic shutdown systems protect operators from dangerous hazards for safe working environment.
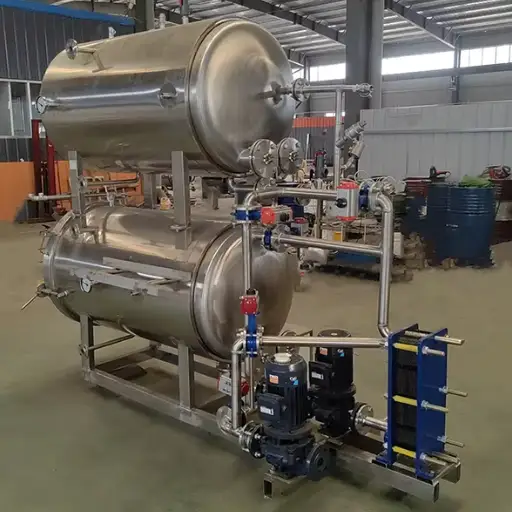
Constituents Of A Microwave Chemical Powder Dryer
That emits electromagnetic waves necessary to dry is usually referred to as a microwave generator, among other items found in a microwave chemical powder dryer. Coupled with this is the waveguide, a critical element that directs these microwaves uniformly into the drying chamber. The drying chamber itself is made from materials resistant to high temperatures and chemical corrosion since it contains some chemicals undergoing drying processes. This chamber has built-in advanced temperature control systems and humidity sensors, which enable real-time adjustments within it, thus making sure that proper conditions are always maintained throughout all phases of the production process. Another crucial element is a variable frequency drive, which enables the regulation of microwave intensity precisely. Besides, there exists a programmable logic controller (PLC) responsible for overall system operation including automatic and customizable drying cycles. Finally, safety mechanisms including electromagnetic shielding and automatic shutdown systems are essential in keeping operators safe as well as safeguarding equipment integrity.
Control System and Automation
A delicate control system in a microwave chemical powder dryer is central to its efficiency. This usually incorporates a programmable logic controller (PLC) that manages the complete drying process from start to finish. Sensors at different points of the chamber collect real-time input information from temperature probes, moisture sensors, etc. Using this data, the PLC controls the microwave power level, air flow rate, and drying duration to maintain optimum conditions for effective drying.
Human Machine Interfaces (HMIs) provide an interface between the operators and a machine allowing for easy programming and monitoring of dryers using simple commands. These permit viewing real time information and alteration of factors such as temperature levels or duration of microwaving among other things within seconds. VFD connected to it is responsible for regulating microwave outputs; hence suitable for various types of chemicals with different drying times.
To illustrate the justifications further, consider these technical specifications:
- Microwave Power Output: It typically falls within the output range of 1 kW up to several hundred kWs, which can be adjusted through VFDs when dealing with different materials.
- Temperature Control: It is done via built-in thermocouples having ±1°C precision, ensuring constant temperature during the dehydration process.
- The moisture sensor has an accuracy of typically within ±0.1% moisture content, providing for accurate monitoring of moisture levels.
- PLC processing speed is another important factor that can make a PLC work in nanoseconds and, therefore, adjust itself and control the process in real time.
- Safety Ratings: Electromagnetic shielding satisfy industrial standards such as IEC 61000-4-3 to protect against electromagnetic interference.
Without these components and parameters, it will be impossible to achieve effective automation and control of microwave chemical powder dryers which are meant for safety, efficiency, and reliability.
MIcrowave Drying Systems Safety Measures
When designing microwave drying systems, operators’ and equipment’s protection is of prime importance; thus, safety measures should be strictly adhered. First and foremost electromagnetic shielding. Compliant with standards such as IEC 61000-4-3 for example shield against electromagnetic interferences through material choice and design preventing microwave leakage. Commonly this includes sealed doors with reliable gaskets, which are interlocked so that if the door is opened the microwave source will not operate.
Secondly, Thermal Monitoring And Automatic Shutdown Mechanisms To Prevent Overheating And Fire Risks Are Incorpated. It monitors temperature with ±1°C Precision using Built-in thermocouples that continuously signal their data converting board. The system automatically shuts down if temperatures rise above preset limits thus mitigating thermal risks.
Thirdly, proper ventilation and exhaust systems for handling vaporized solvents or other by-products need to be installed. These systems must comply with industry standards on occupational health and safety to ensure the efficient removal of toxic vapors from the workplace environment.
Other technical specifications justifying these precautions include:
- Microwave Leakage Detection: The systems are equipped with sensors capable of detecting any leakage in microwaves, making sure no violation occurs according to set regulatory amounts.
- Overheat Protection: Devices like thermal cutoffs or fuses that switch off the current flow when temperatures become unsafe provide additional protection from overheating.
- Emergency Stop Mechanisms: The emergency stop buttons are quickly reachable for operators in case any fault is detected to shut down the system immediately.
- Safety Interlocks: Doors and access panels equipped with interlocking mechanisms disable operation of the microwave source if they are opened hence preventing any contact with harmful radiation.
These safety measures have been integrated into them through strict compliance with technical standards, ensuring optimum performance and the safety of human beings and equipment.
How to Choose the Right Microwave Drying System?
When choosing a suitable microwave drying system, several things should be taken into account. First of all, it is necessary to understand the particular material and its moisture content so as to determine the required performance for drying. Different materials demand varying levels of microwave power and time in order to dry effectively and efficiently. Second, assessing the system’s capacity and throughput is important to make sure it matches your production volume. Higher capacity systems can bring about better efficiency for large scale operations. Thirdly, energy efficiency and operational costs should be considered, whereby energy-saving systems will cut down on operation costs over time. Finally, ensure that your system complies with relevant safety regulations like those set out by OSHA or industry specific guidelines, if applicable. Lastly, reviewing the manufacturer’s support and service options is essential as strong after-sales support can help in maintaining system performance as well as minimizing downtime.
Capacity Cost And Compatibility: Factors To Consider
To assess the capacity of any given microwave drying system, there are some key issues you must keep in mind that will need to match up with what you need to produce. These massive operations usually come with capacities ranging from 50 kW up to 200 kW, and processing takes shorter periods; hence, more throughout also occurs simultaneously. Therefore considering the product materials used may call for a range in output power from 10 kW up to 30 kW.
Cost implications encompass both initial investment outlay and ongoing running expenses, such as current consumption bills, among others. The available choices for microwave drying equipment vary from $50K entry-level models through to +$500K industrial-scale top-end units; cost-effectiveness primarily depends on its design energy utilization (measured typically in kilowatt-hours per kg dried). However, energy-saving versions have long-term savings potential even though their upfront prices might be higher.
Therefore, compatibility is an important aspect that has got to be taken into account because each different type of material requires a suitable dryer that meets all the special drying conditions of its materials. Examples of this would be such as knowing the dielectric properties which determine how it will absorb microwave energy. Furthermore, its fitting into your existing production line should also be considered including things like space constraints, connection to other machines and adhering to industry regulations such as those set by the FDA or EU machinery directives.
With a focus on capacity, cost, and compatibility you can find a microwave drying system that fits your operational requirements, accommodates budgetary limitations and blends well in your production environment.
Personalizing Microwave Drying Solutions For Specific Needs
The customization of microwave drying solutions for specific needs requires one to first understand their own application requirements. It involves analyzing material characteristics, desired drying results, and the manufacturing environment. Some key technical parameters include:
- Power Density: Power density is essential for optimizing the drying process; it is usually measured in kilowatts per cubic meter (kW/m3). However, higher power densities may cause uneven heating or even thermal degradation. Commercial-scale industrial microwave systems typically have power densities ranging from 10 kW/m3 to 30 kW/m3.
- Frequency: The choice of microwave frequency such as 915 MHz or 2450 MHz has an immediate impact on penetration depth and heat uniformity. Where some materials have high dielectric constants they may exhibit greater absorption at one frequency over another. Therefore selection of a good frequency can improve both efficiency as well as product quality.
- Uniform Energy Spread: The creation of a uniformly distributed energy field is significant for maintaining the required drying rate. For example, this can be done with mode stirrers or rotating conveyors. Advanced systems can also include real-time monitoring and feedback to change power levels on demand.
- Control Systems: The advanced control systems allow for precise adjustment of microwave power, conveyor speed, and drying time. Integration with moisture content, temperature, and weight sensors offers better process control so that the desired moisture level is consistently achieved.
- Cooling and Ventilation: Effective cooling and ventilation systems are needed for managing heat during drying processes. These need to include both internal coolings of a microwave source as well as external ventilation which helps to avoid overheating production areas.
Considering these parameters meticulously and employing such technologies as those available in high-end systems, one may tailor microwave drying solutions to meet specific operational needs, thus ensuring efficiency, quality, and cost-effectiveness. This approach is built on cutting-edge materials science and engineering advances that lead to customized drying solutions.
Comparison of various types of microwave drying equipment.
Different types of microwave drying equipment should be compared, taking into account factors such as energy consumption, scalability, cost, and suitability for a specific application. The principal categories of microwave drying equipment include tunnel microwave dryers, vacuum microwave dryers, and hybrid microwave dryers.
- Tunnel Microwave Dryers: These are designed to allow for continuous processing and therefore they can be used in high volume production environments. They have a conveyor belt that takes materials through a field created by microwaves thereby making sure that all parts are dried uniformly. Key technical parameters are typically frequency characteristics – 915 MHz or 2450 MHz, speed of conveyer system, power rating (generally ranges between 10 KWand over 100 KW) and throughput. Important features include mode stirrers as well as PLC-based control systems that ensure accurate process control.
- Vacuum Microwave Dryers: Vacuum microwave dryer operates under reduced air pressure which brings down boiling point of water and thus facilitates faster drying for heat-sensitive substances. For example, these systems are suitable for drying biologicals and pharmaceuticals where retention of properties is critical. Typical technical parameters vary from vacuum levels (between 50-5 Torr), to microwave power (in the range of approximately1-20KW) to processing temperatures. This results in shorter drying times and less thermal degradation
- Hybrid Microwave Dryers: Hybrid systems combine microwaves with other methods like hot air or infrared enabling solutions that can be tailored for specific characteristics of material’s being dried. Such dryers may use lesser energy while improving product quality. The main parameters involved here will include the type of secondary drying method used, combined heat power settings range and control accuracy among others. Dual sources provide better moisture uniformity as well as improved control on both moisture profiles.
Through studying these kinds of microwave driers, including their technological indicators, one may choose an appropriate answer to the problem considering specific operational conditions. Consequently, a broad awareness of the strengths and weaknesses of each type will allow making well-informed decisions, thus enhancing productivity and quality in drying processes.
How to Operate and Maintain Microwave Drying Machines?
A number of steps are involved in operating and maintaining a microwave drier to ensure that it performs efficiently and lasts long. Before turning the machine on, one has to undergo training which provide knowledge on technical aspects of the equipment as well as safety procedures. The entire process begins with conducting pre-operational checks such as ensuring that power connections are intact, there are no foreign materials inside the drying chamber and confirming if a vacuum system is functioning properly where applicable. Configure the equipment to suit specific technical requirements such as power levels, temperatures and drying times for different materials.
While working with a microwave dryer, use its built-in controls that have been programmed to help monitor critical drying parameters like temperature and moisture content. It is important to respond quickly to alarms or other signs of irregularity so as not to spoil either the machine or its product. Always inspect filters, sensors and other vital parts regularly for any build-up or for proper readings.
The maintenance schedule outlined by the manufacturer should be adhered to, including regular inspections, lubrication on movable parts, plus recalibrating sensors, among others. In case any parts get worn out, they need instant replacement before bigger problems arise. In addition, it is important to maintain optimal performance. Having an inclusive operation and maintenance logbook can aid diagnoses of problems while observing operational protocols.
Step-by-Step Guide On How To Operate Microwave Driers
- Initial Set Up And Calibration
- Connect your industrial microwave dryer to a stable power supply’s recommended voltage, usually 220V.
- Ensure environment is clean without any flammable or conductive substances present.
- Using manufacturer’s guidelines (usually temperature sensor adjustment), calibrate internal sensors such that accurate readings can be obtained within±0.5°C.
- Loading Material
- Put the material you want to be dried into the chamber evenly and distribute it all over so that uneven drying will be avoided.
- Do not overload since this may cause damaging the dryer besides leaving areas un-dried; maximum load set by manufacturers is normally given in kilograms or pounds. Overload may cause difficulties in drying and damage the machine at the same time.
- Configuring Parameters
- Material-based drying parameters are to be set. These usually include:
- Power Level – typically can be adjusted within 0.5 kW and 5 kW,
- Temperature, which ranges between ambient values and up to 150°C depending on material heat tolerance,
- Time varies from a few minutes to several hours based on moisture content and thickness of the material.
- Material-based drying parameters are to be set. These usually include:
- Starting the Drying Process
- Activate start button that is located on a control panel.
- Real-time data such as temperature or remaining drying time should appear on display during process monitoring.
- Watch for abnormality signs using in-built alarms like overheating or vacuum system failure indicators.
- Monitoring And Adjustments
- Observations are continuous throughout the drying parameters. To optimize drying efficiency, real-time adjustments could be required.
- If necessary, use an external measuring device for moisture contents checks; adjust a dryers’ time until you reach your desired dryness level.
- Post-Operation Procedures
- After drying finishes, switch off this machinery before unloading it so as not get burned or contaminate yourself with flourishes base materials.
- Check whether the material has attained its desired moisture content; otherwise additional cycles of drying may be needed.
- Cleaning And Maintenance
- Clean the chamber and filters after use, thus removing all residual stuff inside them while ensuring contamination prevention.
- In addition, it is crucial to check filters often by replacing them and recalibrating sensors, as well as inspect electrical connections for wear or damage as directed in maintenance schedules.
Maintaining Equipment Life through Maintenance Tips
This is imperative in several ways. Number one, it is vital to follow the manufacturer’s maintenance schedule as a guideline for conducting regular inspections, cleaning and part replacement. Secondly lubrication must be done on all moving parts so as to reduce friction and wear. These lubricants should be used according to specific indications in the manual. Finally, performance checks should be carried out periodically, which may reveal improper operation or unusual noise indicating potential problems. By following such maintenance routines, you will greatly increase the life span of your equipment.
Microwave Drying Systems Trouble Shooting Common Problems
The most effective way of addressing common problems with microwave drying systems is by taking a step-by-step approach when troubleshooting them. First, uneven drying occurs due to inconsistent distribution of microwave energy. Check waveguides if any obstructions are present and ensure that materials are evenly spread across the conveyor belt. Second, if system fails to start ccheck that electrical connections are properly plugged in and the fuses are not blown out.In addition, safety interlocks and door seals must be checked to ensure they work correctly.Lastly verify that magnetrons are still good , but replace them when they fail; also determine whether or not the microwave generator is fully operational.It is also important for calibration and sensor maintenance purposes.Regular calibration together with sensor maintenance can help keep optimum performance intact
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What is microwave chemical powder drying equipment?
A: Microwave chemical powder drying equipment uses microwave technology to efficiently dry and sterilize various chemical raw materials. This microwave dryer machine is designed for industrial processes, providing rapid drying and heating solutions.
Q: How does microwave drying and heating work in this equipment?
A: Microwave drying and heating involve the use of microwave energy to penetrate chemical raw materials and evenly distribute heat. The microwave equipment accelerates the moisture evaporation process, leading to faster drying and reduced energy consumption.
Q: What are the advantages of using a microwave dryer over a conventional drying oven?
A: Unlike traditional drying ovens, microwave dryers offer several benefits, including faster drying times, more uniform heating, and enhanced efficiency. Microwave drying and sterilization also reduce thermal degradation of sensitive materials, making it ideal for food processing and chemical applications.
Q: Can microwave equipment be used for both drying and sterilizing?
A: Yes, industrial microwave systems are capable of both drying and sterilization processes. These systems, including microwave sterilizing machines, can dry and sterilize materials simultaneously, ensuring both moisture removal and microbial control.
Q: Is microwave drying safe for food processing applications?
A: Yes, microwave drying is safe and widely used in food processing. It preserves the nutritional value and quality of food products while ensuring efficient removal of moisture. This method is popular for fruit drying, vegetables drying, and seafood drying.
Q: What types of materials can be processed with a microwave dryer machine?
A: Microwave dryer machines can process a variety of materials, including chemical raw materials, food products, and pharmaceuticals. They are effective for drying and sterilizing powders, granules, and other forms of raw materials.
Q: What is the difference between microwave vacuum drying and conventional drying methods?
A: Microwave vacuum drying combines microwave technology with vacuum conditions to enhance the drying process. This method reduces drying time and temperature, minimizing the risk of thermal damage and preserving the quality of heat-sensitive materials.
Q: How does microwave drying and sterilization benefit industrial processes?
A: Microwave drying and sterilization offer significant advantages for industrial processes by reducing energy consumption, shortening processing times, and improving product quality. Industrial microwave drying systems are designed for large-scale operations, ensuring consistent and efficient results.
Q: What are the challenges associated with microwave drying techniques?
A: While microwave techniques offer numerous benefits, challenges include the need for precise control over microwave power levels and uniform heating. Additionally, the initial investment in microwave equipment can be higher compared to conventional methods, although the long-term benefits often offset these costs.
Q: What specific applications can benefit from microwave dryer drying machines?
A: Microwave dryer drying machines are versatile and are used in various applications, including food processing, pharmaceuticals, chemical industries, and more. They are particularly beneficial for drying and heating processes that require precise control and efficiency.