This method involves the use of microwave radiation to remove moisture from different materials. Several industries are adopting this method mainly because it is efficient, fast and maintains the quality of the dried product. It differs from traditional drying techniques relying solely on convection, conduction, or radiation by offering quick and uniform heating by selectively focusing on water molecules directly within the material. As a result, drying times and energy consumption are decreased considerably. In this blog, we will look into microwave drying applications across different sectors, investigate what makes it more beneficial, and discuss why such technology is better than traditional drying methods. Therefore, knowledge about its extent and advantages can help industry stakeholders, as well as academicians, recognize its potential for innovation and optimization in multiple processes.
What is Microwave Drying and How Does it Work?
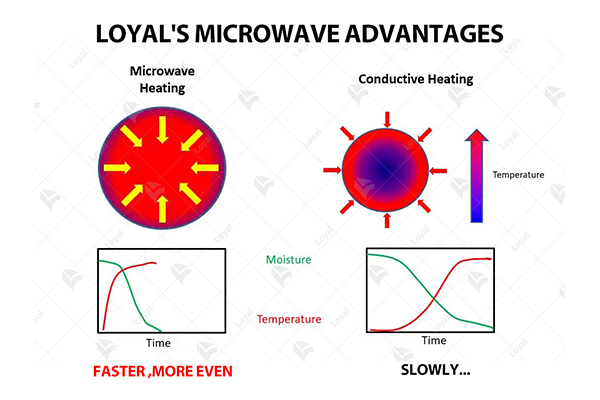
The principle of operation in microwave drying is that moisture within a material can be heated and evaporated by the use of microwave radiation. Microwaves are electromagnetic waves usually with a frequency of 2.45Ghz, which passes through the material and causes violent vibrations in water molecules. The heat generated by this molecular friction increases the temperature, thus supporting moisture evaporation. Unlike conventional drying where heating is done from surface to interior, microwave drying achieves uniform heat through volumetric heating making it more effective in removing moisture quickly. By doing so, these machines take less time to dry and use less energy while, at times, improving the quality of such products as food.
Understanding Microwave Drying Technology
Several distinct advantages are associated with microwave drying technology compared to conventional drying techniques. These include shorter drying times, reduced energy consumption and improved product quality. Depending on material type and moisture content, drying times may be decreased by up to 75%. A dryer’s energy use can be lower than that of traditional dryers if not for 50-70%, as several case studies have demonstrated over many years of industrial practice. Thermal degradation is minimized due to uniform heating during microwave irradiation thus; textural characteristics such as color, taste or nutritional value retain their original state when subjected to this technique.
Some important technical parameters involve: frequency (usually 2.45 GHz) and penetration depth (based on dielectric properties of the material). In terms of power level requirements for different applications range from a few hundred watts used in laboratory scales up-to tens of kilowatts employed at industrial sites. Specific energy consumption (SEC), which is lowly valued for them as compared to traditional methods, is referred to here when talking about efficient heat generation.
The Science Behind Microwave Energy and Heating
Microwave energy being able to penetrate materials and interact with polar molecules like water, leading them to oscillate, resulting in heating, is what defines the microwave heating process.
- Microwave Frequency: To allow effective penetration and heating of most materials, the microwaves are normally set at 2.45 GHz. This frequency is selected based on balancing penetration depth and energy absorption rates across various substances.
- Penetration Depth: This parameter is influenced by the material’s dielectric properties. It characterizes the depth to which microwaves can penetrate a sample before their energy drops off significantly relative to that at the surface. Penetration depths are usually greater for samples containing sufficient moisture or other dipolar compounds.
- Power Levels: Power levels vary by application, from several hundred watts used in laboratory-scale operations to tens of kilowatts employed in an industrial setting for microwave applications. Higher power levels may cause overheating or damage to material if not properly controlled, even though they ensure faster heating and drying.
- Specific Energy Consumption (SEC): The SEC describes how much energy is needed to remove one unit mass of water during drying. Typically, microwave drying has lower SEC values than conventional methods suggesting higher energy efficiency and cost effectiveness.
- Dielectric Properties: These properties, including the dielectric constant and loss factor, dictate how a material interacts with microwave energy. When considering growth rate, it also implies reaction rates due to its importance in determining heat transfer through convection and radiation.
- The energy efficiency for microwave drying systems can be improved, drying times reduced, and the quality of finished products can be sustained when these parameters are considered.
What are the Major Benefits of Using Microwave Drying Systems?
Microwave drying systems have several advantages over conventional drying methods. To begin with, they are fast because of the efficient conversion of microwave energy into heat in the material. This leads to increased capacities and shorter turnaround times. Secondly, heating in microwave drying is uniform, thus eliminating chances of overheating, which would impair delicate parts, hence maintaining the desired quality and integrity of the final product. Furthermore, these machines are more power-effective than traditional dryers; hence they generally require lower specific energy consumption (SEC). This is translated into reduced operational costs and smaller environmental footprints. Additionally, microwave drying systems can be precisely controlled such that parameters can be adjusted to suit different materials and applications that optimize this method for every unique case.
Faster Drying Times and Efficiency
The converse holds true where faster drying times and efficiency in microwave drying depend on the direct interaction between microwaves and the molecular structure of the material through generating internal rather than external sources or radiant heat from other sources. This system consequently evaporates moisture at a faster rate thereby shortening the time required for complete drying. In addition, concentrating energy inherently results in energy-efficient processes by minimizing energy wastage and increasing process efficiencies, on average, within the industry involved between 55-65%. Another advantage of uniformity is that it prevents hot spots which make processing ineffective.
Energy Efficiency and Cost-Effectiveness
There are many factors that contribute to making microwave dryers economical as well as energy-saving appliances. Firstly, since microwaves have spatial resolution properties, localized heating occurs specifically targeting moisture content within materials, leading to a reduction of wasted energy during evaporation processes associated with water loss due to prolonged heating periods involving several hours up to days at most, sometimes referred as dwell time . High SEC values coincide with greater water removal rates during any given period, while conventional techniques may use around 4-6 kWh/Kg and 0.9-1.2 kWh/Kg as applied in microwave drying, respectively.
Additionally, the reduced drying time in microwave drying leads to minimized overhead costs including labor force cost – the only direct or indirect investment involved in using microwaves for drying. By reducing the amount of energy required for drying, shorter duration considerably improves productivity which means higher throughput per unit time for any given production facility thus making it economically viable while lowering total operational costs simultaneously . Also, fewer moving parts result in lower maintenance requirements and costs within a typical microwave system. Such high initial expenditure on capital equipment may eventually be recouped through savings from energy bills and increased productiveness. Therefore, using such driers can be seen as future-oriented because of its monetary and environmental advantages.
Enhanced Product Quality and Consistency
Microwave dryers work by ensuring that there is an even distribution of heat across all sections of the dried substance which results in high-quality products. This kind of uniform heating is made possible by microwaves penetrating throughout materials enabling even temperatures to prevail without surface dehydration or moist interiors. The homogeneity observed during this stage maintains the overall physical and chemical properties intact, including vital attributes like texture, pigmentation, or taste. In contrast, traditional hot air methods lead to thermal degradation with great loss of volatile compounds. An end product has good quality attributes as well as consistency allowing it to meet strict industrial benchmarks set by customers’ demands.
How Does Microwave Drying Compare to Heat and Conventional Drying Methods?
Microwave drying is distinct from thermal and conventional drying processes in several ways. In microwave drying, heat is generated inside the material using electromagnetic waves rather than relying on external heat sources as has been the case with traditional drying techniques. This leads to faster and more uniform drying which reduces the time taken for the process significantly. On the other hand, traditional methods often experience surface drying problems that can result in irregular moisture distribution and even spoilage of the produce. However, this does not happen in microwaves because volumetric heating removes moisture from all parts of material without affecting its quality. In addition, microwave dryers work at lower temperatures which helps to retain nutritional values and sensory properties of delicate materials such as food or medicine. Moreover, microwave dryers are usually more efficient thus making them cost effective over time due to low energy consumption rates and fast processing times.
The Relationship between Water Evaporation Efficiency And Energy
Microwave drying demonstrates greater efficiency in evaporating water than conventional techniques do. This is predominantly attributed to how energy is applied differently by each method. Microwaves go through a substance, prompting water molecules to vibrate at high speed, thereby generating heat till it eventually generates steam internally within it. These include power intensity, frequency, and dielectric constant of materials, as well as some other important technical parameters controlling this process. Commonly, microwaves have frequencies of 2.45 GHz that interact best with water molecules during the heating process. Power intensities may vary but are often maintained between 500-and 1,200 watts depending on the intended application and composition of the material being dried.
One important aspect of microwave drying is that it ensures evaporation occurs uniformly throughout all parts of a product without giving room for superficial overheating or internal retention within material, two typical drawbacks associated with standard methodologies employed in this field (Wang et al., 2018). Due to this conductive heat transfer mode bypassed during microwave treatment much faster drying takes place, sometimes by 50-75% compared to that using hot air. In addition, the ability to adjust power gives great control of the drying process, thereby avoiding thermal decomposition and destroying the material’s quality. This way, energy is saved and the final product acquires an improved overall quality and high nutritional value.
Influences on Water Content and Product Texture
Microwave drying has a significant impact on water content and texture. Since microwave energy interacts directly with water molecules, their drying becomes highly efficient such that residual moisture contents can be reduced to almost zero levels. This ensures that there is no unnecessary loss of energy during the attainment of the desired dryness for the finished products. The technical parameters related to this include microwave power (usually from 500-1,200 watts), frequency (mostly at 2.45 GHz) which are specific dielectric properties of materials taken together in order to optimize water evaporation.
Product texture is also influenced greatly by microwave drying. In contrast to conventional methods that use more time to dry because they heat slow or unevenly microwaves ensure faster heating throughout ensuring more natural textures remain in most materials after processing. Here there happens less surface hardening as moisture escapes uniformly from within. Some factors affecting the texture of dried products include power intensity, exposure time, and initial moisture content of the starting material. For instance, while higher power intensities might be important for speeding up drying rates, they must be controlled properly so as not to lead to textural damage. Additionally, maintaining a controlled environment during drying helps preserve cellular integrity thereby guaranteeing superior dried produce quality
Advantages Over Hot Air and Vacuum Drying
Microwave drying has various benefits over the hot air and vacuum drying methods. Firstly, compared to hot air drying, microwave drying saves a lot of energy. The reason for this is that microwaves directly interact with water molecules enabling targeted heating hence minimizing energy wastage. Moreover, in microwave drying, it shortens the period of drying significantly. This means that while hot air drying may take extended periods to achieve the desired moisture content, microwave can do this within a short time because of its good energy transfer.
In terms of product quality, nutrient retention loss is lower in microwave drying than in vacuum drying due to minimal structural damage. Unlike vacuum drying, where nutritional degradation can occur due to prolonged exposure, the rapid and uniform heating properties characteristic of microwave drying preserve the nutritional components in these products. In addition, surface hardening incidence is minimized by microwave during the process, which occurs frequently in hot air dried products, leading to a more homogenously dried final product.
Technical parameters are key determinants in the advantages associated with using a microwave dryer. Major parameters include the range of power (usually between 500-1,200 watts), frequency (2.45 GHz normally), and dielectric properties of the material which determine the absorption capacity of microwave energy. These collectively improve the efficiency and quality of the dry process, thus making it possible for traditional systems like hot air or vacuum driers to become inferior compared to using microwaves instead.
How is Microwave Technology Applied in Industrial Drying Processes?
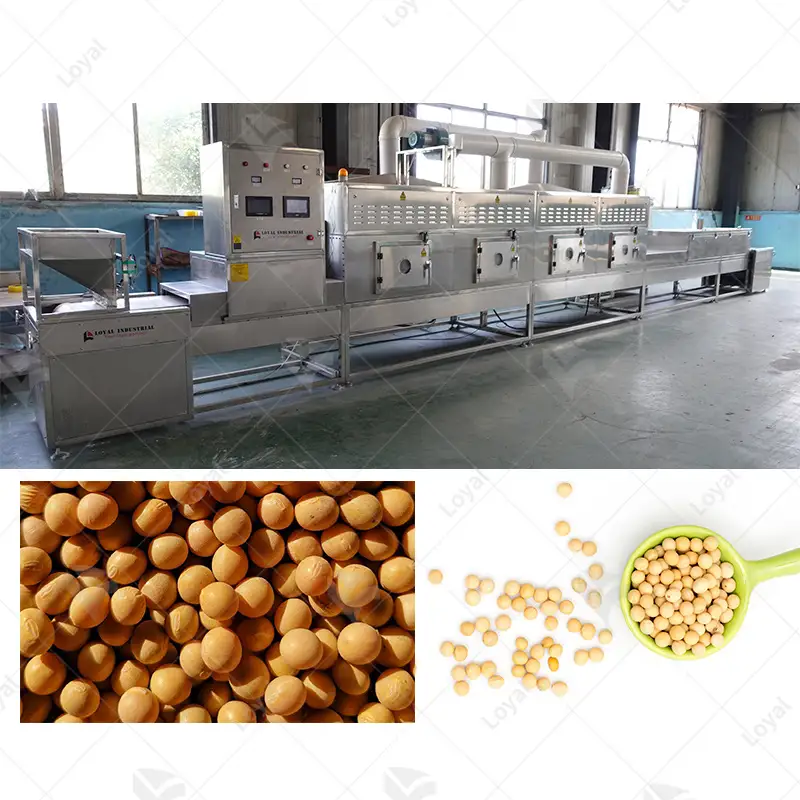
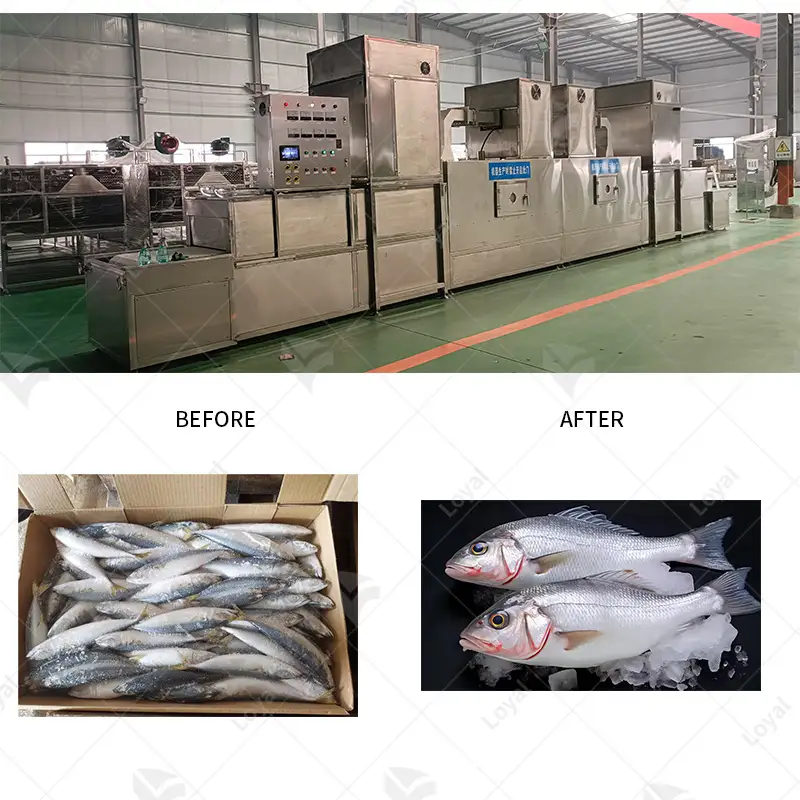
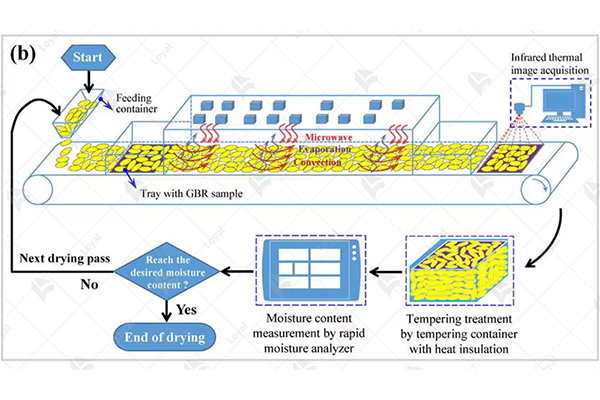
Microwave technology is applied in industrial drying processes to boost efficiency and product quality significantly. This technology resorts to electromagnetic waves to excite water molecules within the material hence causing rapid internal heating and vaporization of moisture. The present method has enabled the control of every aspect of the drying process, cutting down on both the time for drying as well as energy consumed more than traditional methods do. For example, bulk products such as food, medicines, ceramics, and apparel, just to mention a few, can be dried using this technique. These systems can result in better moisture uniformity across the finished product and high throughput.
What Industrial Microwave Drying Systems Entail
The design of these industrial microwave drying systems is based on the effective use of microwave energy in removing moistures efficiently from materials. Some components found in these systems include a microwave generator along with waveguides, applicators, and conveyor belts that transfer materials from one place to another. Here, they are transformed into a form suitable for irradiation by being channeled through wave guides into applicators where microwaves become uniform before being used.
Controlled microwave power is an important feature of these systems with applications ranging between 500 watts up to 50 kilowatts depending on their intent. A frequency of 2.45 GHz is most commonly used because it provides the best balance between penetration depth and energy absorption efficiency. The rate at which materials absorb microwave energy, hence affects how efficient or inefficient its resultant drier will be, is determined by its dielectric properties, including dielectric constant and loss factor.
Moreover, industrial microwave drying systems have flexibility ready made for adapting them for particular purposes like foods, drugs, ceramics and textiles amongst others. Thus, due to their capability for fast controlled heating processes, they take shorter times to dry than conventional methods, therefore saving on energy consumption rates up to above fifty percent (50%) or even seventy-five percent (75%) less time.
In conclusion, these systems control drying through microwave power, frequency and material properties with exactness thus making the process efficient and uniform. This in turn leads to high throughput, moisture uniformity and preservation of the quality as well as structural integrity of the product.
What are the Recent Applications of Microwave Drying in Different Industries?
Various industries have recently applied microwave drying, which demonstrates how versatile and efficient it is. In the food industry, microwave drying is increasingly used to process vegetables, fruits, and herbs. Some of the advantages that make this method popular in the pharmaceutical sector include improved flavor, texture and retention of nutritional components in foods. Besides, for the pharmaceutical industry, microwave drying is essential when drying active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) and excipients because it helps maintain stability and efficacy of compounds while at the same time reducing drying time as well as energy consumption. Similarly, in wood and paper industries microwave drying has been employed to hasten the drying rate of timber products and papers thus improving product quality as well as reducing defects like warping and splitting.
Applications on Food Products and Agriculture
The food industry and agriculture have widely embraced microwave drying due to its efficiency coupled with the preservation of critical attributes in end products. Some leading sources stated that ” microwave-drying food products may improve vitamin retention.” Microwave-dried Fruits contain up to 90% more Vitamin C than those dried through other methods, such as air or sun drying.
For agricultural uses, grains, particularly seeds, do very well under microwave drying conditions, while others, such as legumes, also benefit a lot from this technology. The most common technical parameters mentioned are frequency around 2450 MHz with a power range between 500-1500W, which gives better uniformity during drying without changing the original properties of the material. For example, wheat can be dried quite rapidly down to required moisture levels when operated at 900 W leaving kernels intact.
According to efficiency measures, microwave drying achieves moisture reduction rates up to 15% per minute compared to about 1-2% by hot air dryers. As a result, processing time is reduced significantly, thereby saving energy. Specific energy consumption can fall to around 0.56 kWh/kg water removed relative to approximately 1.5 kWh/kg for conventional hot air methods.
In summary, the advantages of microwave drying in terms of practicality and technique have made it a preferred choice in food products and agriculture for maintaining cost-effectiveness, quality preservation and efficiency balance.
Microwave Drying in the Pharmaceutical Industry
One of the main benefits of microwave drying in the pharmaceutical industry is moisture removal even without damaging heat-labile compounds. Among other observations, “microwave-dried products retained more stability and efficacy than air—or freeze-dried ones”. Furthermore, similar to food processing, technical data from reliable sources confirm that microwave drying takes place at power levels between 100 and 1000 W with frequencies around 2450 MHz to ensure uniform drying and other quality outcomes.
Reliable figures from standard sources also indicate that the drying rate could rise up to 10% per minute under microwave conditions as compared to vacuum drying at about 1-2%. Also, energy consumption is quite low ranging from 0.75 up to about 1.7 kWh/kgH2O removed for pharmaceuticals unlike traditional techniques which consume at least twice as much as this value respectively. This reduction in both time spent during drying and energy used has resulted into reduced costs thus making it efficient for pharmaceutical manufacturers.
Also, microwave drying technology in drug production minimizes thermal degradation, thereby preserving the bioactivity of compounds. Optimizing drying parameters such as control over power and time of exposure to microwaves is important for preventing hot spots and ensuring uniformity in product quality. In pharmaceuticals, this minute control is very important since it has to do with making sure that drugs are uniformly made to achieve their purpose.
These notable advantages make microwave drying applicable in pharmaceuticals, strengthening its position as a useful technology for producing and conserving high-standard medicinal products.
What are the Benefits and Limitations of Microwave Drying?
Microwave drying has several advantages. First and foremost, it has quicker dry-out rates than conventional methods, thus reducing processing times reasonably. This time-saving effect is further coupled with lower energy consumption, which means lower operational costs as a result of microwave drying. Otherwise, microwave drying helps in maintaining the integrity and bioactivity of pharmaceutical compounds through minimal thermal degradation. Moreover, uniform drying and elimination of hotspots within the product are further enhanced by ability of this technology to provide precise control over exposure time and power.
Nonetheless, there are limitations to microwave drying. One in particular is the steep cost of specialized equipment installation. Additionally, if not well controlled, it can lead to uneven heating, thereby compromising process efficiency and resulting in variability in the quality attributes of the dried products. For higher-scale productions, uniform drying will necessitate more complex and costly setups.
Benefits Derived from Drying Time Reduction
Microwave drying has exceptional benefits for minimizing drying time by using the special characteristics inherent in microwave power to hasten water extraction from pharmaceuticals.Therefore, unlike traditional processes that rely on heat transfer from outside sources, microwave energy directly heats up water molecules through molecular friction.It also becomes easier to remove moisture in shorter periods since much less time is consumed when applying direct heating compared with other procedures such as convectional methods.Microwave Drying Shortens Moisture Reduction Time for Increased Pharmaceutical Manufacturing Process Efficiency and Throughput
The leading information explains how 50-90% faster than conventional methods can be achieved using a MW dryer.” The reason behind this fast rate of evaporation lies in volumetric heating effects, where microwaves get into materials to produce heat uniformly over the entire material.Therefore, there is a significant reduction in processing time, which makes it very useful for compounds that are thermally unstable.
Major technical parameters that should be optimized during microwave drying include frequency (usually 2.45 GHz), power density ranging from 0.1 – 1.5 W/g, and dwell time, which depend on the specific product requirements. Control of these factors ensures material quality, decreases thermal degradation, and enhances uniformity, thereby justifying the use of microwave drying in high-end pharmaceutical applications.
Possible Concerns and Methods to Overcome Them
Microwave drying offers several advantages; nevertheless, potential setbacks need to be addressed in order to achieve optimal outcomes. One important problem is non-uniform dryness, which gives rise to areas with enhanced temperatures or regions where there is not enough moisture. Therefore, it is necessary to monitor the output power and exposure time very carefully so that uniformity is observed all over the material. In cases where hot spots have been identified, rotating mechanisms can help improve uniformity while reducing local overheating.
The other worry is that sensitive compounds may undergo thermal degradation. This can be corrected by fine-tuning the microwave frequency as well as power density values used during MW drying process. For example, reducing the power density value close to 0.1 W/g allows for minimum heat build-up with mild but effective drying effects.The hydration level can also be lowered through intermittent application of microwaves or by including short cooling stages so that heat-sensitive ingredients are not damaged.
Lastly, issues pertaining electromagnetic interference (EMI) and safety should not be disregarded either. This is because preventing EMI risks entails utilizing appropriate shielding techniques as well as containment procedures combined with regular equipment checkups.Operator’s safety comprises operating under standardized procedures coupled with additional protection mechanisms such presence of automatic shut off buttons plus temperature limits.In conclusion therefore, microwaving drying should always take into consideration such drawbacks when then processes are going on by maintaining good performance monitoring systems than this will help them overcome these limitations effectively
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What is microwave drying and how does it work?
A: Microwave drying involves using microwave processing technology to heat and remove moisture from materials. This process is quicker compared to traditional methods like drying rooms and convection ovens. In industrial microwave systems, materials are subjected to microwave power, causing water molecules to vibrate and generate heat, leading to rapid drying.
Q: What are the benefits of using microwave drying over traditional drying methods?
A: Microwave drying is quicker and more efficient compared to traditional methods like drying rooms and convection ovens. It provides excellent color drying and adhesive setting properties, ensures uniform drying, and improves energy efficiency. Additionally, it helps preserve the quality and integrity of the material being dried.
Q: Can microwave techniques be used for industrial applications?
A: Yes, industrial microwave systems are widely used for drying and heating in various applications, including food processing, pharmaceuticals, and building materials. These systems offer precise control over drying procedures and can handle large-scale operations efficiently.
Q: How does microwave drying affect the quality of building materials?
A: Microwave drying has been found to maintain or even enhance the quality of building materials. It ensures thorough drying, preserving the structural integrity and preventing issues like warping or cracking. Microwave treatment also results in better adhesion properties and color stability.
Q: What are some common applications of microwave drying in the food industry?
A: In the food industry, microwave drying is used for drying fruits, vegetables, and grains. It helps retain nutritional value, color, and flavor better than conventional methods. The quick drying process also helps in reducing microbial contamination.
Q: How does microwave drying compare to freeze drying?
A: Microwave drying is significantly faster than freeze drying and requires less equipment and energy. While freeze drying is excellent for preserving heat-sensitive materials like pharmaceuticals, microwave drying offers a more efficient and cost-effective alternative for applications where rapid drying is essential.
Q: Are there any specific safety concerns associated with microwave drying?
A: When using industrial microwave systems, safety measures must be followed to prevent exposure to microwave radiation. Proper shielding, user training, and regular maintenance of equipment are essential to ensure safe operation.
Q: What role does infrared heating play in microwave drying processes?
A: Infrared heating can complement microwave drying by providing surface heating while microwaves heat the material internally. This combination can enhance drying kinetics and improve overall drying efficiency.
Q: How does microwave drying benefit adhesive setting processes?
A: Microwave drying provides excellent adhesive setting properties. The uniform heating ensures proper curing of adhesives, which results in stronger bonds and faster processing times compared to conventional drying methods.
Q: What types of materials can benefit from microwave drying techniques?
A: A wide range of materials can benefit from microwave drying techniques, including foods, pharmaceuticals, ceramics, polymers, and textiles. The method is particularly beneficial for materials that require quick and controlled moisture removal.