Microwave drying has changed industry views on drying procedures by providing a more efficient, even and quicker alternative to conventional drying techniques. The purpose of this extensive guide is to give you an in depth appreciation of microwave drying technology, its advantages, areas of application and the things one should keep in mind when selecting the right equipment for their needs. If you are new to the concept or want to enhance your present operations then this article will be everything on microwave drying machines that you will ever need.
What is Microwave Drying and How Does it Work?
Microwave drying is a process that uses microwave radiation to extract moisture from different stuff. In contrary to typical means of drying which are dependent on external heat sources, microwaves produce heat by immediate energy waves in the stuff. The water molecules vibrate upon the impact of the waves causing friction among them and hence heating up. This leads to uniformity during rapid drying.
Some of these benefits include; it cuts substantially time spent while drying, saves energy and keeps moisture removal constant for quality preservation of desiccated commodity. Food processing industries, pharmaceuticals and chemistry manufacturing have been using microwave drying as an efficiency measure that ensures high quality products.
Understanding Microwave Drying Technology
This kind of technology operates through releasing microwaves that go through materials and bring about molecular friction thus inducing heated state within these substances. Means faster yet uniform drying since water molecules become agitated leading to internal heating. Energy absorbed primarily by water content unlike traditional methods where there is uneven drying caused by external heat sources which makes it highly efficient for microwave drying purposes. The reports indicate that this method greatly reduces the time taken for clothes to dry consequently reducing cost; effectively minimizes energy consumption as well as enhancing product quality by avoiding overheating during the process.
Microwave Power and its Role in Drying
The efficiency and effectiveness with which drying takes place are determined by microwave power levels used. It then becomes possible for industries to control how fast their materials dry through altering microwave power settings available on their equipment. For instance, higher power levels will result in shorter but carefully managed periods so as not to overheat thereby spoiling its nutritional value (Gao et al., 2009). Conversely, lower power settings prolong the length required for material dehydration but can enhance uniformity during moisture withdrawal and prevent scorching from happening at surface level (Saravacos & Krokida, 2002). Top resources underline that attaining fastest yet even driers together with proper quality of the processed substance is a matter of combining in microwave drying.
Key Advantages of Microwave Drying Systems
These are among the key benefits that make microwave drying systems gain popularity in various industries;
- Rapid Drying Times: One of the greatest advantages is how quickly materials can be dried. Conventional methods take longer to dry compared to microwaving which directly acts on water molecules within the material (Dong et al., 2013).
- Energy Efficiency: Most of this energy is taken up by the water only hence very little heat loss and therefore it becomes an energy efficient process. This reduces power consumption while cutting costs.
- Improved Product Quality: With microwave drying, nutrients remain intact making it possible for commodities to have higher quality. By avoiding excessive heating due to scorching as well as maintaining accurate power settings, a product whose quality is slightly high is obtained.
- Uniform Moisture Removal: Another important advantage associated with this technique involves uniform moisture elimination from products. When surfaces get over-dried or there are moisture gradients within the objects, such challenges can be avoided through uniformity.
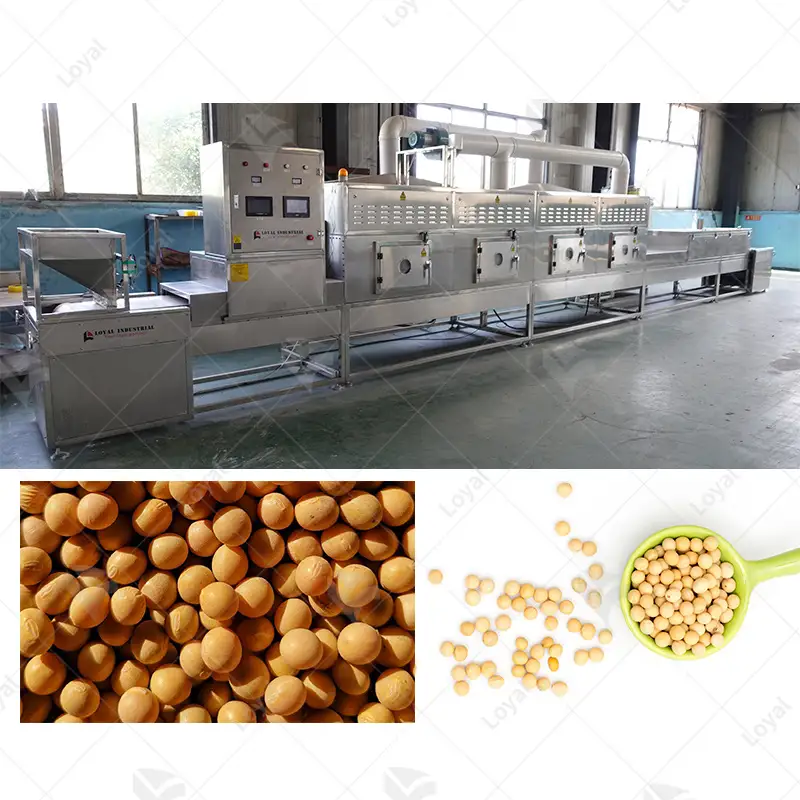
Microwave Drying Systems are very versatile and can be used on various materials such as food, pharmaceuticals and agricultural products. This flexibility makes it an important device for use in different areas.
These benefits show why microwave drying systems are considered so highly, particularly in industries where emphasis is on product quality and energy savings.
Why Choose a Microwave Drying Machine Over Traditional Methods?
The following benefits can be used to compare a microwave drying machine with traditional methods in terms of the available technical parameters and operational benefits:
Fastness and Efficiency
- Dry Time: Microwave drying reduce drying time by 50-70% against conventional methods.
- Power Consumption: 30-50% more energy-efficient due to focused heating, leading to significant cost savings.
Product Quality
- Nutritional Integrity: Studies show that up to 90% of vitamins and minerals are retained during microwave drying while conventional drying has been known to retain much less.
- Structural Preservation: Original texture and color are maintained, making the items more appealing.
Uniform Drying
- Even Moisture Content: Uniformity in moisture content is essential as products cannot be over-dried or have uneven moisture content (McMinn et al., 2010).
- Temperature Control: Depending on the material being dried, precise control settings that maintain temperatures around 60 °C – 120 °C are usually employed.
Flexibility and Scalability
- Material Compatibility: Suitable for many different products such as food materials, pharmaceuticals and agricultural commodities (Fernandez et al., 2008).
- Scalability: These machines can be scaled easily from small lab-scale models to large industrial units designed to handle production capacities varying from few kilos to several tons per hour.
Environmental Effects
- Reduced Emissions: Use of energy reduces carbon footprints as well as emissions thereof.
- Water Utilization : It minimizes water usage which promotes sustainable approaches during drying process (Banaszewska et al., 2015).
These technical parameters along with operational advantages make microwave dryers a better option than traditional methods due to their high efficiency, better product quality, and environment-friendly practices.
Comparison between Microwave Dryers & Hot Air Drying
Comparing microwave dried products with those obtained using hot air drying requires the consideration of several critical factors each explained by corresponding technical terms:
Energy Saving:
- Microwave Drying: More energy efficient due to direct application of energy to the product, leading to shorter drying time and energy savings.
- Hot Air Drying: Often less effective in terms of energy conservation since it relies on convection heat transfer that causes greater energy wastage.
Product Quality
Nutritional Integrity:
- Microwave Drying: Retains up to 90% of vitamins and nutrients.
- Hot Air Drying: Usually results in reduced nutritional value which is related to high temperatures and long exposure times.
Structural Preservation
- Microwave Drying: Better texture and color retention.
- Hot Air Drying: It can cause shrinkage, discoloration, or even texture destructions.
Drying Uniformity:
Even Moisture Content:
- Microwave Drying: Ensures uniform moisture content within the product, reducing risks of over-drying or uneven moisture distribution (Ratti et al., 2001b).
- Hot Air Drying: Uneven drying with more moisture retention at the periphery is often observed.
Temperature Control
- Microwave Drying: Precise temperature control within 60 °C – 120 °C (Wang et al., 2015).
- Hot Air Drying: Final product quality may be affected because temperature control is not as precise as in microwave drying technology.
Operational Versatility & Scalability:
Material Compatibility:
- Microwave Drying :It works well for many different products including food materials, pharmaceutical substances and farm produce (Pandit et al., 2006).
- Hot Air Dying :Mainly used for bulk drying of homogenous materials (McMinn et al., 2010).
Scalability
Microwave drying. Easily scalable from small lab machines to large industrial units that handle production capacities ranging from several kilograms per hour to several tons an hour (Banaszewska et al., 2015).
Hot air dying. Generally scalable but with less flexibility in terms of product types and batch sizes.
Environmental Impact:
Energy Consumption:
- Microwave Drying: A lower carbon footprint is attained as energy consumption is reduced (Ratti et al., 2001a).
- Hot Air Drying: Greater energy consumption implies more emissions.
Water Usage:
- Microwave Drying: This approach promotes sustainable operations due to its low water usage (Banaszewska et al., 2015).
- Hot Air Drying: In some cases, such drying can be accompanied by significant amounts of process cooling water.
Thus, hot air drying is far less efficient than microwave drying in terms of energy savings, quality, and environmental safety, thereby positioning the microwaves dryers as a better option for contemporary drying processes.
Microwave Vacuum Drying vs Conventional Vacuum Drying
There is a distinction between microwave vacuum drying and conventional vacuum drying in terms of moisture reduction in materials, with each having its own advantages and drawbacks. The following comparison answers the questions succinctly and provides respective technical parameters:
Drying Efficiency;
Microwave Vacuum Drying:
- Speed: Faster drying time by direct heating which often reduces the drying time to half.
- Uniformity: It ensures a more uniform drying minimizing over dried or under dried spots.
Conventional Vacuum Drying:
Microwave Vacuum Drying:
- Nutrient Retention: Better preservation of heat-sensitive nutrients and compounds.
- Texture And Color: It preserves texture and color more efficiently thus preventing thermal degradation.
Conventional Vacuum Drying:
Microwave Vacuum Drying:
- Energy Use: In most cases it will lead to less overall energy consumption due to shorter drying times.
- Efficiency: This can be highly energy efficient since energy is directly used for material heating purposes.
Conventional Vacuum Drying:
Material Compatibility;
- Microwave Vacuum Drying; A wide range of materials including sensitive or high value products are compatible with this technology for removing water from them by evaporation.
- Conventional Vacuum Drying; Usually it is applied to relatively robust materials where slow rate of removal of moisture is not an issue.
Scalability;
- Energy Consumption: As mentioned earlier, microwave vacuum drying is less energy consuming which results in lower carbon foot print on the other hand.
- Waste: Microwave vacuum drying cuts down on waste because of accurate control during processing as opposed to other models that may go through imprecise ways resulting to these wastages being higher than expected when using microwaves.
Technical Parameters used in Justification:
- Microwave Power: 1-10 kW, adjustable based on material and batch size.
- Vacuum Level: Often maintained within 50-200 mbar range for microwave assisted processes i.e., with low temperature applications such as drying.
- Drying Temperature: It can dry from 30 to 80°C very precisely within a desired range of these figures while the conventional vacuum dryer cannot be adjusted as fast and may operate in a similar range.
- Drying Time: Dryings may take from one to four hours depending on the nature of material in microwave vacuum drying whereas conventional vacuum dryings may require up to twelve hours.
These comparisons show that microwave vacuum drying is more efficient, has better product quality and is more environment-friendly than conventional vacuum drying, making it an advanced model of drying.
Energy Efficiency and Environmental Impact
Because of its targeted heating mechanism, which avoids energy wastage, microwave vacuum drying consumes far less energy than traditional vacuum drying. As such, it decreases the overall carbon footprint resulting in a greener and more sustainable form of dehydration process. Additionally, this technique minimizes waste by giving precise control over microwaves which is not only beneficial for environment but also saves resources. Therefore this latest technology for evaporation using microwaves does not only provide for best utilization of energy but also ensures high quality end products thus making it a choice above other technologies concerning conservation practices and energy efficiency.
What are the Applications of Industrial Microwave Drying Equipment?
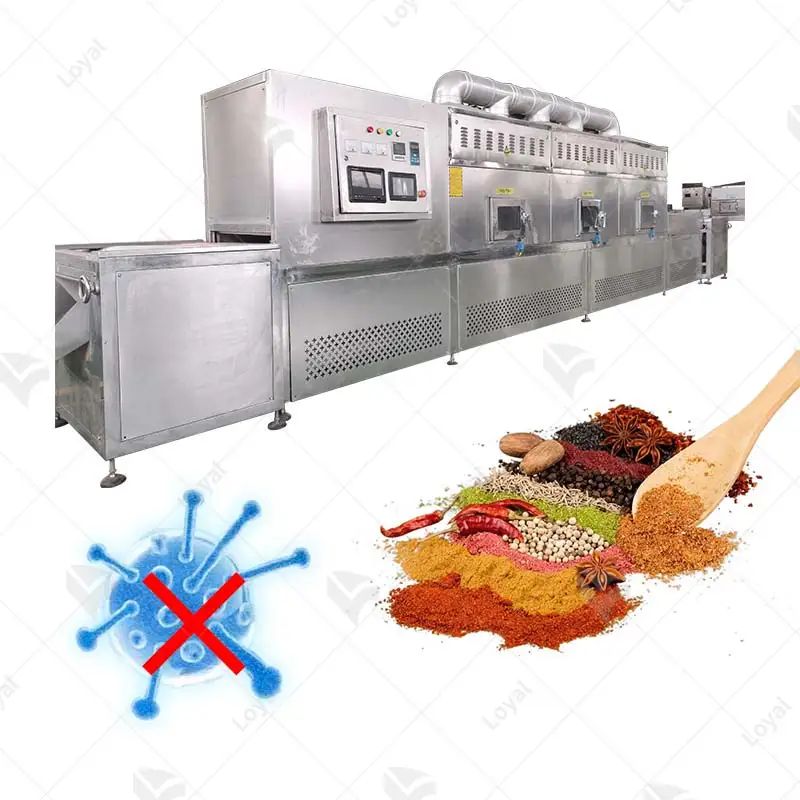
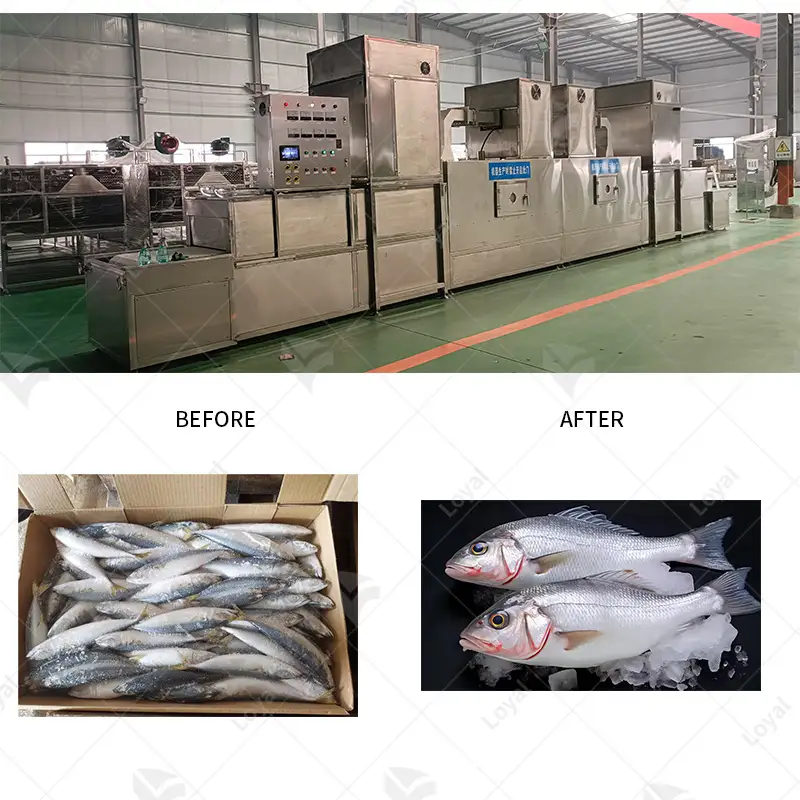
The efficiency and accuracy of industrial microwave drying equipment enable it to be used across many industries. It is widely employed in the pharmaceutical industry for drying active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) and excipients to maintain product quality and stability. Microwaving drying finds its significance in food industry where it is applied during dehydration of fruits, vegetables, and herbs, protecting their nutritional value and flavor as well. Besides that, it’s also applicable in chemicals and ceramics industry during the drying of materials such as catalysts, ceramics, polymers etc., which enhances process speed enhancing, effectiveness of products. In this respect therefore the capacity to dry using a microwave is an invaluable tool.
Food Processing And Preservation
There are several benefits that come with microwave drying in food processing and preservation including maintaining nutritional values and flavors of food products. Unlike traditional drying methods, the uniformity in moisture reduction achieved through microwaves ensures that all foods retain their unique texture as well as color. This technology is especially effective for dehydrating fruits, vegetables, and herbs because it minimizes loss of important vitamins and minerals. Again the fast rate at which they dry reduces microbial contaminations thereby extending shelf life for these products. Microwave drying supports both quality preservation practices by providing a fast method of removing water from foods while ensuring that they do not lose their nutrients.
Pharmaceutical And Chemical Industries
For APIs’ & excipients’ quality assurance microwave-drying remains indispensable techniques in pharmaceutical production processes. To ensure chemical integrity alongside achieving low water content; this technique enables one to customize the conditions required for (moisture) removal without affecting the original properties. The end result is homogenized stable end-products manufactured under strict industry standards.
In chemical industry field materials like catalysts, polymers or ceramics are dehydrated using microwaves hence increasing efficiency during its drier operation processes making them perform better as solutions.. For instance proper heating uniformity achieved when performing microwave drying is key in achieving even moisture content removal that determine the overall quality and reactivity of chemicals. In addition to increasing productivity, this drying method also contributes to energy savings and environmental protection at the same time.
Role Of Microwave Sterilization Machine
Microwave sterilization machines are very important when it comes to the destruction of microorganisms that are harmful and thus ensuring safety as well as durability for variety of products. Such applications are particularly useful in food and pharmaceutical companies which highly emphasize on product integrity and safety.
During microwave sterilization, electromagnetic waves are produced by the machine causing quick heating of products. The heat destroys microbial proteins leading to their death hence making them impotent against bacteria, viruses as well as fungi. Key technical parameters include:
- Frequency: Typically around 2450 MHz, because it is able to penetrate most materials effectively.
- Power Output: Ranges from 1 kW up to 100 kW depending on the volume and kind of material being treated.
- Temperature: Usually maintained between 80°C to 120°C, ensuring effective sterilization without compromising product quality.
- Time: Duration can range from a few seconds to several minutes depending on type of product / degree of microbial inactivation needed.
Thus, microwave radiation technology has several advantages such as reducing processing time; low energy consumption save time during packaging process avoiding use harsh detergents or large amounts chlorine solution etc.; providing convenient ways maintaining high quality standards within an industry; etc.
How to Optimize the Use of a Microwave Dryer?
To optimize the use of a microwave dryer, several key steps must be undertaken to ensure maximum efficiency and product quality. Below are some guidelines and related technical parameters.
1.Altering Frequency and Power Output:
- Frequency: Using a standard frequency of 2450 MHz ensures effective penetration and heating of most materials.
- Power Output: Adjust power output depending on the volume of material as well as its moisture content. Lower power settings such as between 1 kW to 5 kW may be suitable for small batches while larger volumes may require power ratings from 50-100 kW.
2.Temperature Control:
Temperature: Drying temperatures should range between 80°C to 120°C so that moisture is effectively removed without affecting the quality of products, thereby avoiding overheating and degradation.
3.Determining Optimal Drying Time:
Time: The drying time will greatly depend on the initial moisture content in the material as well as desired final moisture content level. For light items, it can take few minutes while for thick ones, it can last even hours. It is possible to find out an optimal drying period by continuous monitoring with slight changes.
4.Even Distribution
Uniformly distribute material within the dryer by filling disperse forms of material to avoid irregularities in heating it . The substance can be stirred or rotated occasionally throughout the drying process with this objective being achieved.
5.Moisture Detection System
Use automated feedback systems which rely on moisture sensors for real-time control over the water content within a product hence allowing dynamic adjustments during drying cycles regarding temperature or duration thus guaranteeing uniformity in manufacturing results.
6.Maintaining/Calibrating Machine Regularly,
Periodically clean out filters located inside machine dryers themselves thereby ensuring that they remain in good working conditions . Inclusion of regular calibration works carried out upon recalibration equipment’s sensors together with controls helps prevent any inaccuracies or inefficiencies from creeping up anywhere along production line whatsoever thus guaranteeing perfect result obtainable.
By following these guidelines and adjusting the technical parameters as appropriate, users can improve their microwave dryer’s performance, achieve efficient drying operations and produce superior quality products.
Best Practices for Microwave Drying Solutions
Adhering to best practices in microwave drying solutions can significantly enhance efficiency as well as product quality. Here are some of the most salient points from the latest industry insights:
Appropriate Pre-treatment:
To ensure uniform moisture levels before drying, materials may be pre-treated through washing, cutting or blanching depending on the nature of material.
Optimal Loading and Spacing:
Place materials uniformly into a microwave dryer or other container with enough gap in between them. This is key because overloading will hinder uniform drying leading to specific hot zones.
Controlled Microwave Power:
The power levels should be adjusted according to the properties of the material being heated and its moisture content. Reduced power settings are advisable for heat-sensitive substrates while higher ones are used for heavy-loaded moist objects.
Monitoring and Adjustments:
Sensors and feedback systems should be used continuously throughout the process. The progress of materials should be checked frequently, changing either power or time setting when required so that drying remains even.
Post-drying Handling:
At this point it becomes essential to allow proper cooling of those substances before packing or any further process is done. Good ventilation prevents condensation which could reintroduce water again.
If these best practices are incorporated well in one’s microwave drying system, there will be better efficiencies realized when it comes to preserving material quality . Regular training by keeping abreast with current technological developments also counts toward achieving improved results throughout all times.
Maintenance Tips for Prolonging Machine Life
- Regular Cleaning:
- Clean your foods dehydrator regularly in order to avoid making residues build up inside it that may cause inefficiency as well as potential breakdowns . Use non-abrasive cleaners recommended by manufactures only.
- Routine Inspections:
- Conduct periodical checks on all parts including, but not limited to, the conveyor belt, sensors, and heating units for indications of wear and tear, rusting or other damage which might impair their performance.
- Lubrication and Calibration:
- Regularly lubricate moving parts to minimize friction and prevent overheating. Also periodically calibrate sensors and controls to ensure they continue working accurately and efficiently.
- Replace Worn-Out Parts:
- Be proactive replacing any worn out or faulty components to stop sudden breakdowns. Have common replacement components in stock to minimize downtime.
These maintenance tips will help users extend the life of microwave drying machines significantly thereby ensuring a constant performance as well as reducing expensive repairs.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting
Uneven Drying:
Issue: Materials may dry unevenly resulting in inconsistent results.
Troubleshooting:
Make sure that the material is evenly spread over the conveyor belt.
Check and adjust power settings of microwave oven.
Make sure that conveyor speeds are set correctly.
Burning or Overheating:
Issue: Certain materials may burn or superheat during drying process.
Troubleshooting:
Reduce microwave power levels.
Increase the conveyor speed so as to reduce exposure time period
Monitor moisture content and then adjust drying time accordingly.
Machine Stops Unexpectedly:
Issue: The microwave dryer suddenly stops working
Troubleshooting:
Inspect material flow for any blockages in it;
Probe into sensors as well as safety interlocks for them to function properly;
Look for problems with electrical connections/fuses first before trying anything else
Inconsistent Performance:
Issue: The machine’s performance changes over time
Troubleshooting:
Recalibrate sensors and controls according to manufacturer instructions;
Always clean components regularly so that they do not become less efficient;
Ensure uniformity of moisture level in feeding materials at all times while checking indicator(s).
Particulate buildup
Issue: Particles accumulating inside equipment
Troubleshooting:
Increase frequency of cleaning.
Use appropriate filters and ventilation in order to minimize dust and debris getting into the system.
In doing so, users can maintain optimal function of microwave drying machines by addressing these common issues with targeted troubleshooting steps. Regular maintenance and adherence to technical specifications are crucial for consistent and efficient operations.
What to Consider When Purchasing a Microwave Drying Machine?
When you are purchasing a microwave drying machine, it’s vital to carefully assess some factors that will help in ensuring the machine meets your specific requirements and operational demands.
Some of these factors include:
Material Compatibility:
- Technical Parameters: Assess if the machine has the capacity to handle all materials you intend to dry. Make sure that the microwave frequency and power can be adjusted to suit various types of materials.
Drying Capacity and Speed:
- Technical Parameters: Determine its throughput rate, usually expressed in kilograms per hour (kg/h). Ensure that the conveyor speed is adjustable so as to match processing requirements.
Control Systems:
- Technical Parameters: Look for advanced control systems with programmable logic controllers (PLCs) as well as human-machine interfaces (HMIs). These systems should have precise microwave power control, temperature monitoring and moisture content measurement capabilities.
Energy Efficiency:
- Technical Parameters: Go for machines with high energy efficiency ratings. Models available with energy-saving functions such as variable frequency drives (VFDs) as well as modulation of microwave power should be considered.
Safety Features:
- Technical Parameters: Ensure that the equipment has comprehensive safety features like emergency stop buttons, interlock systems and overheat protection sensors. Also look into meeting safety regulations such as OSHA and CE marking.
Maintenance and Cleaning:
- Technical Parameters: Opt for a design that allows for ease of maintenance and cleaning. Key attributes like self-cleaning mechanisms or quick release components can cut on too much downtime experienced during cleaning procedures.
Size and Footprint:
- Technical Parameters: Measure the space available at your facility before purchasing so that it does not hinder activities already taking place or even go beyond their limits. The machine’s dimensions and layout need to fit your spatial limitations.
Cost and ROI:
- Technical Parameters: Calculate total ownership costs which includes purchase price, installation costs incurred during operation including maintenance expenses; then evaluate return on investment based on energy savings, improved efficiencies, increased yields or enhanced product quality
By considering these factors and the associated technical parameters, you will be able to make a wise decision on which microwave drying machine to purchase that will best fit your operational goals and production needs.
Key Features to Look for in Microwave Drying Equipment
When choosing microwave drying equipment, focus on the critical features that ensure efficiency and quality in your manufacturing processes. The top sources disclosed these key features as follows:
Energy Efficiency:
Models with high energy efficiency ratings and energy-saving functions such as variable frequency drives (VFDs) and modulation of microwave power can lead to substantial savings on operational costs.
Control Systems:
Advanced control systems enable precise regulation of microwave power, temperature, and drying times during the drying process. Automation features are available to enhance productivity and consistency.
Uniform Drying:
Equipment designed for even distribution of microwaves ensures uniformity throughout the material being dried, which is important for maintaining product quality.
By giving priority to such features, you can choose microwave drying equipment that satisfies both technical specifications at your facility as well as your operational requirements thus enhancing efficiency while maintaining product quality.
Cost-Benefit Analysis: Is It Worth the Investment?
There could be substantial benefits realized in the long run for investing in microwave drying equipment albeit seeming costly at first. These sources indicate that such benefits might often outweigh initial investment costs. One of them is that energy savings are made easier through high efficiency ratings and energy-saving features like VFDs hence this lowers operational costs overtime. In addition, advanced control systems and automation features help enhance productivity and consistency, which may reduce labor expenses as well as minimizing waste. Lastly, uniform drying leads to high-quality products that potentially result in increased customer satisfaction and better market position. All these factors taken together contribute positively on ROI thereby being useful for consideration by many manufacturers who are responsible for adopting microwave drying technology.
Industry Compliance and Safety Standards
Industry compliance and safety standards are necessary when making a decision to invest on microwave drying equipment. Make sure that the equipment adheres to industry-specific regulations such as those set by FDA, OSHA as well as local health & safety authorities relating to operation and maintenance of industrial machinery. Essential points to consider include electromagnetic radiation safety; proper shielding; emergency shut-offs among other compliances. Similarly, regular checks plus worker training on correct usage including emergency procedures will enforce safety rules and ensure adherence to the law. Adhering to these regulations can prevent fines, protect workers’ lives, and maintain credibility of business operations.
Reference sources
-
Scientific Journals and Publications: Research articles and papers in scientific journals such as IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques or the Journal of Food Engineering can offer in-depth insights into the principles, applications, and advancements of microwave drying technology.
-
Industry Reports and White Papers: Industry reports and white papers from reputable organizations like the International Microwave Power Institute (IMPI) or the Microwave Processing Interest Group (MPIG) can provide industry-specific data, case studies, and technical analyses showcasing the efficacy and potential of microwave drying machines.
-
Manufacturer Websites and Technical Documentation: Visiting the official websites of leading microwave drying machine manufacturers such as Muegge GmbH or Kerone can provide technical specifications, user manuals, and product information that demonstrate the capabilities and benefits of utilizing microwave drying technology in various industries.
Related Information: Industrial Microwave Drying Processes for Machinery